India’s largest steel producer by capacity
JSW Steel, the flagship of the JSW Group, is India’s largest and geographically most diversified steel producer. The Company retains its market leadership through agile operations, a strong product portfolio, advanced technology, efficient project execution, and sustainable sourcing. Lower conversion costs, better raw material security, and a future-ready workforce further strengthen its position.
With fully integrated operations spanning mining, raw material processing, steel production and downstream value-added manufacturing, JSW Steel today has an installed capacity of 35.7 MTPA across India and overseas (including 1.7 MTPA under commissioning at JVML). Aligned with India’s strong long-term steel demand growth outlook, JSW Steel has launched a capital expenditure programme covering growth projects, mining and cost savings initiatives, value-added product facilities, modernisation of overseas facilities and sustaining capital expenditure. JSW Steel has set a target to reach 51.5 MTPA capacity by FY 2030-31.
At a glance
WSD’s World-class Steelmaker ranking
Global ranking on production volumes
Total installed capacity
Domestic installed capacity*
* Including 1.7 MTPA under commissioning at Vijayanagar by JSW Vijayanagar Metallics Limited, a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company.
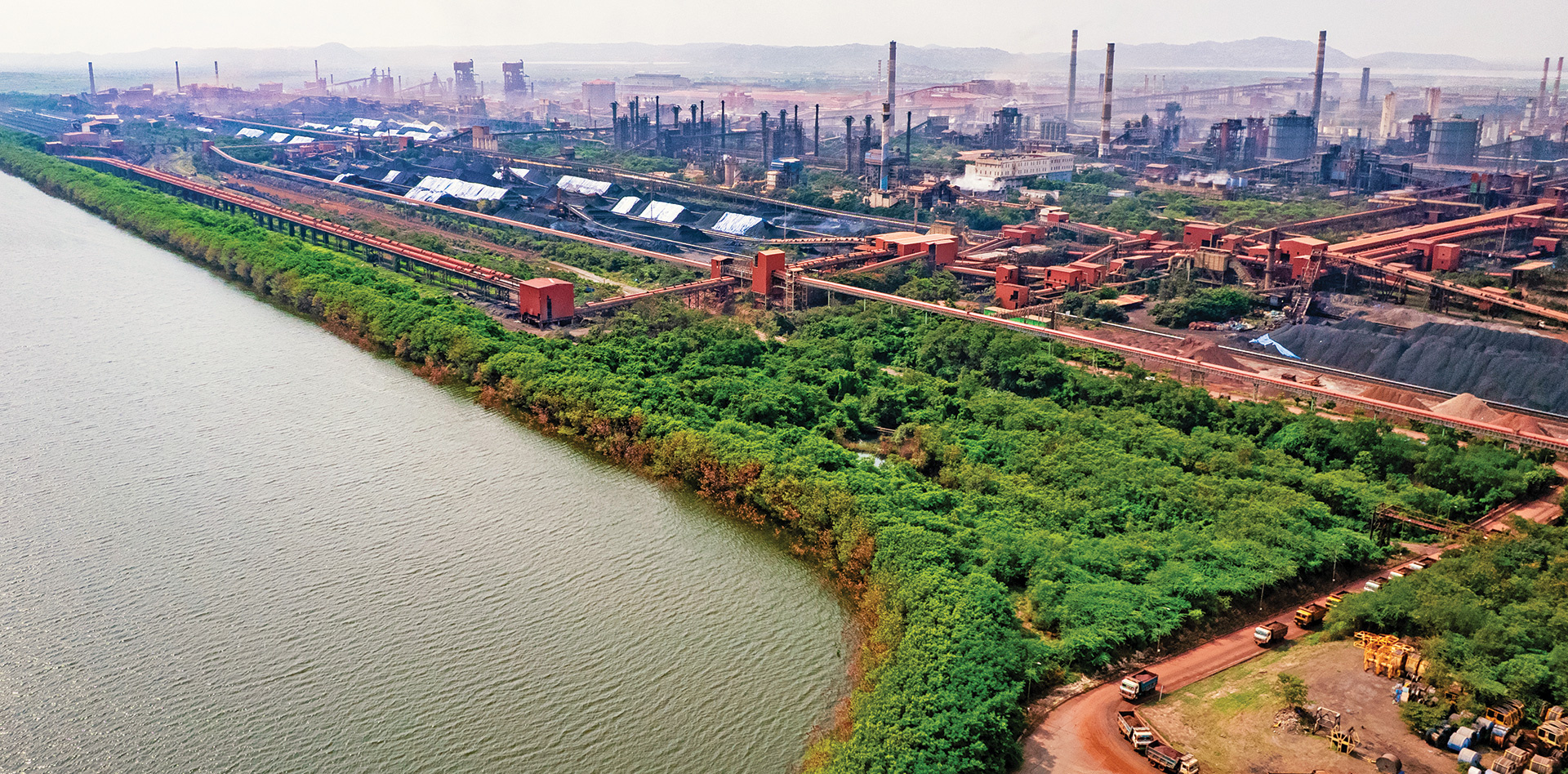



Reinforcing cost leadership through integrated manufacturing
JSW Steel’s global leadership in conversion costs stems from its efficient operations, strategically located plants, cutting edge manufacturing technologies, high manpower productivity and resilient business model. The Company is an integrated manufacturer of a diverse range of products, utilising various industry-leading technologies. Its integrated operations span from raw material processing units, such as beneficiation plants, pelletisation and sinter plants, to downstream value-addition capabilities, such as production of cold rolled, galvanised and colour-coated products. The facilities are well connected to rail, roads and ports, which provides natural competitive advantages in terms of reliable and cost-efficient sourcing of raw materials and delivery of finished steel products to the market.
JSW Steel’s cost-reduction initiatives during FY 2024–25 included a focus on regional sourcing of iron ore, enabling the Company to reduce inbound logistics costs through shorter haulage routes and multi-modal transport strategies. The Company also optimised the coking coal blend to reduce overall coke production costs and increased Pulverised Coal Injection (PCI) to lower fuel costs. Additionally, optimum utilisation of Blast Furnace gas and Coke Oven gas helped generate power and meet heating requirements.
JSW Steel is in the process of implementing plans to increase the usage of renewable energy in its operations and is actively engaged in the strategic integration of renewable energy sources into its operational framework and in exploring innovative avenues to incorporate clean energy solutions into every facet of its business, from manufacturing to logistics. By optimising its energy footprint and embracing renewables, JSW Steel is mitigating the environmental impact while future-proofing the business against volatile energy markets and regulatory uncertainties. This transition to renewable energy also provides cost savings in terms of lower energy costs compared to thermal power costs.
In line with its vision to increase the share of renewables in its overall power requirements, JSW Steel has entered into a power purchase agreement with subsidiaries of JSW Energy Limited to procure wind and solar power of 996 MW in Phase I and 1,470 MW in Phase II.
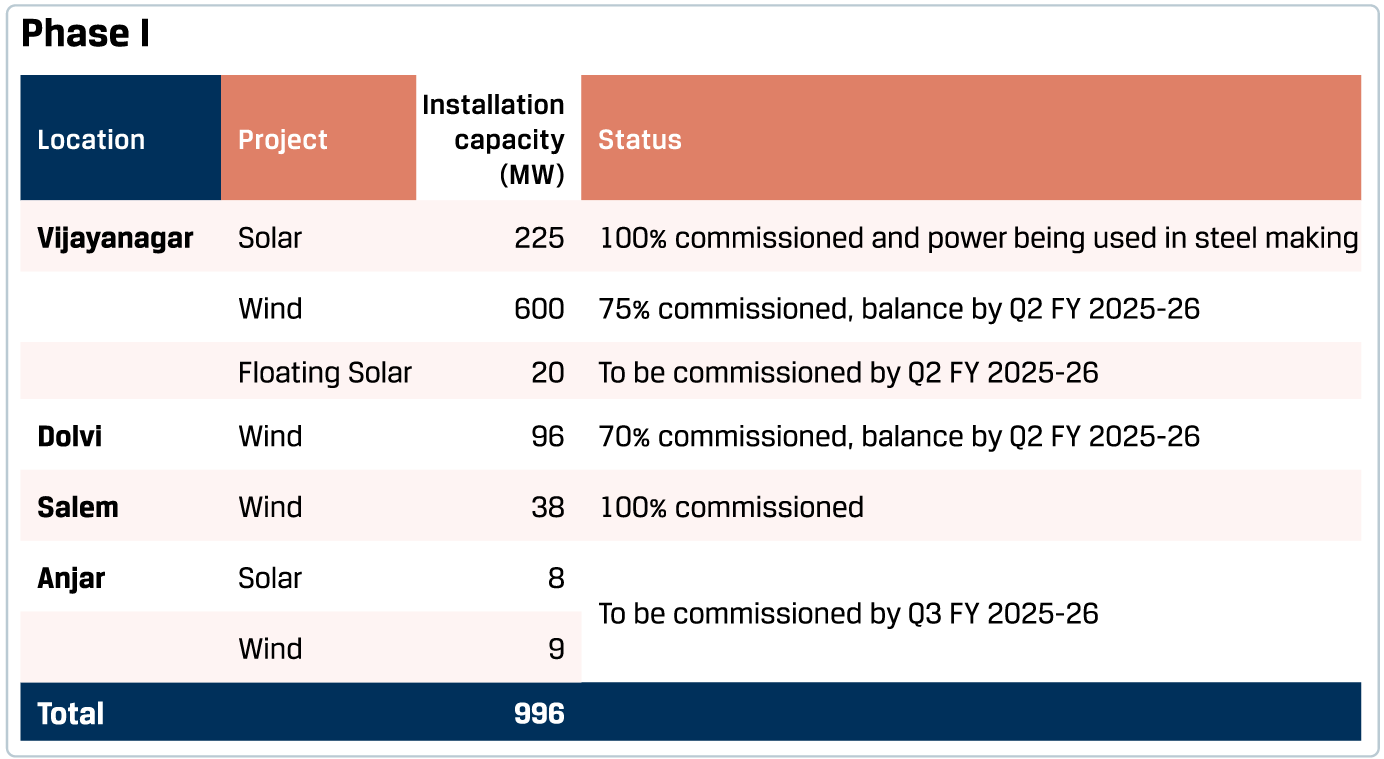
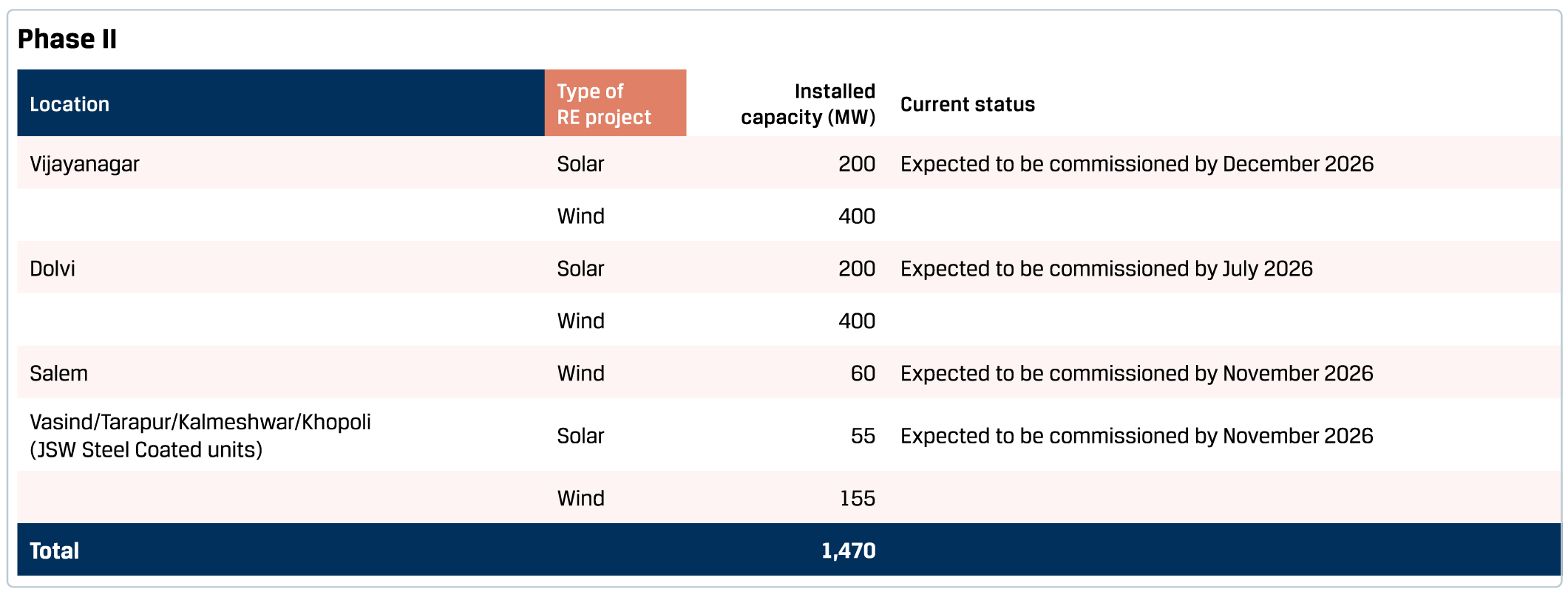
By FY 2026-27, a 30 MTPA slurry pipeline to Jatadhar port and an 8 MTPA Odisha pellet plant will enhance logistics efficiency and raw material security. The planned coke oven facilities and expansion projects across plant locations will drive economies of scale and fortify its cost competitiveness and operational resilience.
Securing raw material, a strategic priority
The Company continues to deepen backward integration, securing 23 iron ore and three coking coal mines in India via auctions in India to boost self-sufficiency and reduce external dependencies. Of its 23 iron ore mines, 12 are operational in Karnataka and Odisha, the rest are in various stages of commissioning.
JSW Steel is targeting to source 25% of the coking coal requirements captively and this can be achieved by establishing domestic coking coal linkages by acquiring mines under auction and setting up or acquiring coal washeries.
JSW Steel has secured two coking coal mines in Jharkhand, Parbatpur Central Coal Mine (0.9 MTPA), and Sitanala Coal Mine (0.3 MTPA). In addition, the Company secured 2.06 MTPA of Non-Regulatory Sector (NRS) coking coal (purchased through long-term linkage) and a washery, i.e., Dugda Coal washery, which comes with a 2 MTPA of Fuel Supply Agreement (FSA) linkage. Raw coal availability from these sources including Moitra Coal Block (1 MTPA) secured earlier, is 6.26 MTPA. Beyond India, the acquisition of Mozambique’s Minas de Revuboe mine (800 MnT of hard coking coal), along with a 20% stake in Australia’s Illawarra coal mines, which would provide ~1.2 MTPA of coking coal, further diversifies the Company’s raw material sourcing.
Strategic acquisitions/partnerships to boost capacity and capabilities
JSW Steel has forged strategic joint ventures and equity partnerships to enhance its value-added offerings, global presence, raw material security and technological edge. The Company’s key collaborations include a 50:50 JV with Severfield UK for structural steel solutions and another with Marubeni-Itochu for Just In Time (JIT) steel services across key Indian markets.
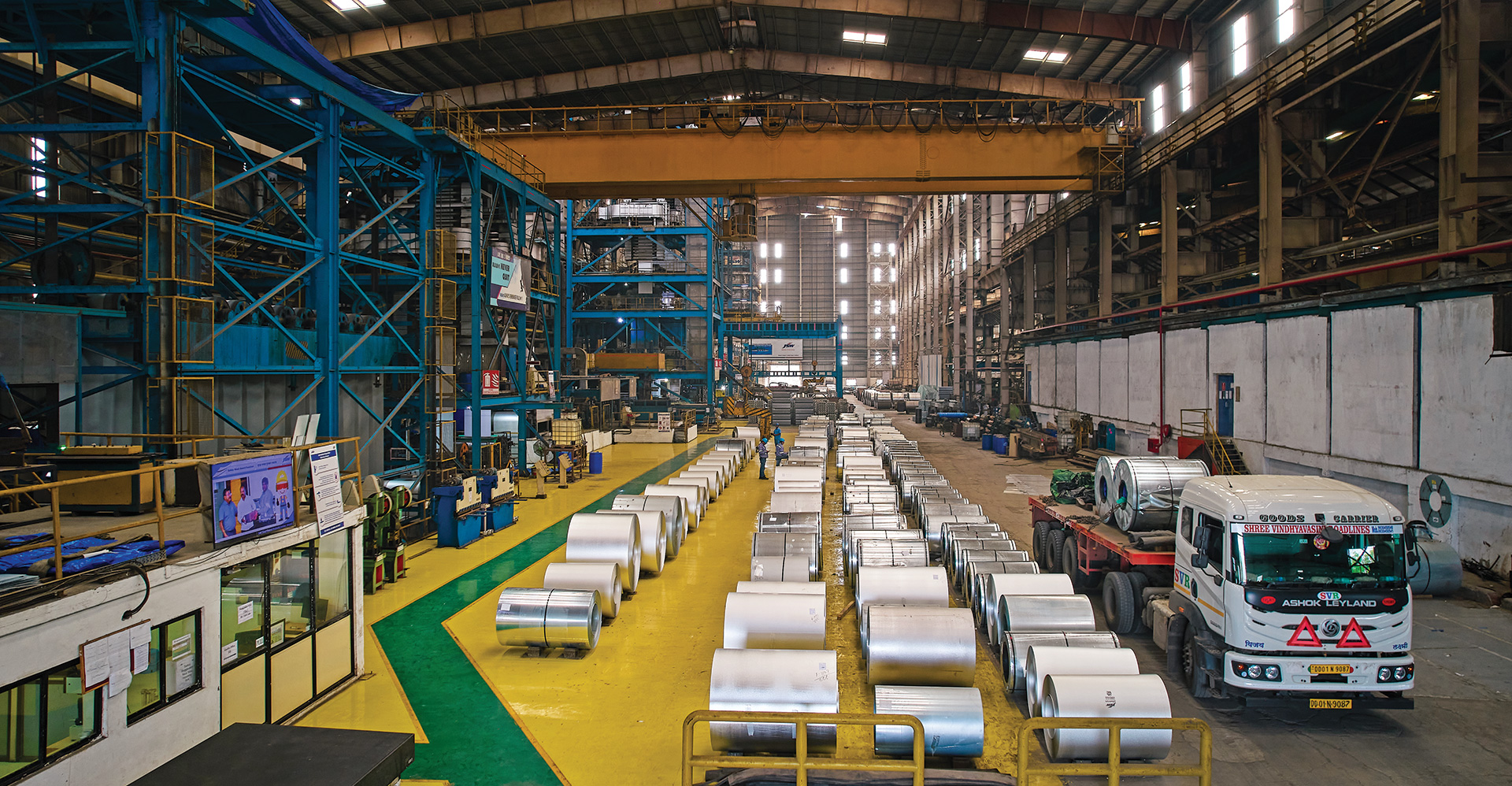


Value-added and special steel products
JSW Steel offers an extensive and diversified product portfolio that meets varied market needs worldwide. As India’s leading value-added steel producer, the Company operates one of the country’s largest galvanising and coated steel capacities, having export footprints in over 100 countries. In FY 2024-25, 91 new steel products were developed/ customised, in JSW Steel standalone, while securing 48 product approvals.
62%
Share of VASP in sales mix (Excluding JVML volumes)
5%
Increase in VASP volume
In February 2024, JFE and the Company had established J2ES, with the aim of setting up an integrated greenfield project for manufacturing GOES in India by 2027. Through this acquisition, J2ES achieves instant market access and can promptly establish an integrated system from manufacturing to sales of GOES in India.
Jsquare Electrical Steel Nashik Private Limited, a wholly owned subsidiary of JSW JFE Electrical Steel Private Limited (J2ES), which is a 50:50 joint venture between the Company and JFE Steel Corporation (JFE), has acquired 100% equity interest of Thyssenkrupp Electrical Steel India Private Limited (subsequently renamed to JSW JFE Electrical Steel Nashik Private Limited) (J2ESNPL). The associated technology package from the Thyssenkrupp group has been licensed/transferred to the Company. The total purchase consideration for the transaction (including closing adjustments) is ₹4,159 crore.
J2ESNPL is one of the first manufacturers of Grain Oriented Electrical Steel (GOES) in India with a manufacturing capacity of 50,000 tonnes per annum. The CRGO manufacturing facility is situated at Nashik in Maharashtra. The acquisition provides the Company with access to cutting-edge technology, thereby aligning with its strategy of enhancing its value-added portfolio.
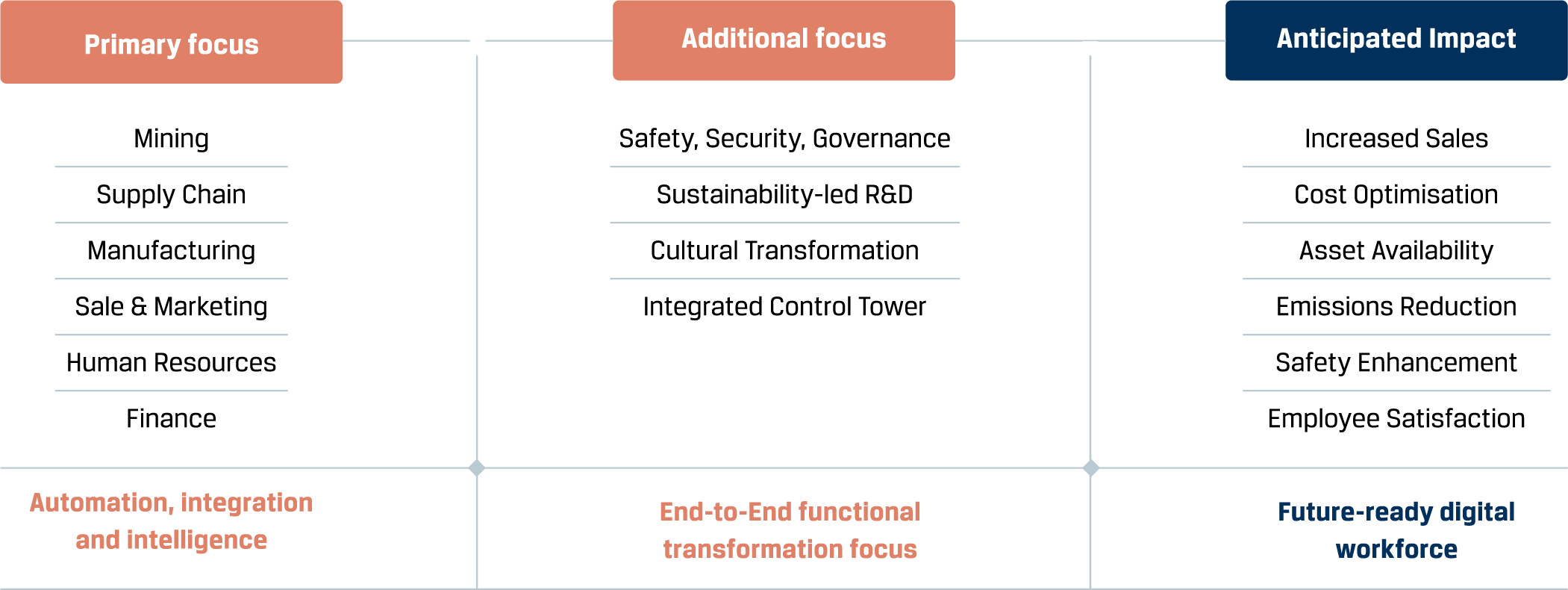
JSW steel’s digital focus areas
Investing in green steel
The Company has also commissioned a pilot green hydrogen project at Vijayanagar, providing a strategic edge for future expansion.
Increasingly, upcoming regulations across the world are expected to source steel with low carbon footprint. The Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) implementation by the European Union (EU) and the Government of India's initiatives to bring down carbon emissions in the steel industry with a target to reach Net Zero by 2070 are likely to develop a global market for green steel. Government projects are likely to mandate the purchase of steel with low carbon emissions in a phased manner in the near future.
To support its strategy of manufacturing low-carbon steel for export markets and adopting green technologies such as hydrogen-based DRI, JSW Steel transferred its Salav unit, comprising a 0.9 MTPA DRI plant and auxiliary units to JSW Green Steel Limited. This move enables separate tracking of CO2 emissions and aligns with the Company’s long-term sustainability goals. The green steel facility at Salav will be developed in two phases, expanding capacity from 0.9 MTPA to 4 MTPA. The transfer was executed through a slump sale, with JSW Steel investing ₹2,233 crore in JSW Green Steel Limited.


Focus on sustainability
Sustainability lies at the heart of JSW Steel’s growth strategy, guiding every aspect of its operations. The Company is committed to achieving carbon neutrality across all operations under its direct control by 2050. JSW Steel has identified 17 key focus areas, based on stakeholder consultations during materiality assessment, setting ambitious targets to drive continual improvement and measurable progress. The Company’s sustainability efforts are overseen by its Board-level Business Responsibility and Sustainability Committee, ensuring accountability at the highest level.
Environment
JSW Steel is focused on addressing the interconnected challenges of climate, nature, and inequalities. In FY 2024-25, the Company reduced its Scope 1 and 2 emission intensity by ~3% and specific energy consumption by 3.5% from the previous year. JSW Steel is also strategically integrating renewable energy into its operations, enhancing resilience against energy market volatility and regulatory changes. This year, the Company expanded its cumulative renewable energy capacity to 782 MW, with the target to reach 1 GW in the near term, further reducing its carbon footprint. In the second phase, JSW Steel is planning to source additional renewable power of 1.5 GW. Its focus on sustainable practices extends to waste and water management, with waste recycled and reused at 99.98%. These initiatives not only reflect JSW Steel’s responsibility to shape a greener tomorrow but also strengthen resilience and future readiness.
Read more in the 'Environment' chapterWorkforce and community
JSW Steel is creating an inspiring and vibrant workplace where talent is recognised, nurtured and empowered to drive operational excellence and long-term growth. As an equal opportunity employer, the Company ensures a culture of diversity and inclusion, with women accounting for 7.0% of its workforce. Safety remains a non-negotiable value for JSW Steel, embedded in every decision and action. The Company’s commitment to achieving a 'Zero Harm' environment resulted in 5.5 lakh safety observations this year. JSW Steel’s talent strategy focuses on identifying and developing future-fit leaders, mapping unique strengths and ensuring robust succession planning with 252 high-potential leaders identified during the year. Its CSR initiatives have positively impacted more than 30 lakh lives across key focus areas, with a CSR spend of ₹363 crore in FY 2024-25 including ₹117 crore deposited in escrow account for CSR spending in coming years.
Read more in the 'Social' chapter2.1 Global economy
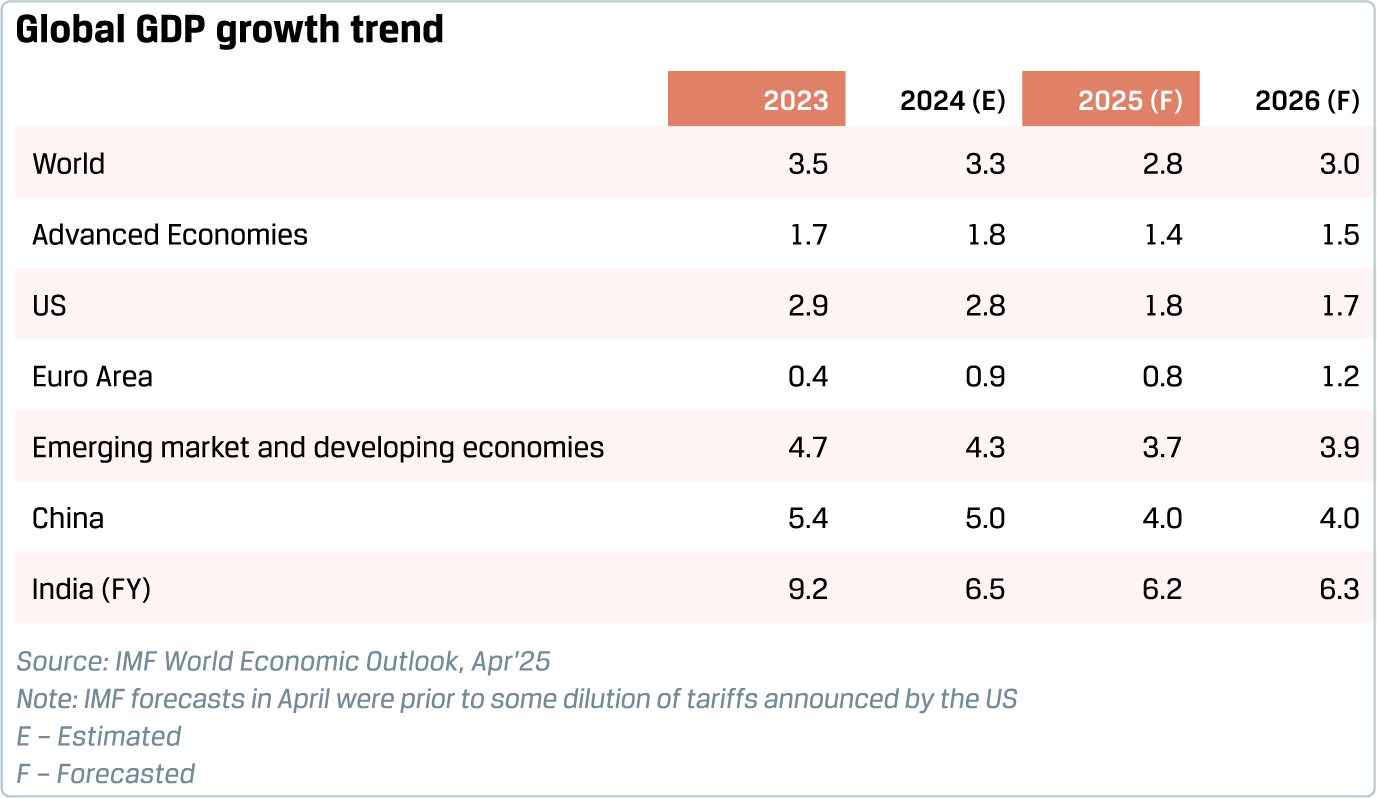
The global economy was resilient over the last year, stabilising from the shocks witnessed in the beginning of the decade, amid the continued overhang of geopolitical risks. As per IMF estimates, world GDP growth eased to 3.3% in 2024 from 3.5% in 2023, with the slowdown seen in EMDEs (Emerging Markets and Developing Economies).
The US economy recorded strong momentum at 2.8% with robust demand conditions and labour market, while growth was subdued in the Euro area and Japan. China managed to meet its growth target of 5% on the back of policy stimulus, despite a weakening property sector.
A key positive feature of the global economy was a gradual moderation of inflation in advanced economies, opening the space for easing of the monetary policy that was tightened earlier during the high-inflation phase. According to the IMF, average inflation in advanced economies fell from 4.6% in 2023 to 2.6% in 2024. This was helped by the normalisation of supply chain pressures, from elevated levels after the outbreak of the Russia-Ukraine war.
World GDP growth in 2024

The outlook for 2025 has been impacted by the trade tensions, sparked by the tariff policies of the new US administration. The initially announced tariffs by the US in early April have been subsequently diluted through various announcements and bilateral trade discussions. Some of the dilution has been in the form of a 90-day pause, the continuation of which would be contingent on further negotiations. Nevertheless, US tariffs are likely to stay elevated in comparison to the levels prevailing before the start of the year. Further, the policy uncertainty is adversely affecting business and consumer confidence.
The eventual tariff scenario may still take time to settle down. Accordingly, sectoral and geographical effects of tariffs may evolve in a complex manner as differential tariffs vis-à-vis different countries could lead to trade diversions and second-/third-order effects for different sectors/geographies.
Apart from trade tensions, geopolitical risks remain significant with continuing conflicts between Russia and Ukraine, and in the Middle East. Amid the heightened uncertainty, the IMF projected world GDP growth to slow substantially to 2.8% in 2025 and 3% in 2026, lower-than-trend growth but still above the mark typically associated with recessionary conditions. IMF forecasts were released before some of the tariff dilution by the US. Accordingly, while the directional drift of IMF forecasts could be instructive, the forecasts may be revised after the trade scenario becomes clearer.
Trade policy effects are deemed by the IMF to be adverse almost across the world, with more severe impacts on the US and China, which are the most affected by tariff escalations. Tariffs could push inflationary tendencies in the US, complicating the future trajectory of US Fed rates. The Fed has adopted a wait-and-watch stance amidst the risks to both sides of its mandate, viz. inflation and employment, and indicated that it would wait for more data on the economy’s direction before changing interest rates.
The IMF projects China’s growth to slow to 4% in 2025, even as the Chinese government is targeting 5% growth and is undertaking fiscal and monetary policy support to meet the target.
Some of the positive impulses seen in the early months of 2025 included: advancing of export orders to beat tariffs, some pick-up in fixed assets investment other than in the real estate sector in China and reasonably solid labour market conditions in the US. Japan recorded a second straight year of strong growth in wage negotiations, which could support consumption. In Europe, plans to boost defence and infrastructure spending are being initiated, which could be a supportive factor in the medium term.
Broader global growth concerns are likely to weigh on commodity prices, in general. Financial markets remain vulnerable to potential risk-aversion episodes in this macro backdrop, besides continuing geopolitical risks. However, in case of a significant dilution in trade frictions through trade deals resulting out of the ongoing bilateral negotiations by the US administration, the global economic outlook could get re-rated upwards.
- Tariff-related policies weighing on global outlook – impacting through trade and investment channels.
- Moderating inflation a positive, though tariff effects need to be watched.
- China’s policy support and potential dilution of tariff concerns through trade deals are possible upsides.

India’s growth outlook for FY 2025-26 is likely to be supported by resilient domestic drivers, even though the overhang of global headwinds remains. Consumption will be buoyed by personal income tax cuts, easing food inflation, positive monsoon outlook and the RBI’s rate cuts. The Union Budget announced cuts in personal income tax amounting to ₹1 trillion. The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) has forecast monsoon rainfall to be above normal in 2025, which bodes well for continued rural recovery. Consumer confidence has shown an uptrend, and the RBI’s policy easing and liquidity support will aid consumption demand.
Central government capex is budgeted at ₹11.2 trillion for FY 2025-26, versus the revised estimate of ₹10.2 trillion for FY 2024-25. Rising trends in capacity utilisation in the manufacturing sector, along with strong balance sheets of banks and corporates, are expected to support private capex, though the impact of global trade frictions on confidence levels needs to be watched. While the US tariffs scenario could take some time to solidify, early indications suggest that the realignment of global supply chains could benefit India in the medium term.
Lower international oil prices are expected to bolster India’s macroeconomic fundamentals, along with the continued fiscal consolidation and adequate forex reserves. The RBI has projected India’s consumer inflation to soften further to 4% in FY 2025-26.
With some likely softening of external demand, the IMF expects India’s economy to grow at 6.2% (this forecast was based on original April tariff announcements by the US), whereas the RBI has projected growth to be steady at 6.5% during FY 2025-26. These projections reflect a potentially modest dent to India’s growth performance due to the global slowdown, even as the domestic growth impulses remain supportive.
2.2 Indian economy
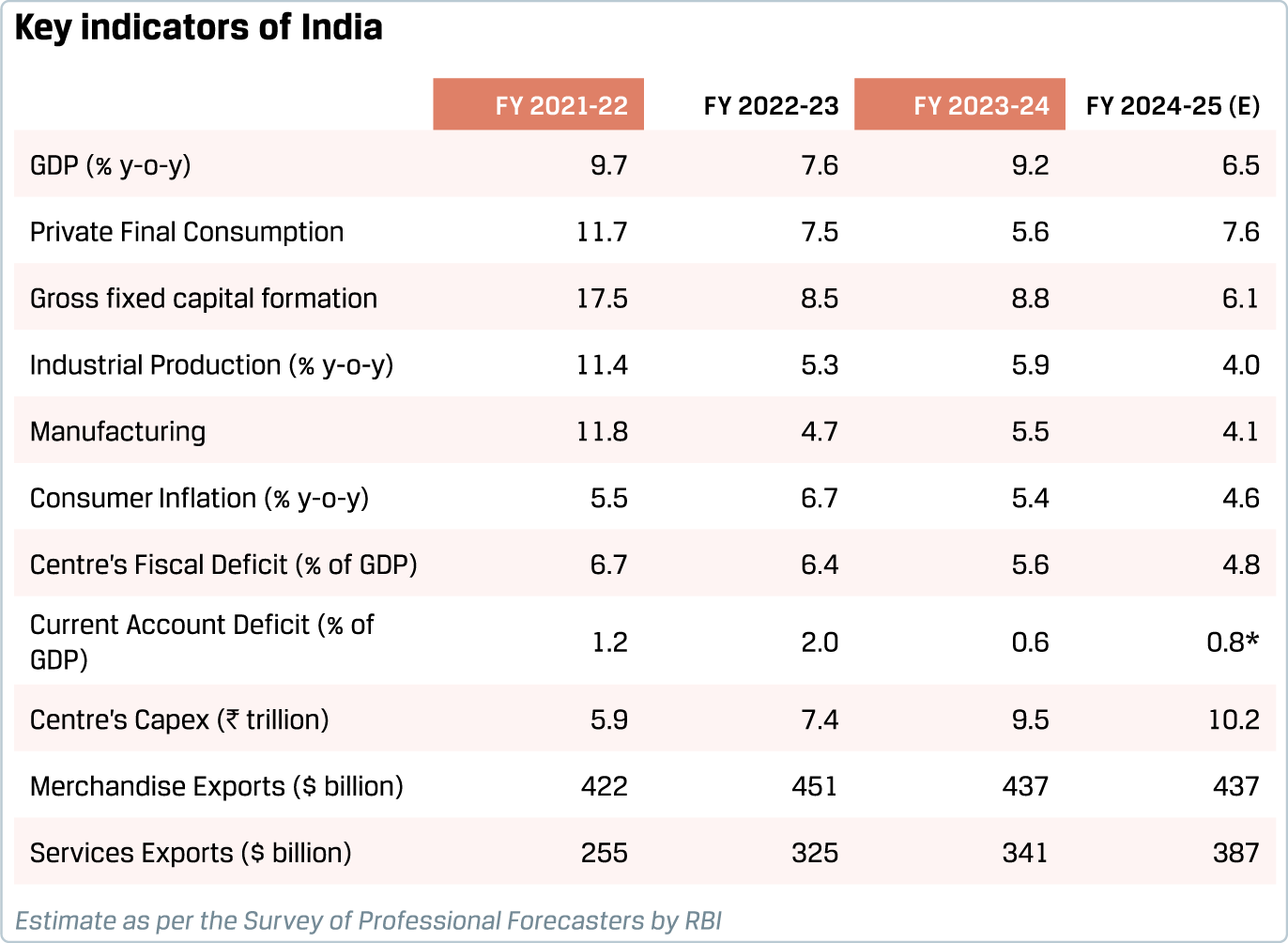
India continues to be one of the fastestgrowing major economies. The Indian economy is estimated to have recorded a solid growth of 6.5% in FY 2024-25, on top of a strong 9.2% growth in the previous year. Private consumption expenditure accelerated during the year, whereas gross fixed capital formation decelerated.
Growth was slower in the first half of the year, with the election-related code of conduct slowing down public capex and heatwave incidences impacting consumption, along with the elevated food inflation. Growth recovered in the second half of the year.
Retail inflation eased from 5.4% in FY 2023-24 to 4.6% in FY 2024-25. Inflation fell below the 4%-mark in the last quarter of the fiscal, as food inflation declined substantially. This opened the space for policy rate cuts by the RBI; policy rate was cut by a combined 50 basis points in February and April 2025 meetings. Liquidity conditions that had tightened in early 2025 have eased with a slew of liquidity measures by the RBI.
India’s macroeconomic situation continues to be resilient with fiscal consolidation on track, a healthy level of foreign exchange reserves and current account deficit well within prudent levels. Merchandise exports stagnated in FY 2024-25 while services exports remained buoyant. Accordingly, despite a widening of merchandise trade deficit, the overall current account deficit is estimated to be contained. Thanks to buoyant tax collections and increased transfers from the RBI, the central government’s fiscal deficit reduced by nearly 0.8 percentage points to 4.8% of GDP in FY 2024-25.
6.5%
Estimated growth of the Indian economy in FY 2024-25
- India’s macroeconomic position resilient; well positioned to navigate global challenges.
- Tax cuts, easing inflation, healthy monsoon outlook and RBI’s rate cuts to support consumption.
- Central government capex target at `11.2 trillion, which will maintain traction in infrastructure development.
- Private capex to be supported by improving capacity utilisation and strong balance sheets.
3.1 Global steel industry
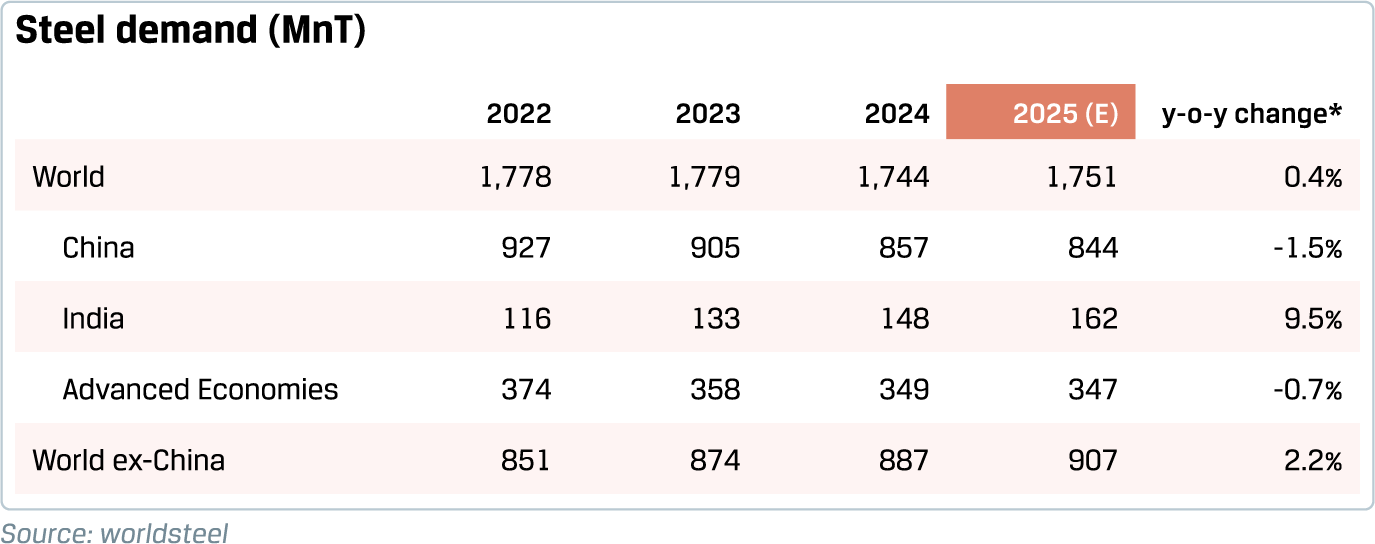
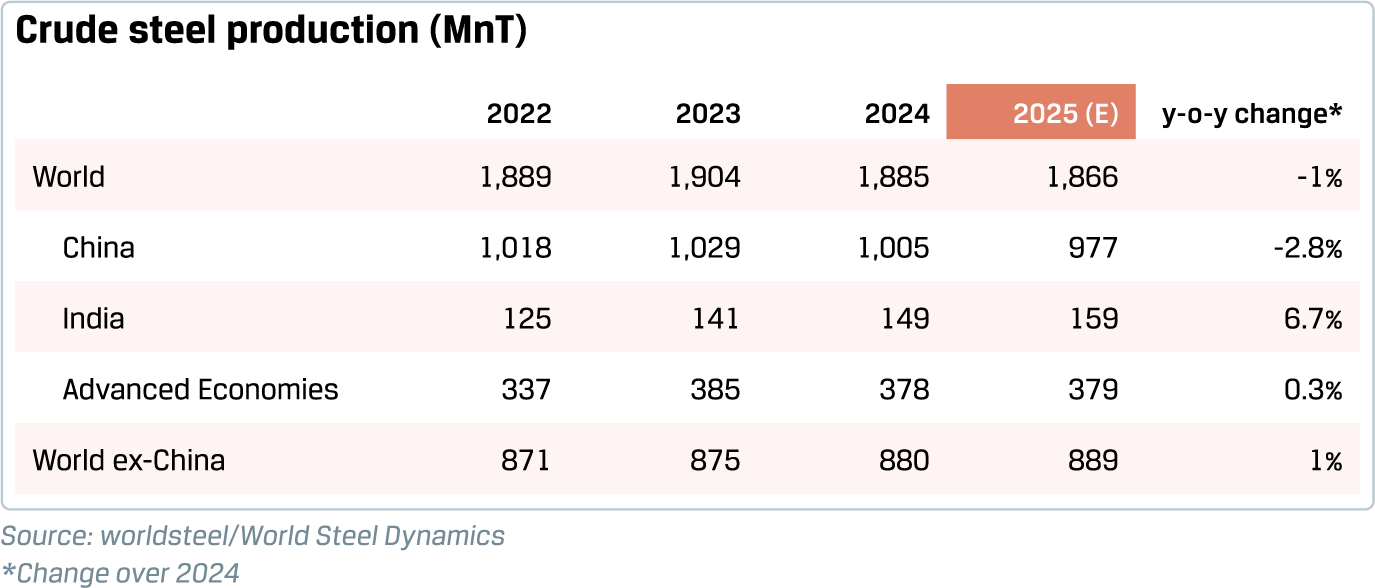
World finished steel demand and crude steel production declined marginally by 2% and 1%, respectively, in 2024. In the last five years, global steel demand has moved sideways. However, these global numbers hide wide variations across different markets.
China, which accounts for nearly half of the world's steel industry, recorded a 5% decline in consumption in 2024, mainly due to the structural challenges that its real estate industry is witnessing. India has been a key driver of global steel demand growth in recent years. Developed economies, including the US, the EU, Japan and Korea recorded a contraction last year, while demand increased in ASEAN, GCC, Turkey and Vietnam. Broadly, similar geographical divergences were observed in terms of crude steel production as well in 2024. World crude steel production stood at 1,885 MnT in 2024.
The US administration has removed exemptions on its 25% tariff on steel imports (under section 232 for national security reasons) and brought derivative products under the coverage of tariffs. Tariff on steel products in the US is currently on par for most exporters, other than China, though a subsequent trade deal with the UK could possibly exempt the country’s steel exports from the duty. Countries like Japan and Korea have lost their erstwhile preferential access to the US steel market (though one needs to watch out for the outcomes of US’ bilateral trade talks for a clearer picture), which could lead to trade diversions. From an India perspective, the direct impact of the tariff action is likely to be negligible on steel exports, but there could be indirect effects of trade diversions and of increased tariffs on exports of steel-intensive manufacturing sectors, besides the negative macro impulse of tariffs on global steel demand.
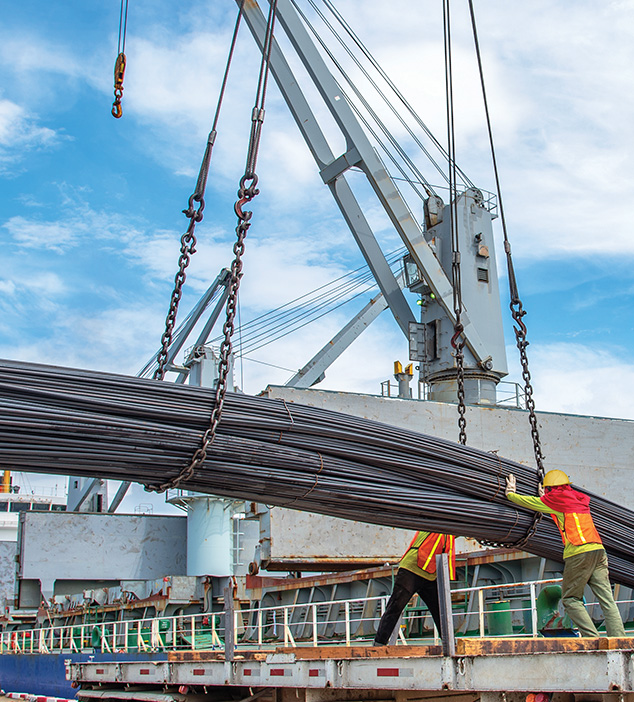

Worldsteel Association’s estimates suggest that China’s steel demand could marginally decline in 2025 at a lower pace than last year. While the downturn in China’s housing market is likely to continue, the pace of decline is likely to be contained amid various targeted measures by the Chinese government. China’s fiscal and monetary policy stance is likely to be supportive, which would support demand from other sectors, particularly infrastructure.
Robust growth in steel demand is expected in India, Turkey and MENA in 2025, while the trade-related concerns could weigh on the steel demand outlook in ASEAN and Latin America. The outlook for steel demand in Japan and Korea is clouded by constraints on domestic demand, including high costs, low affordability and labour scarcity, besides the weak external environment. In the US and Europe, easing of financial conditions and a weak base could support bottoming out of demand, though the trade-related developments need to be watched.
At a global level, steel demand is likely to be broadly flat to slightly improving, depending on the ongoing progress of trade negotiations.
Demand outlook for major consumption sectors
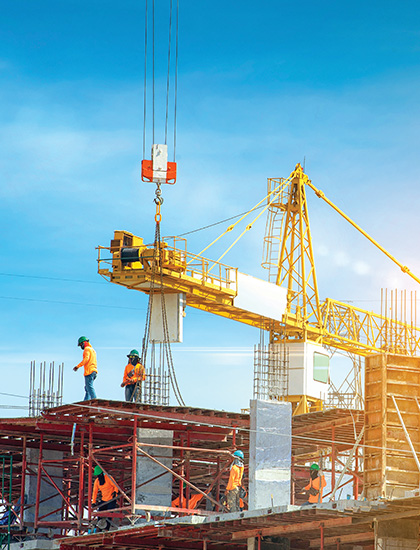

Residential/Construction
Residential construction activity in key markets like the US and the EU is expected to be supported by easing financial conditions and persistent housing deficits in some of the markets. China’s housing activity may continue to moderate, albeit at a slower pace, helped by government measures.
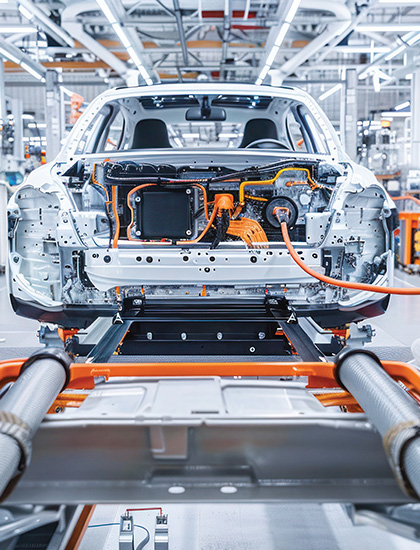

Automotive
Automotive markets may expect modest demand with the introduction of new, more accessible EV models and the untapped market potential in developing markets like India. However, tariffs may adversely affect affordability and consumer confidence in developed markets.
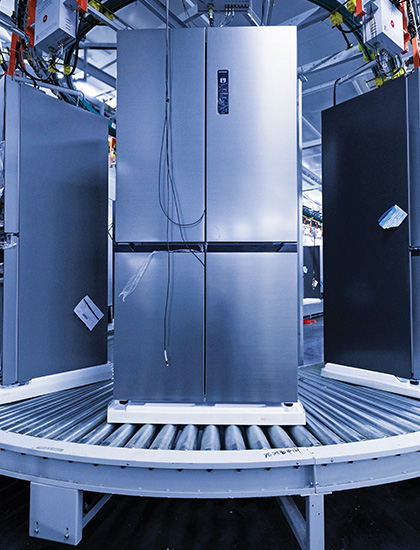

Manufacturing
Investments in manufacturing facilities and public infrastructure could see some headwinds from challenged business confidence and normalisation of the fiscal support in the US. However, possible stimulus measures in China and the recent shift to an expansionary fiscal stance in the EU will be supportive factors. The realignment of global supply chains may also support investments in manufacturing in some countries.

- Structural challenges faced by China’s real estate industry adversely affected steel demand; pushing exports further higher. Chinese government’s policy measures likely to support demand in 2025.
- India expected to continue to be a key driver of global steel demand growth.
- Global steel demand likely to be broadly flat to slightly improving, amidst negative impulse of tariffs.
- Potential trade diversion impact of tariffs a key monitorable.
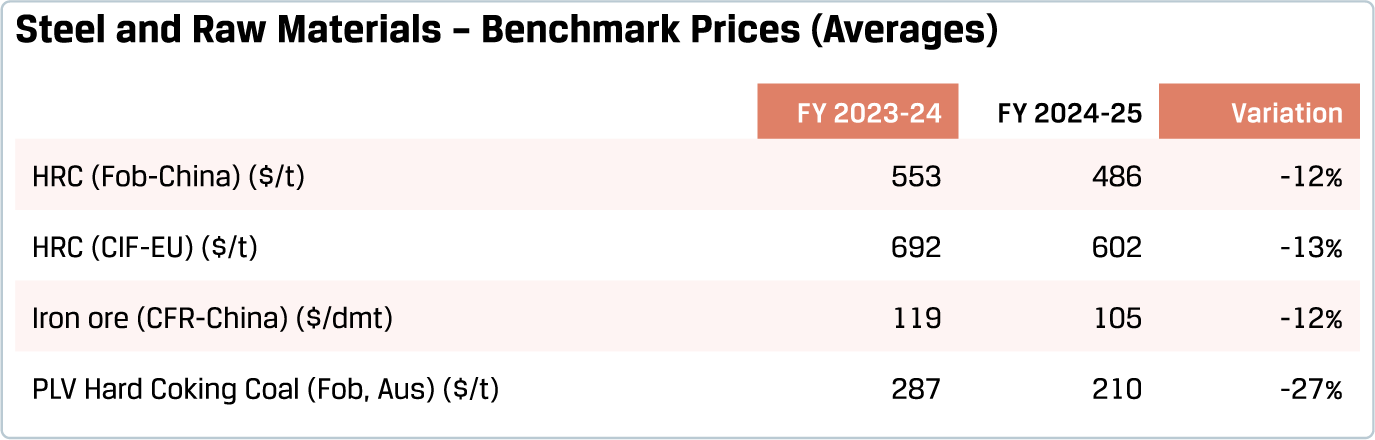
3.1.1 Steel prices and raw material costs
Steel and raw material prices were broadly lower in FY 2024-25 compared to the previous year. This reflected the weak macro sentiment through much of the year. With China’s production not adjusting adequately to the moderation in its steel demand, China’s steel exports continued to trend upwards in 2024. China's exports of semi-finished and finished steel hit an all-time high of 111 MnT in 2024, up 23% over the previous year. This exerted downward pressure on steel prices. Estimates based on market benchmarks suggested that a median Chinese steel mill operated with negative spreads through a substantial part of the year. In the US, however, steel prices increased towards the end of FY 2024-25, mainly reflecting the tariffs. In case of iron ore and coking coal, besides the steel-related dynamics, relatively low incidence of adverse weather events and broadly improving supply conditions helped ease prices compared to the previous year.
The macro impulse for commodity prices in FY 2025-26 is likely to be softer, on account of concerns over the impact of tariffs and weak risk sentiment. Many countries have initiated trade actions against China, and China’s industry body has expressed the imperative for curtailing production. While China’s steel exports continued to increase in the first four months of 2025, one could expect some moderation of production and exports from China. If such a moderation occurs, it could support steel prices. Any significant stimulus measures from China could also help improve the sentiment for steel pricing.
The price outlook for iron ore and coking coal in FY 2025-26 is expected to be tilted towards moderation, with favourable supply conditions. A new, large iron ore mine in Guinea is expected to commence production in 2025. Improved connectivity from Mongolia to China and expected growth in Australia’s exports could keep the coking coal market well supplied.

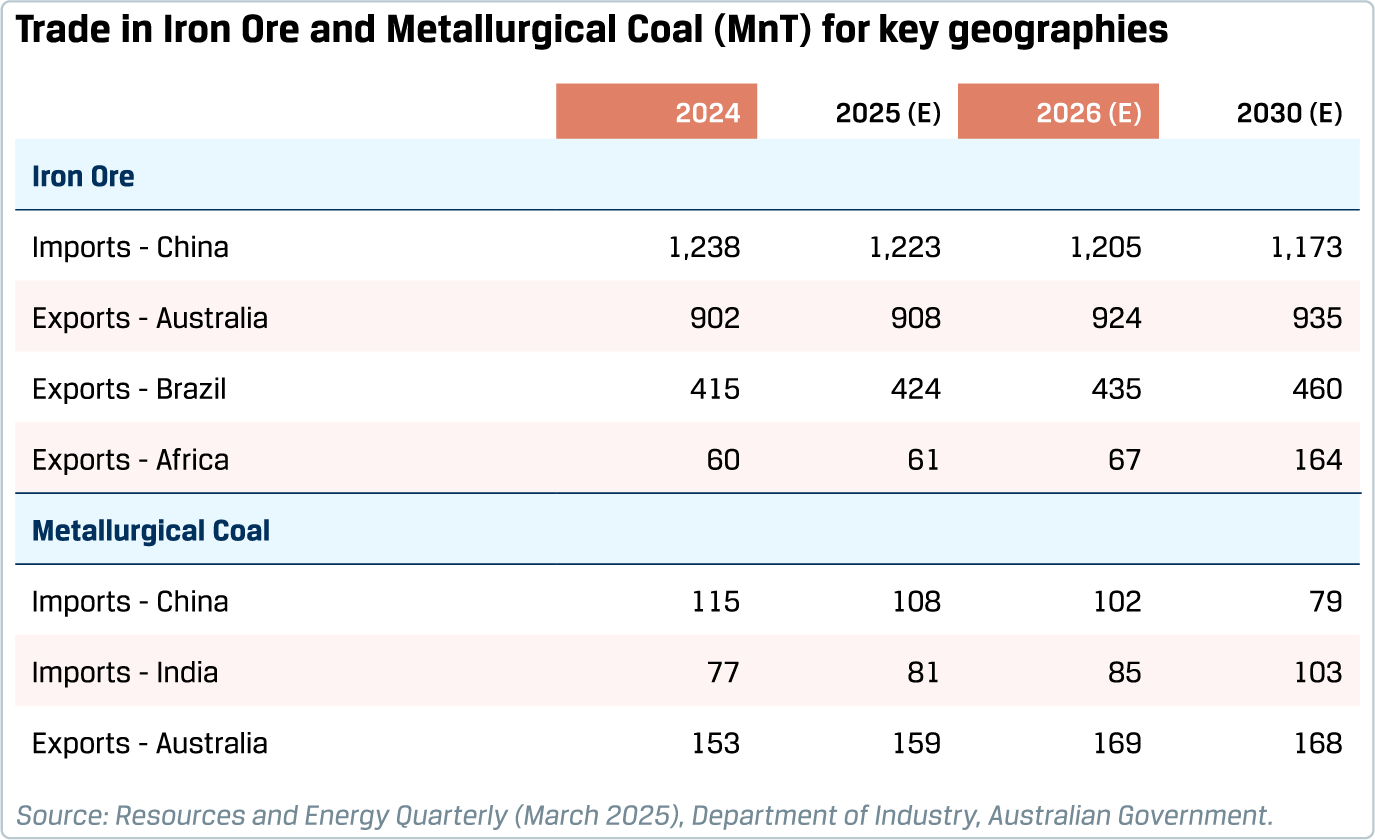
3.2 Indian steel industry
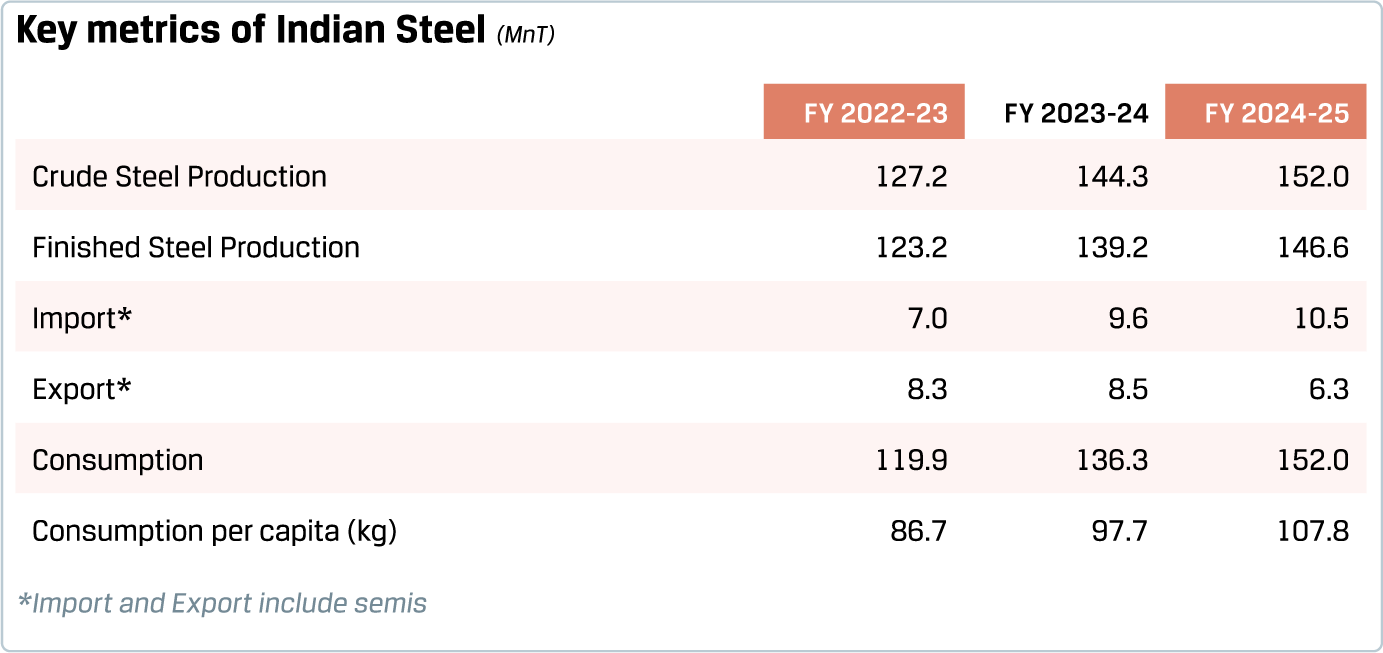
India, the second-largest steel producer globally, has been a key driver of growth for the global steel industry. India’s steel consumption recorded a robust growth of 11.5% in FY 2024-25, the fourth consecutive year of double-digit growth. In the four years ending FY 2024-25, India’s GDP at constant prices increased 37% while steel consumption grew 60%. Over this period, the elasticity of steel consumption to economic growth (computed as the ratio of growth in steel consumption to growth in real GDP) was recorded at 1.5, compared to an elasticity of 0.8 during the decade before the pandemic. Such a step-up in elasticity of steel consumption reflects the phase of nation-building in India, characterised by a strong pick-up in infrastructure building and robust structural underpinnings of consumption, viz. urbanisation and rising penetration of consumer durables. This phase is expected to continue into the medium term, heralding a strong backdrop for growing steel consumption.
Although the consumption scenario in India was robust, domestic steel pricing was under pressure in FY 2024-25 amidst elevated levels of imports and weak global prices. Domestic iron ore prices were, however, range-bound, reflecting strong demand conditions.
11.5%
Growth of India’s steel consumption in FY 2024-25

CRISIL (March 2025 forecast) has projected India’s steel consumption growth to remain robust at 9-10% in FY 2025-26 with flat steel products (projected growth of 12-14%) leading the demand growth, in comparison to long steel products (projected growth of 5.5-7.5%). The following sectoral factors will have a bearing on India’s near-term steel consumption outlook:
- The trend of rising public capex on infrastructure is expected to continue. The central government has budgeted a capex of H11.2 trillion in FY 2025-26. Long-term interest-free loans for capex purposes to state governments would boost their capex spending. Modernisation of railways and development of high-speed highway corridor projects are thrust areas in the development of transport infrastructure.
- Residential real estate launches are expected to accelerate in FY 2025-26, with reduced inventory of units. Commercial real estate is witnessing strong traction, helped by the rapid growth of Global Capability Centres and Data Centres.
- The public housing programme has received a renewed thrust with the extension of the PM Aawas Yojana (PMAY) with a target of building 2 crore additional houses over five years. Guidelines under the extended phase of PMAY were finalised last year, and the scheme’s implementation is expected to gather momentum in FY 2025-26.
- Private capex is being supported by the government’s production-linked incentive schemes, improving trend in capacity utilisation, strong balance sheets and easing monetary policy. While global trade concerns create some overhang over business confidence, the realignment of global supply chains is supportive in the medium term.
- The demand outlook for consumer durables is broadly positive, with recovery in rural consumption, improving trend witnessed in consumer confidence, lower interest rates and easing of food inflation.
- Auto industry growth is expected to be steady amid the launch of new models (especially EVs), increased infrastructure activity, replacement demand and government incentives for e-buses. Auto exports have robust medium-term prospects, though the near-term trade-related concerns may need to be watched.
- The imperative for defence preparedness, government policy thrust on indigenisation of India’s defence procurement and expected increase in defence spending globally are likely to support growth in defence-related manufacturing and exports.
While India’s domestic steel demand growth scenario continues to be robust, trade-related developments need to be watched. Import of finished steel (including semis) was elevated at 10.5 MnT in FY 2024-25, whereas exports slowed amid rising protectionist measures in other countries.
Accordingly, India was a net importer of steel for the second consecutive year in FY 2024-25, with the magnitude of net imports being the highest in several years, barring the exception of FY 2015-16.
The provisional safeguard duty, enforced with effect from 21 April 2025 for 200 days, is expected to act, to some extent, as a speed bump for the import of steel into India, though any possible trade diversions arising out of the removal of exemptions for steel import duty by the US, the productiondemand imbalance in China and the trade remedial measures by other jurisdictions (especially against China) need to be watched carefully.
In order to increase the availability of iron ore in line with the National Steel Policy, more than 120 mines have been auctioned in India since 2016. The government is also trying to improve the domestic availability of coking coal by setting up coking coal washeries.
The Indian steel industry is estimated to have added more than 50 MTPA capacity in the last five years. The momentum of investments is expected to continue into the coming years, for capacity building to meet additional demand, for value addition and for decarbonisation. The government has created a green steel taxonomy, which has been an important step to catalyse the industry’s decarbonisation efforts. Broadly, the outlook for the Indian steel industry for FY 2025-26 is one of cautious optimism, with resilient domestic demand drivers and monitorable global dynamics.
- Robust steel consumption growth in India to continue with thrust on infrastructure and real estate.
- India was a net importer of steel for the second successive year in FY 2024-25, pressuring steel pricing.
JSW Steel remains steadfast in its pursuit of excellence by leveraging its world-class, fully integrated manufacturing facilities and a diverse, high-value product portfolio. The Company focuses on efficient capital allocation, cost leadership through resource optimisation, enhanced raw material security and continuous innovation driven by R&D. Embracing technology-led transformation and digitalisation, it is preparing to meet the future with confidence, supported by a robust financial profile and strong credit ratings.
In FY 2024–25, the Company achieved consolidated production of 27.79 MnT and sales of 26.45 MnT, meeting the revised volume guidance announced in Q3 FY 2024-25. The average capacity utilisation was at 91% in India. The Company aims to maintain its Value-Added Steel Products (VASP) share above 50%+, supporting sustainability initiatives across packaging, roofing, lightweight materials for automobiles and energy transition. Achieving ~100% self-sufficiency in coke and pellets, the Company has optimised its coking coal blend and expanded waste-based energy generation. Further, to enhance its raw material security, JSW Steel is developing coking coal assets across the globe.
FY 2024-25 was marked by record-breaking performance across key customer segments. The Company achieved its highest-ever industrial sales, registering a 20% y-o-y growth, led by exceptional gains in GI/GL, Colour Coated, Longs, CR and HR. The Auto Segment also saw peak sales with a 7% y-o-y growth, enabled by strong contributions from CR, GA/GI and Longs. Appliance Segment sales soared by 54% y-o-y, driven by GI, Colour-Coated and GL. Meanwhile, the Renewables sector (Solar + Wind) hit a new high with a 40% y-o-y growth, enabled by standout growth in Magsure and GL.
FY 2024-25 highlights
Consolidated sales
 7% y-o-y
7% y-o-y
Coated steel sales
 10% y-o-y
10% y-o-y
Total JSW India Domestic sales*
 15% y-o-y
15% y-o-y
Branded Sales
 15% y-o-y
15% y-o-y
Highest-ever industrial sales
 20% y-o-y
20% y-o-y
Sales in Auto sector
 7% y-o-y
7% y-o-y
Value Added and Special Products Sales
 5% y-o-y
5% y-o-y
* Against domestic consumption of 152 MnT with JSW SoB at 15.5%
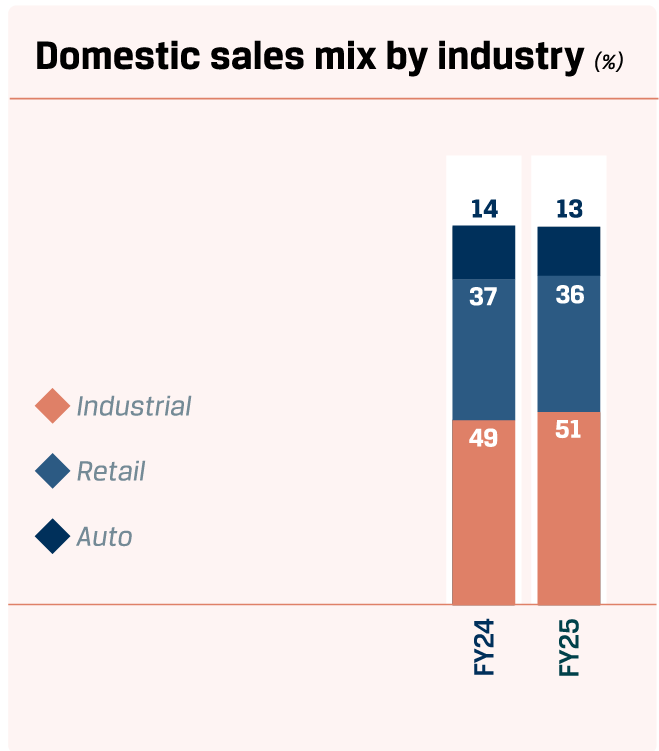
Domestic performance
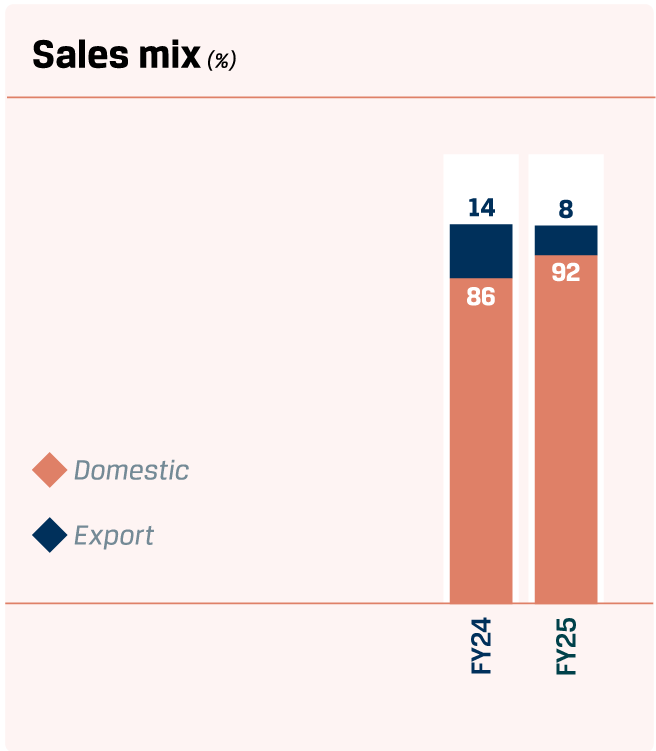
In FY 2024–25, domestic sales remained the cornerstone of the Company’s performance, contributing a robust 92% to the overall sales mix, with volumes rising by an impressive 15% y-o-y. This was further bolstered by record-breaking achievements in Value-Added & Special Products (VASP) portfolio, which reached an all-time high of 15.40 MnT. Value added sales also reached an all-time high at 11.24 MnT, reflecting a strong 9% y-o-y increase.
The share of VASP in consolidated sales stood at a remarkable 62%, underlining the Company’s focus on high-margin, differentiated products. JSW Steel’s manufacturing efficiency remained consistently strong, with its India operations achieving 91% capacity utilisation during the year. Notably, the newly commissioned JVML Blast Furnace reached over 90% utilisation in March 2025.
y-o-y growth in supplies to key sectors

India’s ambition to become a developed nation by 2047 rests heavily on the strength of its infrastructure, vital to shaping liveable, climate-resilient and inclusive cities that fuel sustained economic growth. In FY 2024–25, the Company’s contributions to this national vision grew stronger with a 5% annual increase in supplies for key infrastructure projects across the country. The Company is proud to have supported landmark developments such as the Mumbai–Ahmedabad Bullet Train, the Mumbai Trans-Harbour Sea Link, the Versova–Bandra Sea Link and metro projects across Mumbai, Pune, Nagpur, and Chennai. Its footprint also extends to major energy and pipeline initiatives, including partnerships with NEOM, GAIL and CGD. These efforts are yet another step towards building India’s core infrastructure and enabling cleaner mobility, enhanced connectivity and energy security, cornerstones of a modern, developed India.
Market share held by JSW Steel*
y-o-y growth achieved in steel supplied to Auto industry
* y-o-y market share increased by 1% in FY 2024-25
# As per SIAM auto production data for FY 2024-25

The Indian auto industry achieved a remarkable milestone in FY 2024-25 the 31-million-unit mark registering a 9.1% y-o-y growth. This momentum was primarily driven by growth in PV, Two wheeler and Three wheeler segments. PV grew by 3.3% with EV PV penetration at 2.0%, 2Ws grew by 11.3% with EV 2Ws penetration at 4.7% and 3Ws grew by 5.5% with EV 3Ws penetration at 44.0%. The overall EV penetration stood at 6.2%. JSW Steel registered a 7% y-o-y growth in steel supplies to the automotive sector in FY 2024–25, surpassing the industry growth rate in the 4W Passenger Vehicle (PV) segment, its core area alongside Commercial Vehicles (CVs).#
JSW Steel’s market share gain in the solar space
Highest-ever sales to the overall renewable segment with
y-o-y growth

In FY 2024-25 the Renewable Energy (RE) sector in India grew by 33% with major growth in Solar segment while JSW Steel's sales to the overall renewable segment recorded its highest-ever growth at 40% y-o-y. In FY 2024–25, steel supplies to the solar sector soared by 87% y-o-y. This momentum reflects India’s exponential rise in solar capacity, powered by falling photovoltaic (PV) technology costs, a favourable investment landscape and over 300 sunlit days a year. With a national ambition to reach 280 GW of solar capacity by 2030, forming a major share of the broader 500 GW renewable energy target, the sector is poised for transformative growth.
The Company’s proactive approach has paid off with a 9% market share gain in the solar space, driven by the strategic introduction of Magsure alongside its trusted GL and GI offerings. Backed by robust government support through financial incentives and regulatory clarity, solar projects are becoming more viable than ever. Positioned at the intersection of innovation and sustainability, JSW Steel is proud to be contributing to India's low-carbon journey.
Key projects
- Chennai Thermal Power plant
- Mukhyamantri Saur Krushi Vahini Yojana
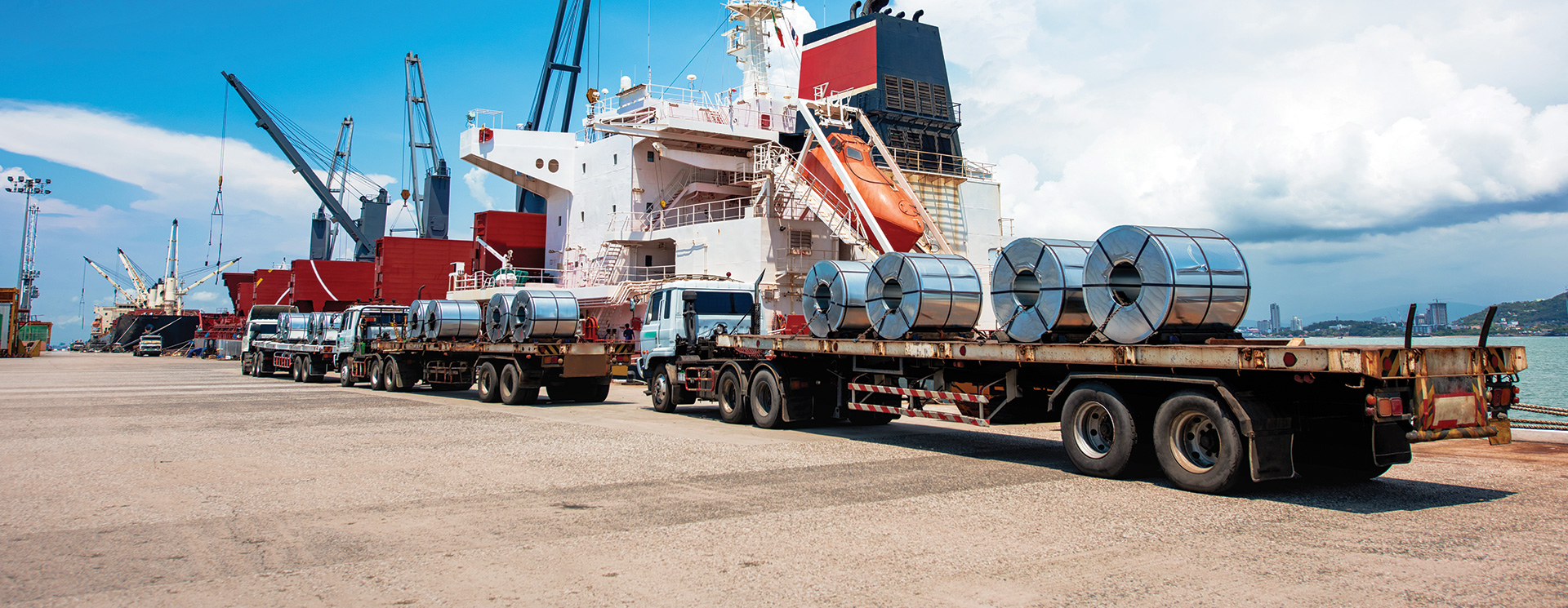
Exports performance
In FY 2024-25, the Company remained firmly anchored in the domestic market, while maintaining a steady foothold in exports, striking a strategic balance that reinforced both competitiveness and resilience across geographies.

Awards and recognition

JSW Steel has been recognised with the prestigious ET Edge Best Organisation in Customer Experience 2024 award

JSW Steel’s World MSME Day film won Silver in the Thought leadership category at AFAQ’S Digies Awards held in February 2025

JSW Steel has been honoured with the Best localisation award in the Steel category by Hyundai Motors for second consecutive year

JSW Steel recognised and awarded for its efforts in the category Electrical Steel by BHEL in SAMVAD 4.0
Data Visionary award for Project Kshitij
JSW Steel has been awarded as 'Excellence in Cooperation and Support' by KIA Motors
4.1 Product performance
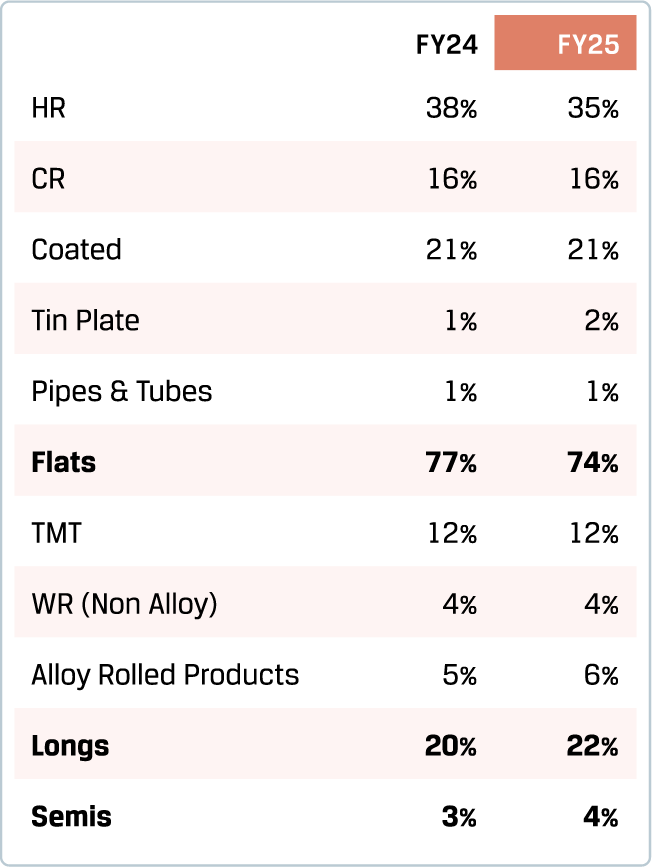
JSW Steel has strategically prioritised increasing the share of value-added and special products (VASP) within its overall sales mix, backed by robust investments in product innovation. This focused approach yielded significant results in FY 2024-25, with VASP sales volumes rising by 5% y-o-y. As a result, the contribution of VASP to the Company’s total sales mix grew to 62% (excluding JVML volumes).


Product mix (%)
Mix (%)
4.1.1 Flats
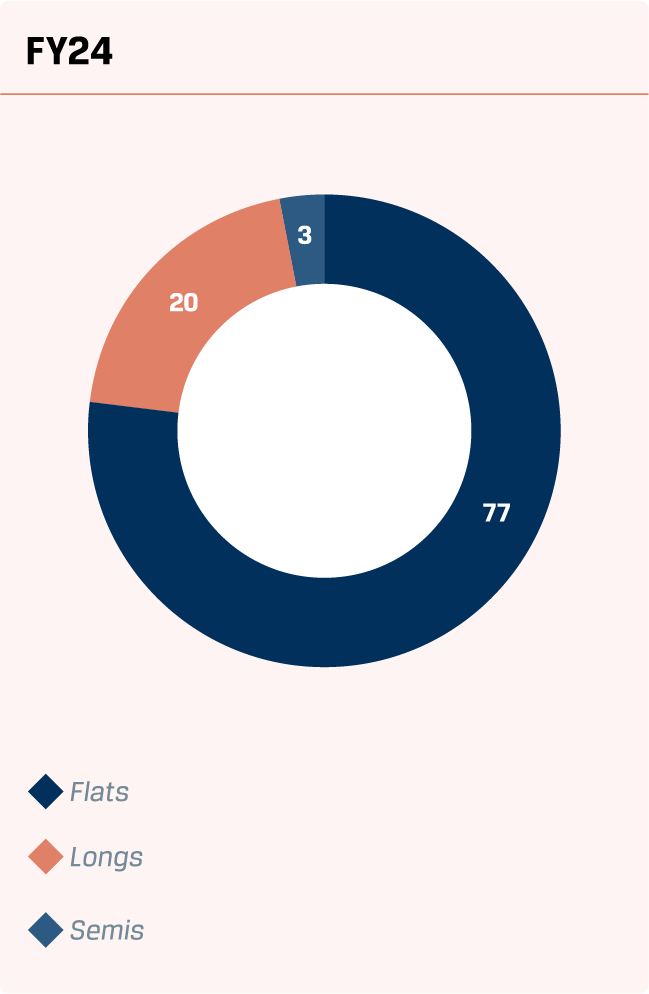
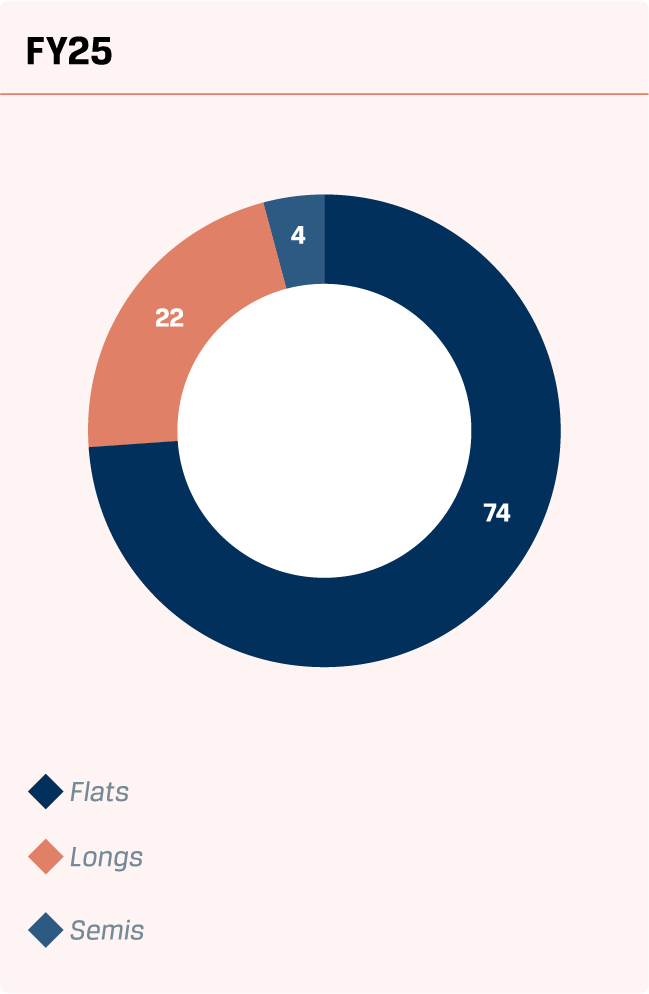
Flat products include Hot Rolled, Cold Rolled, Colour Coated, Galvanised and Galvalume, contributing a robust 74% to the top line in FY 2024-25. This segment recorded a 4% y-o-y growth, reinforcing its critical role in the Company’s revenue mix.
74%
Contribution to overall product portfolio
4%
y-o-y growth
Plates
JSW Steel's Anjar plate mill in the West has been playing a pivotal role in supporting India's ambitious plan in the hybrid renewable energy sector. The facility has also boosted the Indian infrastructure projects through production of thicker plates, contributed to energy segment through supply of plates for boiler applications and has developed capabilities to produce steel grades for defence sector applications.

Hot Rolled
JSW Steel is widely recognised for the superior quality and reliability of its hot-rolled products. Manufactured using cutting-edge technology at Hot Strip Mills in Vijayanagar, Dolvi, BPSL and PM Plate mill at Anjar, catering to a broad spectrum of applications from structural and general engineering to Infrastructure projects. Serving core sectors such as Industrial & Engineering, Automotive, Energy and Capital Goods, hot-rolled products accounted for a substantial 35% of its overall product portfolio in FY 2024-25.
10%
Domestic y-o-y sales growth
35%
Of overall product portfolio

Key projects served in FY 2024-25
Water pipeline
Contributed to ~2,182 km water pipeline constructions
Major projects served
- Gujarat & Narmada river linking project
- Rajiv Gandhi Canal Project, Rajasthan
- Aurangabad water supply project
- MP water linking project
- Telangana & Karnataka water irrigation projects
Oil & Gas
Contributed to ~888 km pipeline constructions
Major projects served
- NEOM
- GAIL & CGD projects

Cold Rolled Close Annealed (CRCA)
During the year, the Automotive sector drove the Company’s CRCA sales to record levels. JSW Steel partnered with top automakers to develop advanced steel grades like HSLA and AHSS, engineered for high impact resistance and reduced weight. The Company also achieved the highest level of localisation by a domestic steel mill for a major auto Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM), leading to significant import replacement. Additionally, the Company made a breakthrough by developing steel supplies for Defence vehicles through JSW Gecko, the first such effort in the country.
10%
Overall y-o-y sales growth
11%
Domestic y-o-y sales growth

Electrical steel
JSW Steel has the first integrated mill to produce superior core loss material substituting imports. Electrical Steel continues to play a vital role in boosting energy efficiency across motors, pumps, fans, appliances, power generators and transformers. Continuous development of CRNO grades now cater to fast-growing segments like EVs and AC compressors. The Company has also maintained its position as a trusted partner in Wind Energy and Railway Traction Motors by consistently delivering high-performance, energy-efficient electrical steel solutions to power a greener tomorrow.
3%
Overall y-o-y sales growth

Coated
Coated steel, prized for its anti-corrosive properties, is witnessing rapid growth, particularly in galvanised, Galvalume and colour-coated segments. With India’s per capita consumption at just 7 kg which is far below the 50–60 kg seen in the US and Europe, growth prospects are immense, especially across rural areas. Demand is set to grow at a steady rate, outpacing both steel and GDP. JSW Coated Steel leads with flagship brands like Vishwas, Colouron+, Radiance, Galvos, Galveco, Silveron+, Everglow, and Pragati+.

Colour-coated
JSW Steel’s colour-coated steel, known for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, caters to construction, warehousing and roofing needs. With a dominant 49% market share and 1.44 MnT in domestic sales, JSW Steel is the only player offering a full brand spectrum from super-premium Everglow to mass-market Indradhanush. The colour-coated segment grew 5% y-o-y, supported by innovations like Anti-Dust, Hi-Gloss and sustainable Cool Roof paints, developed in partnership with JSW Paints. These coatings enhance thermal efficiency and long-term durability. The Company continues to strengthen its presence in the appliance market with new colours and finishes and support global clients through Early Vendor Involvement. By aligning with the ‘Make in India’ movement and driving import substitution, JSW Steel is enhancing domestic supply chains through localisation and global collaborations. The Company has the only Indian mill qualified for premium PCM grade in refrigerator doors.
49%
Market share
5%
Domestic y-o-y sales growth

Galvanised and Galvalume
Galvanised and Galvalume products accounted for 14% of its overall product mix in FY 2024-25. As India’s largest Galvalume producer, JSW Steel is renowned for roofing and cladding solutions with superior corrosion resistance and heat reflectivity. With rising demand from the solar sector, the Company introduced innovative grades under the Galvos brand, designed to endure corrosive, alkaline environments. Notably, the Company pioneered HSLA torque tube grades for solar trackers which are approved by global players. Domestically, GI has 33% and GL has 72% market share, with a 14% rise in sales y-o-y. For the first time, the production or sourcing of Galvalume steel used in switchgear panels has been done locally. Galvalume has also seen increased adoption in the HVAC and solar heating sectors, supported by the introduction of advanced coatings such as Magsure and ZAM.
14%
Overall y-o-y sales growth
33%
Market share of GI
72%
Market share of GL


JSW Magsure
India’s first indigenously designed and patented Zinc-Magnesium-Aluminium alloy coated steel offers five times the corrosion resistance of conventional galvanised iron, even in the harshest conditions. Produced at Vijayanagar and Vasind Coated plants, it’s trusted across solar structures, cooling towers and water storage applications. With standout features like exceptional chemical resistance, enhanced workability and eco-friendliness, Magsure is India’s first Zinc-MagnesiumAluminium product for the renewable sector, engineered for performance in demanding environments, making it a durable and sustainable solution for a wide range of industrial and infrastructure needs.

Tinplate
JSW Platina, a Tinplate product, is a highly sustainable packaging material, offering endless recyclability, making it more eco-friendly than many alternatives. It is one of the most valuable downstream products in the flat steel segment. With rising global demand for sustainable packaging, domestic consumption is growing, driven by urbanisation, changing food habits and diverse retail options.
The Company has seen a 38% y-o-y growth in premium tinplate, capturing 55% of the domestic market. Strengthening its foothold further, the brand has forayed into the Cable Armour segment, targeting a 50% market share. This expansion is fuelled by the growing momentum of localisation, reinforcing JSW Platina’s position as the go-to choice for high-performance, homegrown solutions.
55%
Domestic market share
38%
Overall y-o-y sales growth
4.1.2 Longs
Long products are crucial for key infrastructure projects, including roadworks, metro and rail development, bridges and power plants. During the year, JSW Steel achieved sales of 5.66 MnT of long products, reflecting a 15% growth y-o-y.
22%
Contribution to overall product mix
15%
Overall y-o-y sales growth
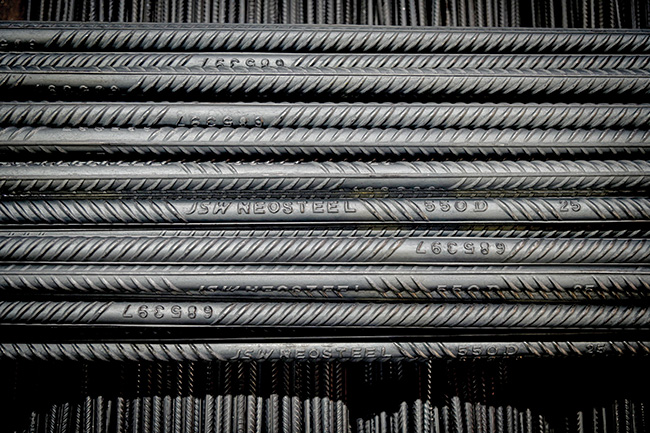

TMT
TMT bars, crafted from virgin iron ore for unmatched purity, offer exceptional strength and flexibility. Manufactured using the advanced HYQST process through the METCS system, these bars are known for superior quality, weldability, corrosion resistance and malleability. With rising demand driven by infrastructure development, the Company supplies TMT products to various marquee projects including roadworks and metro rail, contributing to large-scale initiatives in sectors like construction, power and nuclear energy. The Company has a patent from the Patent Office, Government of India, for high corrosionresistant TMT bars with yield strength of 600 MPa. The Company has seen a 12% y-o-y growth in TMT sales, capturing 6% of the domestic market share.
6%
Domestic market share
12%
Product mix FY 2024-25
Key projects served in FY 2024-25
- Mumbai – Ahmedabad High speed rail project.
- Metro projects across Chennai, Mumbai, Pune and Nagpur.
- Kundankulam Nuclear Power project.
- Navi Mumbai Airport.
- GAIL & CGD projects.

Wire rods
Engineered with advanced technology for exceptional quality, manufactured at Vijayanagar, JSW Steel’s wire rods cater to industries like automotive, engineering, welding and machining. As India’s automotive and industrial sectors expand, the demand for these versatile products continues to rise. The Company sharpened its focus on Electrode and High Carbon grade steel, achieving an impressive annual growth of 20% and 31% respectively. These specialised grades continue to meet the evolving demands of the electrode manufacturing and auto component industries. The Company has seen a 12% y-o-y growth in WR sales, capturing 12% of the domestic market share.
12%
Overall y-o-y sales growth*

Low relaxation prestressed concrete steel strands
JSW Steel introduced its cutting-edge Low Relaxation Prestressed Concrete (LRPC) Steel Strands at the Vijayanagar– Neotrex facility with an annual capacity of 144,000 tonnes. Designed to optimise structural performance, LRPC reduces project costs, enables longer spans and supports sleeker, safer designs. In its debut year, the product swiftly gained market traction, securing a 29% market share in FY 2024–25. It now plays a pivotal role in landmark infrastructure projects, including the Mumbai-Ahmedabad Bullet Train and key NHAI road developments.
29%
Domestic market share
62%
Overall y-o-y sales growth
Key projects served in FY 2024-25
- Mumbai – Ahmedabad High speed rail project.
- Bangalore – Chennai, Kanpur – Lucknow, Delhi – Vadodara Expressway.
- Metro projects across Chennai, Mumbai, Pune and Nagpur.
* Non-alloy wire rods of Vijayanagar considered

Alloy steel
JSW Special Alloy Steel, produced at Salem and BPSL plants witnessed a 21% rise in alloy longs sales in FY 2024-25, making up 4% of the product mix. Further, sales of Bearing Steel grew 11%. New grades cater to automotive, textile machinery and general engineering.
Salem secured various product approvals across sectors like automotive, oil & gas and mining. Its strategic location ensures lower transport costs and faster deliveries. Additionally, the successful development of Boron Wire Rod grades at the Company’s Vijayanagar plant has further enhanced its product portfolio.
In alignment with the growing acceptance of BPSL products, the Company is in the process of securing necessary approvals from leading automotive manufacturers, including Maruti, Ashok Leyland, VE Commercial Vehicles, and Daimler India to name a few.
~30%
Market share held by us in the domestic Bearing Steel market
21%
Overall y-o-y sales growth#
Key projects served in FY 2024-25
- Seamless tube grade developed for ONGC through Maharashtra Seamless Tube.
- Grade developed and commercialised for defence shell bodies.
- Grade approved by RDSO for Vande Bharat railway suspension spring.
#Alloy rolled long products from Salem and BPSL considered
applications

While the Company’s steel is already being supplied to various key sectors for critical applications, its strategic growth plans are increasingly aligned with sectors of national importance. JSW Steel aims to contribute to these priority areas by delivering high-quality, reliable steel that fully meets the demanding application requirements, thereby supporting the nation’s development objectives.
Railways
Steel for railway wagons are specifically designed to ensure exceptional strength and durability, meeting the stringent performance requirements of heavy-duty rail transport operations.
Key applications
- Wagon
- Springs for Railway Coach
Defence
With rising government expenditure on defence, a strong push for self-reliance under the 'Make in India' initiative, and an increasing number of defence contracts being awarded to domestic industries, the defence sector remains a strategic focus area for us.
Key applications
- Aircraft Hanger
- Missile launcher
4.2 Marketing initiatives
In our ongoing commitment to customer-centricity, the Marketing function has embarked on a transformative journey to deepen engagement and responsiveness across both digital and physical touchpoints. Through strategic enhancements to our websites which cover all our products & special engagement for MSMEs, dynamic social media campaigns, and a more agile customer contact centre, we have created seamless and personalised experiences for our audiences. Simultaneously, our branded retail outlets have been revitalised to reflect our brand ethos and foster stronger in-person connections. These integrated efforts are designed to ensure that every interaction — whether online or offline — reinforces our dedication to understanding and serving our customers better.
2,300+
Nationwide stores
300
More stores planned for FY 2025-26

The JSW experience centre
The Company launched 'The JSW Experience Centre', a cutting-edge facility designed to highlight its extensive range of products and services, strengthen brand engagement and empower customers to make informed purchasing decisions. The centre features the JSW Legacy Wall, showcasing its journey and impact on the steel industry. The interactive Product Wall allows visitors to explore JSW’s diverse offerings, while the Digital Portal with kiosks provides easy access to product information and brochures via QR codes. With 30 Experience Centres spread across 20+ key markets, JSW brings its vision closer to communities, customers, and partners throughout India.
JSW shoppe
JSW Shoppe is a distinctive franchise model that forms a key part of the Company’s retail strategy, offering customers direct access to its extensive product range. Launched in 2007, these outlets, run by franchisees and managed by its channel partners, provide exceptional customer experience with assured product quality and brand consistency. Serving both cities and rural areas, nearly half of the Company’s 2,300+ nationwide stores are located in semi-urban and rural regions, with 300 more planned in financial year 2025-26. Looking ahead, JSW Steel aims to expand internationally, starting with Sri Lanka and Nepal in the SAARC region.
JSW branded outlet training programme
The company understands the importance of standardisation across all its retail touchpoints to achieve enhanced customer experience and brand loyalty. It has commenced a training programme aimed at upskilling the personnel associated with these branded outlets. This initiative provides product knowledge, skill development, and customer service training.
Collaboration with autocar
JSW Steel partnered with the renowned automotive magazine, Autocar to launch an innovative four-part video series titled, ‘Future of Mobility’. This engaging series spotlighted steel’s pivotal role in shaping the automotive industry’s evolution, featuring insights from leading global car manufacturers. Promoted through YouTube, social media and programmatic advertising, the campaign generated significant buzz, reaching a cumulative audience of nearly 50 million across platforms, reinforcing JSW Steel’s position at the forefront of future-ready mobility solutions.
Mass communication
JSW Steel uses festivals as a pivot to create awareness about its products in regional markets. As part of this ongoing initiative, JSW Steel launched a campaign centred around the festival of Pongal to create awareness about Colouron+ in the Tamil Nadu market. The campaign was brought to life through static images denoting the cultural nuance of the festival and highlighting the key features & variants of Colouron+ roofing sheets. This campaign was promoted across social media platforms and programmatic sites. The campaign achieved a cumulative reach of ~60 million across platforms. The digital campaign was supplemented by a regional OOH campaign across the state. The OOH campaign got recognition from the Madras Advertising Club (Maddys) with a Sliver in the Regional Tamil OOH category.

Celebrating the spirit of MSME’s
JSW Steel launched a film on World MSME Day on 27th June, 2024. The film showcased, JSW Steel’s commitment to MSMEs and how these micro, small & medium enterprises through their innovative and resilient attitude are reimagining the possibilities for a new growing India. This film was promoted on various social media platforms and You Tube. Across platforms, this film had a cumulative reach of ~62 million and a total viewership of ~41 million. The film got recognised for its creative storytelling with a Silver at the AFAQ’S Digies, 2025 in the Thought Leadership category.

IPL association with Delhi Capitals
JSW Steel connects with its channel partners through the association with the IPL team, Delhi Capitals. JSW Steel associated with DC Utsav, a channel connect initiative where channel partners are invited for a meet and greet and an opportunity to watch the Delhi Capitals live in action at one of the designated venues. DC Utsav was conducted in Kolkata & Mumbai. Close to 100 channel partners were part of the DC Utsav in each of the cities.

4.3 The JSW experience centre
The Company launched 'The JSW Experience Centre', a cutting-edge facility designed to highlight its extensive range of products and services, strengthen brand engagement and empower customers to make informed purchasing decisions. The Centre features the JSW Legacy Wall, showcasing its journey and impact on the steel industry.
The interactive Product Wall allows visitors to explore JSW’s diverse offerings, while the Digital Portal with kiosks provides easy access to product information and brochures via QR codes. With 30 such centres across 20+ key markets, the Company brings its vision closer to communities, customers, and partners throughout India.
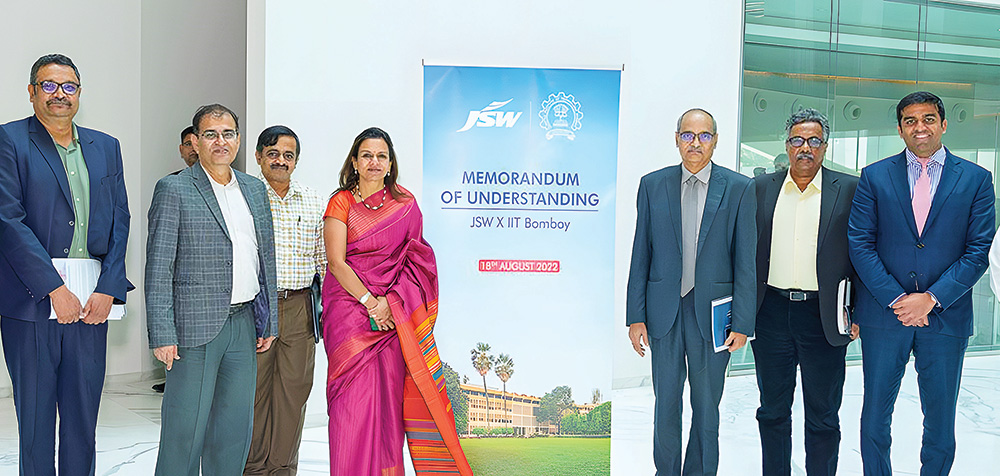

JSW Steel has partnered with IIT-Bombay to establish the ‘JSW Technology Hub’, a state-of-the-art facility to drive research and development in steelmaking. This collaboration focuses on advancing new and emerging steel technologies through cutting-edge research, training and technical studies, ensuring that both industry and academia can work together to pioneer innovative solutions for the future of steel.
5.1 Indian operations
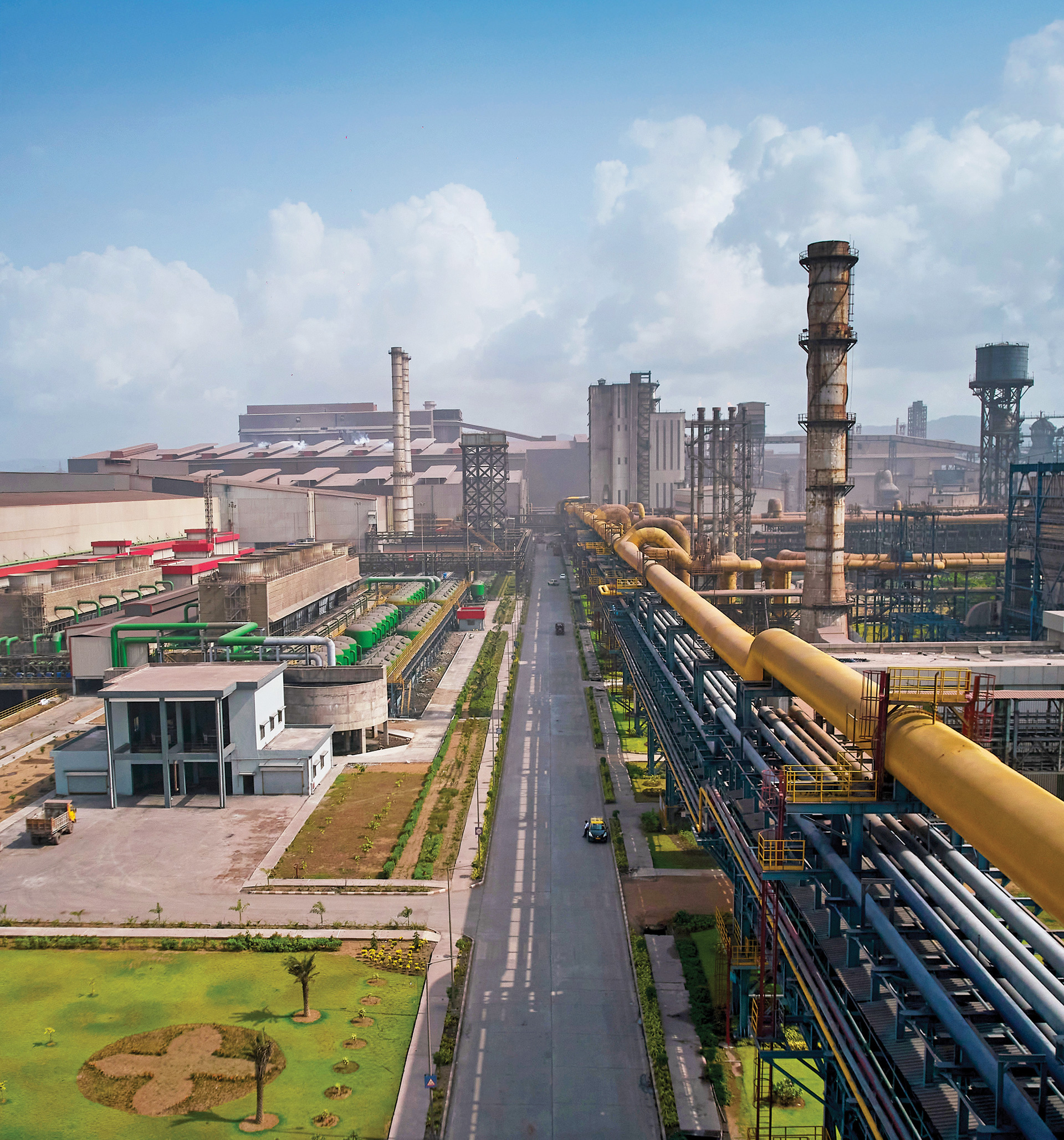


JSW Vijayanagar Works located in Karnataka, is India's largest integrated steel facility, with a 12.5 MTPA capacity (at the beginning of FY 2024-25). From humble beginnings 26 years ago, it has evolved into a benchmark of cutting-edge technology and operational excellence, showcasing the Company’s focus towards innovation and sustainability in steelmaking.
FY 2024-25 highlights
30%
Iron ore consumption from captive mines
30
Safety digital initiatives optimised with Man-machine Interface (MMI)
205
Digitalisation projects completed
Competitive strengths
- Largest single location with 17.5 MTPA crude steelmaking capacity (including 1.7 MTPA under commissioning).
- India’s largest beneficiation plant, boasting a 20 MTPA capacity, the facility is equipped with cutting-edge infrastructure to process low and medium-grade iron ores, enhancing resource efficiency and feeding agglomeration units with optimised inputs.
- 20 MTPA pipe conveyor system transports iron ore seamlessly from the mines to the plant, offering a green, cost-effective logistics alternative that significantly reduces transportation costs and environmental impact.
- India’s largest Pellet Plant (PP#3) with a capacity of 8 MTPA, employing low-pressure gas for pellet induration, delivering energy-efficient, high-quality pellets.
- Captive power capacity of 865 MW ensures reliable energy for operations, complemented by a 225 MW solar power plant. Wind Power, ~450 MW already commissioned and balance 150 MW under commissioning.
- Equipped with the Maximised Emission Reduction of Sintering (MEROS) system, the Sinter Plant complies with stringent environmental norms by significantly reducing stack emissions.
- Produces premium coke through stamp charged coke ovens with dry quenching, enhancing fuel efficiency by reducing coke moisture.
- Achieves 100% process waste utilisation via techniques like micro-pelletisation, briquetting (mill scale, LF slag, DRI fines), tailing beneficiation and converting slag to sand, pioneering circular economy practices.
- Implements unique clean steelmaking technologies such as the KR facility for deep desulphurisation, sub-lance systems, Electromagnetic Stirring (EMS) in slab casters auto mould-width adjustments and Twin RH degassing for superior steel quality.
- India’s largest auto-grade steel facility with a 2.3 MTPA capacity, offering an extensive portfolio of automotive and electrical steels to meet diverse industrial demands.
- Committed to import substitution and first-time adoption of Best Available Technologies (BAT), ensuring global standards in quality, efficiency and innovation.

20 MTPA
Capacity Iron ore Beneficiation plant
865 MW
Captive power generation capacity
20 MTPA
Pipe conveyor capacity
Digitalisation
- 239 projects undertaken and 205 projects completed during the year.
- 7,648 sensors were deployed across 1,725 critical rotating equipment for predictive condition-based monitoring, thereby enhancing performance monitoring and operational efficiency.
- An Automatic Guided Vehicle (AGV) system has been implemented at Blast Furnace (BF)-3 for handling coal mill rejection material, eliminating man-machine interface through sensor-based hopper level detection, line-following coal collection, algorithm-driven reporting, electronic valve control and intranet connectivity for seamless automation and communication.
- At BF-4, AI and machine learning have been deployed to identify incoming raw materials to the stock house and assess conveyor health, with the system’s output integrated with the distributed control system for interlocking and alarm generation, enhancing automation, accuracy, and operational safety.
- Remote slag skimming has been implemented using a thermal camera to detect slag levels during skimming, resulting in reduced hot metal handling losses, fewer chemical defects caused by sulphur, and enhanced operator safety.
- A slag detection system has been implemented using a low-wavelength infrared camera, which alerts the operator when to lift the converter, effectively preventing slag from entering the steel ladle.
- Implemented a robotic sticker pasting system at Colour Coating Line, where a robot with a printing head marks the coil number post band-strapping, retrieves the label from the printing machine, and pastes it on the coil using data received from the Level 2 interface.
- Introduced digital flare monitoring for gas volume analysis using AI-based cameras to track flare stack flame length and width, enabling optimised gas utilisation, quicker decision-making, and enhanced operational efficiency.
₹16 crore
Invested towards digitalisation
Environmental initiatives
- Installed and commissioned in-house source mounted De-Dusting System (DDS) at PP1 (Pellet Plant 1) to reduce dust emissions from the conveyor.
- 500 KLD (Kilo Litres per Day) Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) plant commissioned to treat and reuse sewage generated within the plant (office & canteen) and treated sewage water is reused in steel melt shop 3 for secondary application there by reducing its water requirement.
- Installed a dust suppression system in Junction House (JH) 7 & 8 of RMHS (Raw Material Handling System) and a DDS at JH-12 which resulted in reduction of Fugitive Emission.
- Noise study carried out in Agglomeration units to monitor high/ critical noise sources.
₹12 crore
Invested towards environment

Health and safety initiatives
- Replacement of 5.95 kilometres of vulnerable gas pipeline segments has enhanced safety and reduced leakage risks.
- Safety Culture Survey covered over 90% of employees, enabling targeted safety improvements.
- Contractor Safety Management (CSM) system was externally audited for compliance and improvement.
- Roof sheeting safety was strengthened through deployment of certified agency’s teams.
- A new software was implemented for advanced Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA) studies.
- Two additional fire tenders were added to strengthen emergency response capabilities.
- Seventy new road signboards were installed to improve traffic safety and visibility.
- A Digital Asset Management System was deployed to monitor and maintain firefighting equipment.
- Three more Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) units were installed, totalling 17 units for quick vehicle identification.
- Twelve advanced radar-based speed display units were installed to promote safe driving behaviour.
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) were installed in 13 heavy vehicles to reduce on-road risks.
₹26 crore
Spent on health and safety
Awards received
- IIM National Sustainability Award for initiatives in quality, higher product development, profit making, human resources management and environmental performances.
- CII DX 2024 Award for best practises in digital transformation for innovative category (10 awards).
- Responsible Steel Certification for Vijayanagar Manufacturing Sites.
- Jury Choice Award at Annual Sustainability Symposium and Excellence Awards by Indian Chamber of Commerce (ICC) for ESG Performance.
- Best Industry Award (Iron & Steel Industry) in safety performance from the Directorate of Factories, Boilers, Industrial Safety & Health, Government of Karnataka, during 53rd National Safety Day event.
- Manufacturing Occupational Health Safety & Environment excellence award by World Safety Organisation.
- GreenCo Platinum Certification from the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) is a prestigious recognition acknowledging exceptional environmental performance and sustainability practices in their operations.
- Golden Peacock Eco-Innovation Award for 2024 for development of a corrosion protective coating to steel composed of Magnesium, Aluminium and Zinc.
Capacity expansion initiatives
During FY 2024-25, JSW Vijayanagar Metallics Limited (JVML) a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company, successfully commissioned a 4.5 MTPA Blast Furnace, with the Blast Furnace ramping well and operating at over 90% capacity utilisation in March 2025. JVML has also commissioned Steel Melt Shop with a 3.3 MTPA capacity, with one converter and both casters fully operational. The second converter at the SMS is expected to be commissioned in Q2 FY 2025-26 (1.7 MTPA under commissioning in JVML).
FY 2025-26 priorities
Blast Furnace 3 upgradation
Revamp and upgrade of Blast Furnace 3 from 3 MTPA to 4.5 MTPA along with associated auxiliary units. This upgradation will increase the crude steel capacity to 19 MTPA at Vijayanagar and provide cost savings due to larger Blast Furnace operations. The project is expected to be commissioned in Q4 of FY 2025-26.
Operationalise three iron ore mines in Karnataka
Increase the production from the existing nine iron ore mines and operationalise three new iron ore mines viz. Vyasankere, Jaisinghpura South, Jaisinghpura North to cater to the iron ore requirements at Vijayanagar.
Operationalise other key projects
- Modernisation of Hot Strip Mill 1, increasing the capacity from 3.2 MTPA to 3.8 MTPA.
- Commissioning of the Coke Oven – 5 battery C of 0.75 MTPA by Q4 of FY 2025-26.
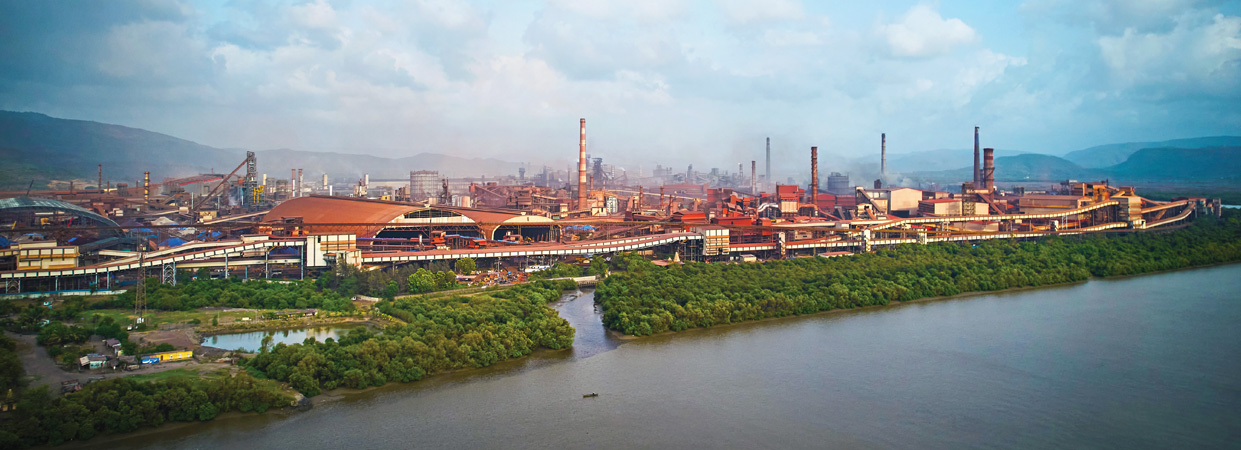

JSW Dolvi Works is a 10 MTPA integrated steel facility that stands as a symbol of transformation and technological advancement. Since its acquisition in 2010, the Company has expanded the plant’s capacity from 3.3 MTPA to 10 MTPA through strategic brownfield expansion. Specialising in flat steel production, Dolvi boasts 8.5 MTPA capacity in flat products and 1.5 MTPA in long products. It pioneered the use of Conarc technology in India for steelmaking and compact strip production for manufacture of Hot Rolled Coils. The site also features a dry Gas Cleaning Plant and Energy Recovery System in its Steel Melt Shop.
FY 2024-25 highlights
27%
Iron ore consumption from captive mines
25
Digitalisation projects completed
4
Safety digital initiatives optimised with Man-machine Interface (MMI)
Competitive strengths
- JSW Dolvi Works leverages its strategic coastal location for seamless logistics and efficient supply chain management. This advantage is further strengthened by the mechanised operations at JSW Jaigarh Port, which enable substantial raw material handling capacity, reducing road transport reliance.
- Dolvi Works is the first plant in India to adopt a combination of Conarc technology for steelmaking and compact strip production for producing hot rolled coils, providing the unit with flexibility to use a combination of solid charge and liquid hot metal.
- The plant is also powered by sustainable infrastructure, including 175 MW Waste Heat Recovery Boilers (WHRB) and a 60 MW captive power plant, which utilise flue gases and CDQ steam to efficiently meet the energy needs of the Phase II 5 MTPA expansion.
- Further strengthening operational resilience, the site has upgraded its 220 KV Air Insulated Substation to a more durable and space-efficient Gas Insulated Substation, supporting future capacity and enhancing system reliability.
- A state-of-the-art central store project has introduced automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS), alongside AI-led inventory management to streamline operations and reduce manual errors.
- Dolvi’s product portfolio is as diverse as its capabilities, catering to industries such as automotive, infrastructure, machinery, construction, LPG cylinder manufacturing, cold rolling, oil and gas and consumer durables.
10 MTPA
Capacity
301 MW
Captive power generation capacity
8.5 MTPA
Capacity in flat products

Digitalisation
- Machine learning-based predictive model to estimate the Reduction Degradation Index (RDI) of sinter in real-time for proactive process control and consistent product quality.
- A real time laser technology monitoring system to track the overlap position of belt in pipe conveyors to ensures belt alignment, preventing belt damage, and enhance equipment reliability.
- High-precision infrared line scanners were installed and integrated with level 1 system for online monitoring to enhances casting quality and operational consistency at both casters.
- Online Condition monitoring sensors deployed along with dashboard for critical rotating equipment & Conveyors for predictive conditionbased monitoring, thereby enhancing performance monitoring and equipment reliability.
- High-voltage (33kv and 6.6KV) protection relays were networked centralised for recording and monitoring of faults and events. This initiative improves power system reliability and troubleshooting time through end-to-end visibility on dashboard.
- Condition monitoring of critical material handling conveyors to prevent spillage and improve cost efficiencies using digital solution.
- A centralised Operational Technology network health monitoring system has been set up to assess the condition of communication and control systems in the Compact Strip Production (CSP) Mill to avoid network system failures, resulting in operational efficiency.
- A hot metal de-slagging system with automated raking and vision system has been implemented to enhance operator safety and reduces manual intervention during slag removal.
- Digital Twin technology based digital solution has been deployed for condition monitoring of universal joint bearings in roughing Mill to predict the anomalies and their respective measures to enhance the equipment reliability and operational efficiency.
- Digital Twin technology based digital solution has been deployed for condition monitoring of Coke Oven Exhausters (4 Nos.) to predict the anomalies and their respective measures to enhance the equipment reliability and operational efficiency.
- SAMPARK Digitalisation for logistics and material tracking was implemented for inbound materials and is under implementation for in-plant movement. This initiative ensures end to end visibility and logistics efficiency.
- Machine learning based model was introduced to optimise the addition of ferro alloys in Steel Melting Shop 1 resulting in optimum alloy consumption and consequent reduction in production cost.
- Long Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN) based connected workforce solution implemented in Coke Oven 1 and Coke Oven 2 for workforce safety.
₹7 crore
Invested towards digitalisation
Environmental initiatives
- Installed and commissioned 300 KL per day STP (Sewage Treatment Plant) which will reduce fresh water consumption.
- Installation of feeding system along with Dust Extraction (DE) system in Sinter Plant 2 for feeding and consuming waste material.
- Installed low-pressure and high-pressure Dry Fog Dust Suppression (DFDS) system at pellet yard on the back side of incinerator area and jetty yard to eliminate fugitive emissions during bulk material handling.
- Installed Dust Extraction for Product Building for Induration Feed end & Pneumatic Conveying System to eliminate any fugitive emission generation during operation.
- Fogger System was installed in the Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) Slag pit area to control fugitive emissions during slag handling.
- Conducted the Biodiversity Dependency-Impact Assessment for NNL (No Net Loss on Biodiversity) Study; in the process of publishing its first report on Biodiversity.
- 1,766 trees planted inside the plant boundary.
₹100 crore
Invested towards environment


Health and safety initiatives
- ‘Safety Culture Survey’ was conducted for 11,643 employees (including on role, associates and contract employees) and action plans were prepared.
- 5 Subject Matter Expert (SME) certification programmes were conducted.
- 12 GEMBA walk downs conducted during FY 2024-25 and achieved 96% of average compliance on opportunity for improvements (OFIs) identified during GEMBA walk downs.
- Conducted 245 departmental areawise Cross-Functional Safety Audits in FY 2024-25 by identified leaders.
- The Company advanced safety and emergency preparedness through Rakshak’s connected workforce alerts, immersive VR and simulator-based trainings, 3D animated case studies, extensive e-learning modules and a revamped Safety Experience Centre.
₹16 crore
Spent on health and safety
Capacity expansion initiatives
JSW Steel Dolvi Works, a 10 MTPA integrated steel plant, is expanding to 15 MTPA by September 2027. through installations of state-of-theart facilities such as 4.8 MTPA Blast Furnace, Steel Melt Shop of 5 MTPA and Hybrid Continuous Strip Mil that can produce plates and coils. The project includes setting up of 250 MW captive power plant which will utilise the excess gas available from the Blast Furnace reducing the overall power cost at Dolvi. The project is expected to be commissioned by September 2027. Progress includes 60% engineering completion, ordering completion and innovative initiatives like Power BI dashboards, drone surveys, BIM models and automated welding solutions.
FY 2025-26 priorities
Capital Shutdown of Blast Furnace-1
Capital shutdown of Blast Furnace-1 for replacement of staves and improve operational efficiency in terms of fuel cost reduction, increase in Pulverised Coal Injection to enhance production and reduction in costs
Higher scrap usage at steel melt shop
Increased usage of scrap at Steel Melt Shop for enhancing production volumes.
Renewable power sourcing
In phase I, Dolvi had planned to set up 94.5 MW of wind power for replacement of coal-based power to reduce the CO2 emissions and reduction in power cost. Currently ~70% of wind power capacity is commissioned and the entire 94.5 MW wind power is expected to be commissioned by Q2 of FY 2025-26.
Awards & recognition
- Achieved ‘Core Site Certification’ against the Responsible Steel International Production Standard.
- ‘International Winner Award’ from Greentech Foundation recognises global-level excellence in implementing innovative and impactful EHS practices including digital safety systems, behavioural safety programmes and leadership engagement.
- National OHS Award-2024 (Large Enterprises-Steel Sector) from Global Safety Summit for outstanding Occupational Health & Safety (OHS) performance for implementation of proactive safety culture, health risk mitigation, and compliance excellence.
- Platinum Award from Grow Care India OHS Award-2024 for exemplary safety leadership, system implementation, and employee engagement.
- Platinum Award from 9th Apex India OHS Award-2024 acknowledges high-performing organisations in OHS policy execution and industry benchmarking.
- Gold Award from Indian Chamber of Commerce in 6th ICC National OHS Awards-2024 Recognises leadership and continuous improvement in OHS systems.
- First Prize – Manufacturing (Large) category from CII Western Region ‘SHE Excellence & Innovation Awards 2024’, appreciates innovation and sustainability in safety, health, and environment practices.
- Winner Award – ‘Workplace Safety Excellence 2024’, both from Greentech Foundation and Green Enviro Foundation for recognising excellence and continuous improvement in workplace safety and employee wellbeing.
- Silver Award – 7th CII-IQ National Safety Practice Competition, encourages sharing of innovative and replicable safety practices across industry

JSW Steel’s Salem Works stands as India’s largest specialty steel facility, boasting a production capacity of 1 MTPA. Renowned for its advanced manufacturing capabilities, it is among India’s leading producers of special alloy steel long products, serving a wide array of industries with precision and innovation.
FY 2024-25 highlights
60%
Iron ore consumption from captive mines
45
Digitalisation projects completed
8
Safety digital initiatives optimised with Man-machine Interface (MMI)
Competitive strengths
- Strategically nestled in South India’s mineral-rich belt, JSW Steel’s Salem Works enjoys assured raw material access.
- It is supported by robust rail and road connectivity.
- Ideally positioned to serve automotive hubs in southern and western India, the plant manufactures up to 850 special steel grades, supplying all major domestic automotive OEMs.
- It leads the market in specialised steels for bearings, cold heading quality wires and forging applications, reinforcing its reputation as a trusted partner in high-performance metallurgy.
1 MTPA
Capacity
97 MW
Captive power generation capacity
~850
Special Steel Grades
Digitalisation
- Implemented a Real-Time Analytics and Fault Prediction System in MRSS, delivering key benefits such as minimising production loss by preventing tripping, reducing Mean Time to Repair (MTTR), eliminating manual troubleshooting and enhancing accuracy in fault identification.
- Introduced Robotic Hot Bloom Labelling for Continuous Casting Machines (CCM), reducing the Risk Priority Number (RPN) score from 48 to 16 to enhance workplace safety, while significantly improving labelling accuracy, reliability, and overall customer satisfaction.
- Implemented a VR Safety Training Module covering Electric Overhead Travelling (EOT) Cranes, Fire Extinguishers, Conveyor Safety, Work at Height, Confined Space Entry and Lancing, enabling real-time training and assessment for EOT crane operators, enhancing emergency preparedness, simulating high-risk scenarios, reducing risks and accidents and allowing for adaptable, customised training experiences.
- Deployed a Predictive Maintenance Platform, resulting in a reduction of 190 hours of equipment downtime and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
₹5 crore
Invested towards digitalisation
Environmental initiatives
- Utilisation of Compressed Bio Gas (CBG) in place of High-Speed Diesel (HSD) which has eliminated HSD usage in the annealing plant and GHG (Green House Gas) emissions reduced.
- Usage of Biochar in Iron Making replacing Pulverised Coal Injection (PCI) coal enabling the unit to achieve GHG emission reduction.
- Increased blending of biomass from 5% to 7% with steam coal in Captive Power Plant (CPP) which contributed to GHG emission reduction.
- Initiated the use of Compressed Bio Gas (CBG) instead of Diesel in the annealing process which reduced GHG emissions.
- Stack Emission reduction in Sinter Plant 1 process by installing Electro Static Precipitator (ESP) which reduced dust emissions.
- Reduction of fines in raw materials by minimising fall height during material handling in Sinter Plant which resulted in GHG emission reduction.
- Reduction of fugitive emissions at Ladle Refining Furnace (LRF) alloys transfer area by installing a localised dedusting system has substantially decreased fugitive emissions.
- Upgradation of scrubber system at Etching lab for stack emission control has ensured Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) practices at the Pickling plant and Etching Lab.
- Inauguration of “Climate Action Centre” which has monitored Sustainable Energy Environment & Decarbonisation (SEED) projects and other sustainability initiatives which streamlined tracking and governance.
- Deepening of rain water harvesting pond to enhance the main rain water harvesting pond capacity.
₹6 crore
Invested towards environment

Health and safety initiatives
- Virtual Reality training modules were developed for fire safety, confined space entry, working at heights, conveyor safety, and lancing operation to provide immersive and high-impact safety training experiences.
- Noise exposure assessment was conducted by Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) at identified areas and necessary corrective actions have been initiated to safeguard employee hearing health.
- 113 EOT crane hooks were inspected to detect internal structural deformation along with complete thickness inspection of the Blast Furnace (BF) gas line to prevent equipment failure and ensure mechanical integrity.
- Management of Change (MoC) and Pre-Startup Safety Reviews (PSSR) were completed for all new projects and modifications, and 14 additional PSSRs were conducted for major shutdowns to proactively identify and mitigate operational risks.
- Smoke detectors were installed in all electrical panel rooms and integrated with the central fire control room to enable early fire detection and faster emergency response.
- Firefighting capabilities were enhanced by upgrading one dieseloperated pump, one electrically driven pump, and one jockey pump at the fire pump house to ensure reliable water supply during fire emergencies.
- Fire hydrant water capacity was increased from 1,350 m3 to 2,350 m3 by converting an existing sump to strengthen the site’s fire preparedness.
- Safety Champion Certification programme was launched for Associate Safety Champions and Contract Supervisors, with 187 individuals successfully certified to build ownership and reinforce onground safety leadership.
- Subject Matter Expert training was delivered for 10 Group Safety Standards resulting in 201 SMEs being certified to drive consistent safety implementation and ensure standard compliance across operations.
₹8 crore
Spent on health and safety
Capacity expansion initiatives
The steelmaking capacity is being expanded to 1.2 MTPA from 1 MTPA by way of debottlenecking and expected to be completed by FY 2025-26.
The new auto-inspection lines at Salem Works feature a fully integrated system, including an in-line straightening machine, internal soundness, surface defect detection and surface conditioning stations, marking a first in India for such advanced surface inspection. These lines eliminate manual inspection, enhance reliability and improve inspection throughput and ensuring comprehensive inspection for all products.
FY 2025-26 priorities
- Commissioning of a Bearing Steel Project, Ladle Furnace 5 and 3rd Vacuum degassing system.
- Automated Slow Cooling Facility at Blooming Mill.
- Level 2 automation in Steel Melt Shop and Blooming mill.
- Construction of Safety Experience Centre and an additional Coal Bin.
- Installation of online heat flux monitoring system and a Tuyere camera in BF-1.

Awards received
- Responsible SteelTM certification for high standards set in ESG practices within the steel industry.
- 16 Teams were participated and won 16 Gold (First category) awards in Chapter Convention on Quality Concepts (CCQC) and two teams won Best of Best award in this competition.
- 8 Teams were nominated and won 8 Par Excellence (First category) awards in National Convention on Quality Concepts (NCQC)@ Gwalior.
- 4 Teams participated and won 3 Gold (First category) awards and 1 silver award in International Convention on Quality Control Circles (ICQCC) at Sri Lanka through a virtual mode.
- Blast Furnace team participated in the MQH Best Practice competition conducted by IMC Ramakrishna Bajaj National Quality Award and won the prestigious MQH (Making Quality Happen) Trophy under Manufacturing category.
- ISQ TOPS convention – SMS team won the winner award for the project “Quality improvement in 18CrNiMo7”.
- CII IQ National Safety practice competition – 3 of the Company’s teams (WT, SP & SMS) participated in this competition and won 1 Gold & 2 Silver awards.
- CII Indian Industry Master Mind Quiz – the Company’s cross functional team (Blast Furnace, Iron Zone & Business Excellence) participated & secured Second runner-up award.
- Received “Platinum Award” for Environment Improvement in 16th Exceed Green Future Awards 2024 held in Hyderabad on August 2, 2024.
- Received “Gold Award” for Waste Management in 16th Exceed Green Future award.
- Received “Gold Award” for Human Resources wellness in 16th Exceed Green Future award.
- Honoured with the prestigious Gold Award and EHS Leadership Award at the 16th Edition of the Confederation of Indian Industry – Southern Region (CII-SR) EHS Excellence Awards 2023.
- Achieved the prestigious "Aspiring Water Neutrality/Positive Plant" certification in 10th CII Water Innovation Summit 2024, organised by the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII).
- Three of JSW Steel’s teams participated in 6th ABK AOTS Maintenance Competition, Blooming Mill and Steel Melt Shop teams won Rhodium award and Sinter Plant team won Platinum award.
- 3 Teams participated and won 2 Par Excellence (First category) awards and 1 Excellence award in 10th National conclave on 5S conducted by Quality Circle Forum of India (QCFI).
- Received the “Silver Award” for Innovative Human Resources Practices in National HR Excellence award organised by NIPM (National Institute of Personal Management).
- Recognised with ‘Platinum Award’ in the EHS Excellence Awards 2024 organised by EKDKN.

JSW Steel Raigarh Works is a fully integrated steel facility with a crude steel capacity of 0.95 MTPA. Renowned for its precision and quality, the plant specialises in producing high-grade special alloy steel across both long and flat product segments, serving a diverse range of industrial applications.
FY 2024-25 highlights
78%
Iron ore consumption from captive mines
3
Digitalisation projects completed
Competitive strengths
- Strategically located within the resource-rich coal and iron ore belts of Chhattisgarh and Odisha, JSW Steel Raigarh Works enjoys seamless access to essential raw materials.
- Backed by robust rail and road connectivity.
- The facility manufactures a diverse range of special-grade long and flat steel cast products, high-grade sponge iron, iron pellets and TMT bars.
- Its long products find critical applications in rails, seamless pipes, wire rods and specialised forging components such as flanges.
- The plant produces up to 157 special steel grades and remains the only JSW unit to manufacture 350 mm round bars.
0.95 MTPA
Capacity
170 MW
Captive power generation capacity
Digitalisation
- Energy Monitoring System (EMS) – EMS has been installed & commissioned for Power plant, Switch Yard and SVC, enabling continuous real time monitoring for each location.
- Manufacturing OT Data foundation – Approximately 10,000 tags and 65+ controllers integrated to the Site OT historian. This strong foundation will enable many real-time performance monitoring and digital use cases.
- Surveillance command centre integrating multiple camera systems across sites that have the potential to deploy AI powered detection and alerting for violation of essential safety practices, contributing to overall safety improvement at site.
- Power Optimisation by installation of Variable Voltage Variable Frequency (VVVF) Drive – 3 nos VVVF Drives were installed in Blast Furnace & Sinter Plant for controlling process suction and directly optimisation of power by reducing the speed of motor.
₹5 crore
Invested towards digitalisation
Environmental initiatives
- 100% reuse of waste water for ash conditioning, cleaning, sprinkling and greenbelt development by laying of wastewater treated line for reduction in fresh water consumption.
- Use of STP treated water into power plant cooling towers as a makeup.
- Primary water is replaced with 100% waste water use in DRI, Sinter & Pellet plant for cooling purpose.
- Modification of Hood Cast House at BF to increase the suction of fume extraction system.
- Installed a Fume Extraction (FE) system at PCM (Pig Casting Machine) lancing area to reduce Fugitive Emission the Blast Furnace Lancing Area.
- Installation of 3 Mist Cannons – SMSCrusher Area, Slag pit and billet caster area for reduction of fugitive emission at SMS and improved Air Quality (fugitive emission) and visibility, enhanced safety for personnel, less water consumption.
₹2 crore
Invested towards environment
Health and safety initiatives
- Chetna, a behavioural science-based safety intervention, was introduced at Raigarh Steel following the Safety Culture Survey.
- Machine guarding and fall protection barriers were installed across critical equipment and height-risk areas to prevent contact injuries and fall incidents, enhancing workplace safety.
- A new fire tender was procured to strengthen the site’s emergency response infrastructure, ensuring faster mobilisation and improved firefighting capability across high-risk zones.
₹8 crore
Spent on health and safety
Capacity expansion initiatives
Installation of 20 TPH PCI mill at Blast Furnace
Installation of this mill will improve the PCI injection capacity from 150 Kg/thm to 180 kg/thm and will also enhance the Blast furnace production volumes.
Awards received
'SHE Excellence Awards' from CII-Chattisgarh as certificate of appreciation in 'Large Scale Manufacturing Sector' for its contribution towards Safety, Health and Environment in FY 2023-24.

FY 2025-26 priorities
Capital shutdown of captive power plant
Overhauling of turbine, coil replacement at boiler, tube replacement, ESP overhauling and cooling tower overhauling for improving operational efficiencies of the power plant.
Effective utilisation of the bast furnace gas
Installation and commissioning of system allowing usage of Blast Furnace Gas in AFBC boiler.
Installation of battery energy storage system
Installation and commissioning of Battery Energy storage system reducing garbage power by storage in BESS.

5.3 MTPA
Capacity
Acquired by JSW Steel in March 2021 through the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, BPSL is an integrated steel producer based in Sambalpur, Odisha, currently operating at a capacity of 4.5 MTPA. BPSL also boasts a downstream capacity of 1.8 MTPA across Sambalpur, Kolkata and Chandigarh. Renowned as one of India's largest alloy steel producers, BPSL has an impressive 1.2 MTPA alloy steel manufacturing capacity.
FY 2024-25 highlights
72%
Iron ore consumption from captive mines
Competitive strengths
- India’s first Transportation and Power Generation (TPG)-accredited heat treatment process for long products certified - Administered by performance review institute (PRI)- United State of America, setting a new industry benchmark.
- Holds the highest number of Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) product licences in India, with 32 operational and 7 pending approvals.
- The captive power plant (CPP) equipped with high energy drain (zero leakage) valves for enhanced efficiency.
- Home to an India’s first Dual fuel (Blast Furnace Gas + Coal) using Circulating Fluidised Bed Combustion Boiler (CFBC) boiler technology, boasting a remarkable 250 TPH capacity.
- Fully automated Captive Power Plant, where all boiler (Circulating Fluidised Bed Combustion Boiler, Atmospheric Fluidised Bed Combustion Boiler & Waste Heat Recovery Boiler) are seamlessly interconnected.
- Houses of a largest tube mill complex at a single site, with a production capacity of 0.5 MTPA.
- Recognised as India’s largest bright bar producer at one location, with a 0.1 MTPA capacity and advanced three-roll technology.
- First plant in India with the capability to produce hexagonal bars ranging from 18.5 mm to 60 mm, including custom decimal sizes.
- First plant in India offering the widest range of wire rod sizes, spanning from 5.5 mm to 60 mm.
- Compact Strip Production (CSP) line enables the manufacturing of thinner sheet coils, down to 1.2 mm thickness.
- Blast Furnace-2 stands as the second plant in India equipped with a dynamic Pulverised Coal Injection (PCI) distribution system.
4.5 MTPA
Capacity
516 MW
Captive power generation capacity
Digitalisation
- Implemented a Data Historian and Dashboard for monitoring and analysing the Iron Zone operations.
- Electrical - Energy Management System for Blast Furnace-1, Blast Furnace-2, Sinter-2, Pellet & Beneficiation Plant, Cold Rolling Mill, Coke Oven-2 completed for performance monitoring which led to improvement in operational efficiencies.
- Ladle Management System for Steel Melting Shop - 1 completed.
₹3 crore
Invested towards digitalisation

Environmental initiatives
- Optimised utilisation of flared by-product gases (Blast Furnace Gas and Coke Oven Gas) across shops and the 250 TPH steam generation unit, resulting in reduction of Blast Furnace Gas flaring from 30% to 10% and Coke Oven Gas flaring from 26% to 4%.
- Upgraded obsolete mod motor control systems to electronic expansion control for 8 chillers, and phased out 2 x 250 TR chillers using R-22 refrigerant in Steel Melting Shop-1, which led to electrical energy savings.
- Achieved significant energy savings by stopping idle running equipment, including Sinter Plant 2, Coke Oven -II, and Compact Strip Production (CSP).
- Replaced 45 steam traps across various shops, contributing to the reduction of steam losses.
- Utilised Coke Oven Gas (COG) in the coal dryer at the Coal Washery, enhancing fuel efficiency.
- Installed desuperheaters, resulting in steam savings of 130 TPD, annual power savings and a reduction of CO2 emissions.
- Enhanced steam generation in the Coke Oven from 1.4 to 1.6 tonnes per ton of coke through effective heat loss reduction.
- Significant reduction in tar fog through installation of new Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) controller at Coke Oven-2.
- In Coke Oven Plant Implemented an Auto-Ignition system in Gas Bleeders to minimise environmental emissions by ensuring reliable and automatic ignition of released gases.
- Commissioned Acid Recycling Plant-5 (ARP-5) in October 2024, leading to reduced LPG usage in older ARPs through increased use of COG.
- Commissioned a Zero Power Furnace (ZPF) at Steel Melting Shop-II in April 2024, enhancing energy efficiency in steelmaking.
- De-staged boiler feed pumps at Circulating Fluidised Bed Combustion (CFBC) Boilers and Direct Reduced Iron (DRI), resulting in energy savings.
- Installed a 3.5 MWh micro turbine at the 340 TPH Boiler Pressure Reducing and De-superheating System (PRDS) in the Power Plant to harness waste heat energy.
- Implemented Top Pressure Recovery Turbine (TRT) power generation system at Blast Furnace-2, converting top gas pressure into useful power.
- Installed Coke Oven Gas network boosters to improve gas pressure across the system and reduce energy losses.
- Organised an Energy Conservation Programme on 14th December 2024 across various shops to raise plantwide awareness on energy efficiency.
- Commissioned the Wire Rod Mill Gas Mixing Station, enabling the use of an additional 6,500 NM³/hr of flared Blast Furnace Gas.
- Optimised compressed Air pressure in network and Automated pneumatic conveying system, caused a reduction in specific compressed Air consumption by 50 nm3/Ton per Crude Steel.
₹303 crore
Invested towards environment
Health and safety initiatives
- Recorded 2,25,507 safety observations across operations, reinforcing a proactive safety culture.
- Achieved 2,96,161 man-hours of safety training, enhancing workforce preparedness.
- Completed skill assessments for 20,399 employees to identify and bridge competency gaps.
- Inaugurated a state-of-the-art Safety Experience Centre for immersive induction training on high-risk standards.
- Conducted a 3-day Felt Leadership Programme for 56 senior leaders to deepen commitment to safety.
- Certified 129 Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) through two on-site training.
- Launched Virtual Reality (VR) based safety modules to simulate high-risk scenarios and enhance training effectiveness.
- Carried out a comprehensive safety culture survey covering 14,100 employees to identify key safety initiatives.
- Initiated external training on Process Safety Management (PSM) including Process Technology (PT) sessions and documentation.
- Organised road and home safety awareness programmes for employees, women staff, and township residents.
- Trained and certified 756 operators for Farana and Electric Overhead Traveling crane (EOT) cranes through external agencies.
- Standardised and implemented updated safety protocols across the plant.
- Installed 450 ABC modular (A type, B type, C type) fire extinguishers in cable galleries, taking the total to 950 units.
- Commissioned a multi-purpose fire tender and installed a compressor for Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus (SCABA) cylinder refilling.
- Enhanced road safety with Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) cameras, speed radars, poles, and blinkers to minimise accidents.
- Established interlocks in between all battery moving machines to enhance operational safety and prevent unauthorised or unsafe equipment use.
- Implemented oven identification system in all battery moving machines to improve tracking, monitoring, and operational efficiency.
₹14 crore
Spent on health and safety
Capacity expansion initiatives
- BPSL completed the Phase 2 capacity to increase from 3.5 MTPA to 4.5 MTPA during the year.
- Key capacity enhancement projects have been commissioned, including upgrades to Blast Furnace -1 and Blast Furnace-2 with advanced Pulverised Coal Injection grinding, drying units and dynamic flow control valves to boost hot metal production, alongside Lime Calcination Plant (LCP) -6 to support calcined lime needs for the steel melting shop and sinter plant. Additional infrastructure improvements such as the coal drying unit, Raw Material Handling System (RMHS) capacity augmentation, and Wire Rod Mill-1 upgradation have been implemented to reduce coal moisture, streamline raw material handling and raise Wire Rod Mill-1 production capacity from 0.5 to 0.6 MTPA. Also commissioned the Wire Rod Mill-2 of 0.6 MTPA taking the total Wire Rod capacity to 1.2 MTPA.
- A new Acid Regeneration Plant has been commissioned, utilising mixed gas and coke oven gas in place of Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), offering greater energy efficiency along with ease of maintenance and cleaning. Additionally, the Cut to Length (CTL) facility has been completed, now consistently producing approximately 20,000 tonnes per month.
FY 2025-26 priorities
Business excellence
- Responsible Steel Certification of Sambalpur Works
- All 8 Pillars implementation of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
Coke oven
- Trails of coking coal for optimisation of coal blend to achieve significant cost savings while maintaining fuel quality and operational efficiency
- Implementing Coke dry quenching to recover waste heat, improve energy efficiency, and reduce environmental impact in the coke production process
Central utility
- Usage of PNG (Piped Natural Gas) in place of Liquefied Petroleum gas to reduce LPG consumption.
- Introducing a Reverse Osmosis and Zero Liquid Discharge (RO & ZLD) system with a capacity of 2,200 m³/day to reduce freshwater consumption and eliminate liquid discharge from the plant.
- Implementing an auto positioning system for all battery moving machines to enhance operational accuracy, improve safety, and optimise movement efficiency within the plant.
Awards received
- 5 gold trophies bagged in International Convention on Quality Control Circles (ICQCC 2024), Colombo, Sri Lanka.
- 38 national awards bagged across Platform Govt. of India, Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), National Convention on Quality Concepts (NCQC), Council of Enviro Excellence (CEE) and Green Maple Foundation (GMF).
- 54 state level awards bagged across Platform Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), National Productivity Council (NPC) and Chapter Convention on Quality Concepts (CCQC).
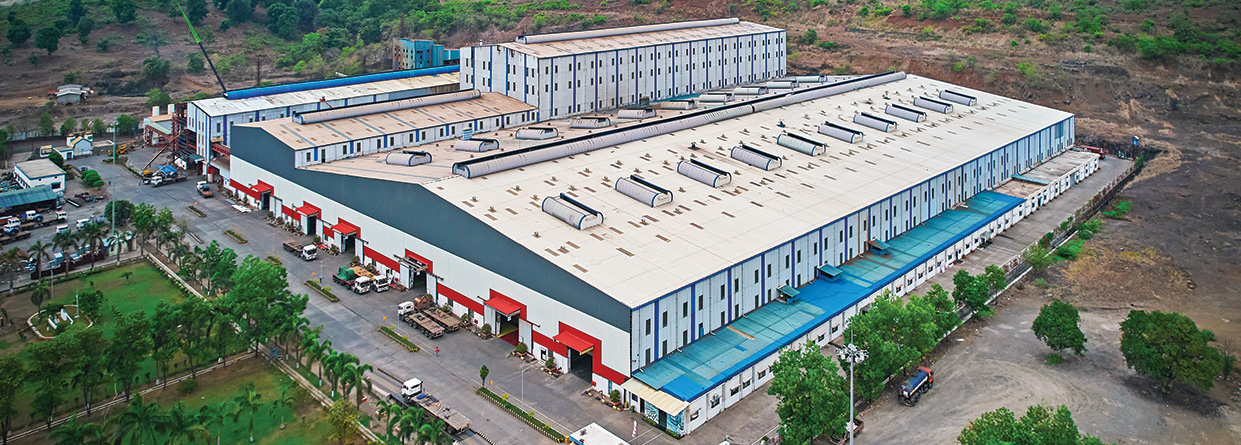

JSWSCPL is India’s largest manufacturer and exporter of coated steel products, with a 5.3 MTPA capacity. With eight plants nationwide, it leads in innovation, offering galvanised, galvalume, CRCA, colour-coated and tin mill products. With over 45% domestic market share, it aspires to be a global consumer-centric brand.
FY 2024-25 highlights
8
Digitalisation projects completed
2
Safety digital initiatives optimised with Man-machine Interface (MMI)
Competitive strengths
- World-class manufacturing facilities spread across eight strategic locations in India.
- A strong distribution network with over 44,000 Fabricators, 15,000 retailers and 210 distributors, ensuring deep rural reach.
- Enabled channels and faster distribution capabilities, offering prompt service and extensive market coverage.
- Best-in-class customer experience through Shoppe Connects and immersive Experience Centres.
- Robust influencer ecosystem, delivering quality service through a loyal fabricator network with the only player offering structured training programmes and continuous engagement.
Digitalisation
- Enhanced internal capabilities and laid the groundwork for scalable, data-driven operations.
- To strengthen digital expertise, 30 employees completed the Post Graduate Diploma in Smart Manufacturing (PGDSM) in collaboration with BITS Pilani, equipping them to lead Industry 4.0 transformation across shop floors.
₹40 crore
Invested towards digitalisation
Environmental initiatives
- Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) via Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) and Acid Regeneration Plant (ARP) systems installed for industrial waste, with treated domestic wastewater from Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) reused for process and landscaping needs.
- Use of Natural Gas to ensure Total Particulate Matter (TPM) and other emissions are consistently maintained within SPCB-prescribed limits.
- Energy, waste, GHG emissions and water conservation metrics are monitored per tonne of production to strengthen accountability and efficiency.
- Internal audits to ensure sustained environmental and regulatory compliances.
₹26 crore
Invested towards environment
Health and safety initiatives
- Multi-tiered safety reviews via the Group Safety Council, Apex Safety Committee, and daily plant meetings ensure constant vigilance.
- Certified under ISO 45001:2018 with annual external audits to uphold international benchmarks.
- Internal and third-party audits on a regular basis to evaluate and enhance safety systems.
- Standard operating procedures and emergency work instructions are available for all operations.
- Regular safety drills, monthly awareness sessions and competitions engage the workforce in continuous learning.
- HOD-led shop floor visits help identify quick-win safety improvements and boost engagement.
- Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) KPIs benchmarking and awards to cultivate a culture of competition and excellence across coated plants.
- Online interactions to reinforce top-down EHS commitment and monitor progress.
- Strengthened compliance in areas such as Lockout Tagout (LOTO), confined spaces, machine guarding, and electrical safety.
- Operators, electricians, welders and fitters undergo specialised training from external experts.
- Active involvement of women in all EHS programmes and committees.
- 90%+ safety observation closures, 23 Safety Centre of Excellence (CoE) projects, extensive Subject Matter Expert (SME) training, mock drills, and successful audit completions.
₹1 crore
Spent on health and safety

Capacity expansion initiatives
- The Colour Coating Line (CCL) at JSW Steel, Pulwama, with a capacity of 1.2 lakh tonnes was successfully commissioned.
- Annealing facility at Tarapur has been commissioned post capacity enhancement from 2.5 lakh to 3.25 lakh tonnes per annum.
FY 2025-26 priorities
- Yield improvement initiatives to reduce cost of production.
- Deployment of Connected Workforce tools, Digital PTW, advanced fire and medical response systems, PPE detection cameras and updated Group Safety Standards across key plants.
- Implementation of Visible Leadership Programmes, Safety Culture Assessments, VR-based safety training and advanced risk tools like TapRoot and Bow-Tie analysis for critical operations.
Awards and certifications
All JSWSCPL plants are certified for:
- ISO 14001:2015 (Environmental Management)
- ISO 45001:2018 (Occupational Health and Safety)
- ISO 50001:2018 (Energy Management)
Tarapur Coated Plant achieved the prestigious “Responsible Steel” certification for ESG best practices
5.2 Overseas operations

JSW Steel Italy Piombino S.p.A. (formerly Aferpi S.p.A.), along with Piombino Logistics S.p.A. (PL) and GSI Lucchini S.p.A., plays a key role in the Company’s European footprint. Based in Piombino, Italy, the integrated plant specialises in special long steel products and houses a rail mill (0.32 MTPA), a grinding media facility (0.05 MTPA), and a captive industrial port. PL oversees the strategic logistics of the Piombino port area, which has the capacity to accommodate vessels of up to 60,000 tonnes—strengthening the Company’s supply chain capabilities across Europe and beyond.
FY 2024-25 highlights
83
Capacity utilisation
Competitive strengths
- Historically strong foothold in local Italian Market.
- Supply of rails across European markets including Balkan regions along with North Africa, Middle East and South American market.
- Entered into long term contracts for ~300,000 tonnes with Rete Ferroviaria Italiana ('RFI').
- Collaboration with Italian Railways within the framework of existing multi-year contracts.
- Secured multi-year contracts and framework agreements with leading international railways, boosting the order backlog by approximately €100 million and enhancing commercial and operational visibility.
0.32 MTPA
Rail mill capacity
0.05 MTPA
Grinding media facility
Digitalisation
- Operations are fully integrated with digital programmes to achieve operational excellency and further upgradations are carried out.
Environmental initiatives
- Reduced water and electricity usage through modernisation of the distribution network.
- Continued drive towards energy efficiency with the installation of low-consumption LED lighting.
- Secured environmental clearances for the rail rolling mill modernisation project.
- Reused treated wastewater from the city’s sewage plant to replenish closed-loop cooling systems.
€2 million
Invested towards environment
Health and safety initiatives
- The Company has achieved the targeted parameters.
€0.5 million
Invested towards environment
Capacity expansion initiatives
In March 2024, JSW Steel Italy SRL signed a landmark MoU with the Ministry of Industry and Made in Italy, the Tuscany Region, and the Municipality of Piombino to revitalise the Piombino Steelworks. The agreement sets the foundation for sustainable rail production, regional economic development, and a future Programme Agreement (ADP) expected in FY 2025–26. JSW Piombino has begun upgrading its rail mill, doubling capacity to 600,000 tonnes annually. With a Tandem Mill, Head Hardening facility, and 120-metre rail production, the investment aims to deliver best-in-class efficiency, productivity, cost-effectiveness and product quality by FY 2027–28.
FY 2025-26 priorities
- The investment plan for the modernisation of the rail mill is crucial, as it is one of the necessary conditions for the increase in the value of the supply contract with RFI.
- Signature of the new 'Accordo di Programma' which should establish the commitments to be addressed to the Public parties and a series of interventions focused on relaunching the Company in its production strengths with the clear intent of giving an important environmental turnaround.
Accreditations
- Accredited with ISO 14001:2015 (Environmental Management Systems)
- Accredited with ISO 45001:2018 (Safety Management System)
- Accredited with ISO 50001:2018 (Energy Management Systems)
- Accredited with SA8000:2014 (Social Accountability)


JSW Steel USA serves the US markets with its production facilities in 2 locations, Mingo Junction, Ohio and Baytown, Texas. The Mingo Junction Works has a 1.5 MNTPA steelmaking facility and a 3.0 MNTPA Continuous Caster. The assets were acquired in 2018. A full modernisation of the Consteel Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) and caster was completed in 2022. The plate mill registered the highest ever annual performance for multiple key operational metrics including trade rolling, shipping, conversion cost, prime yield and mill availability in FY 2024-25.
To further strengthen its market offerings, a strategic alliance was formed with Allegheny Technologies Inc., (ATI), a state-of-the art specialty rolled products facility, to toll roll hot rolled coils in Brackenridge, PA. The Mingo Junction facility serves segments such as metal buildings, utility structures, renewable energy, pipe and tubing, steel grating, service centres and railcar manufacturing.
The Baytown facility has a 1.2 MNTPA plate mill and a 0.55 MNTPA large diameter LSAW pipe mill.
The facility completed a comprehensive modernisation of its plate mill in 2022 and is in the process of implementing the second phase of improvements slated to be completed in 2026. The Baytown facility serves segments such as railcar manufacturing, utility structures, marine applications, tank fabrication, offshore structures, service centres, wind energy, bridge construction, heavy equipment and API line pipe for oil and natural gas applications.
FY 2024-25 highlights
61%
Steel making capacity utilisation
Competitive strengths
- The Mingo Junction facility houses the largest and most modern Consteel™ EAF technology in North America, the technology enables the production of some of the cleanest and highest quality steel with low carbon emissions.
- The US operations support domestic manufacturing mandates as a vast majority of its products are melted, cast and rolled in the United States. This enables the Company to buy American provisions and reduce reliance on international supply chains.
- The plate mill is one of the widest plate mills in the country that can produce lengths of more than 1,000 inches and widths of 156 inches, allowing JSW USA to participate in specialty value-added end markets.
- Located in the Gulf Coast, the Baytown site benefits from proximity to major ports and intermodal logistics infrastructures enabling efficient and easy access to key sectors including energy and marine markets.
- Both the locations are logistically equipped with all 3 major modes of transport – road, rail and barges, connectivity with the state and national road network and inland waterways ensures easy inflow of raw materials and outflow of semi-finished and finished goods between facilities and delivery to our customers.
- The pipe mill offers unique small-lot deliveries with UOE production supporting customised pipe orders with superior quality performance. The mill is licensed by American Petroleum Institute (API) to produce up to API 5L X70 grades.
- The facilities hold key product certifications such as API, ASTM, ABS, Lloyds Register (LR), ISO, PED, DIN, JIS and ASME. These certifications, technological capabilities and strategic alliances enable the business to serve diverse product sectors from infrastructure to energy and stay resilient to dynamic shifts in the market and economy

1.5 MNTPA
Steelmaking capacity at the Mingo Junction Works and a 3.0 MNTPA continuous caster
1.2 MNTPA
Plate mill capacity at the Baytown facility
0.55 MNTPA
LSAW pipe mill at the Baytown facility

Environmental initiatives
- Reduction in specific freshwater consumption by for crude steel in Mingo Junction and plate in Baytown during FY 2024-25.
- Developed mass-balanced Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) to access Buy Clean plate market.
- A US Department of Energy (DOE) compressed efficiency study and training in Mingo Junction is planned for 2025 that will be leveraged to further drive efficiency and cost savings.
- Replacement of 4 main ID fan and reserve air fan rotors at Baghouse to maintain clean air.
$2.37 million
Invested towards environment
Health and safety initiatives
Replacement of old runways of West Bay Crane as preventive measure for safety and improving overall performance.
$1.68 million
Spent on health and safety
Capacity expansion initiatives
JSW USA has undertaken a comprehensive capital expansion project which includes the installation of a Vacuum Tank Degasser (VTD) and Caster Dynamic Soft Reduction technology (DSR) at its Mingo Junction facility. Commissioning is planned in FY 2025-26. In addition to improving the quality of existing product offerings, the VTD and DSR projects will allow the Mingo Junction facility to access the growing markets of HRC, support API applications and produce domestic slabs for all requirements of the Baytown plate mill including heavy plate and line pipe. The upgrades will further insulate JSW USA from any offshore dependence for its semifinished raw materials.
The Baytown plate and pipe mills are also in the process of modernising their existing facilities. The first phase of the plate mill modernisation was completed and commissioned in FY 2021-22. The second phase is expected to be commissioned in FY 2026-27. In addition to offshore wind, this capital expansion will enable the Baytown facility to produce plates for applications including heavy plates for pressure vessels, bridges, mining and agricultural equipment, shipbuilding and offshore structures for oil and gas production by FY 2027-28.
FY 2025-26 priorities
Demand signals increasingly favour regional suppliers who offer reliability, technical sophistication and lower lifecycle costs. As such, JSW USA will continue to build a future grounded in a powerful vision, disciplined operations and focused strategic execution, positioning it to take full advantage of upcoming infrastructure projects in the US, as well as energy related modernisation and expansion of the US energy grid coupled with onshoring of commercial and industrial facilities.
Accreditations
- Recognition by the US Department of Energy (DOE) at the Better Buildings and Better Plants programme annual summit in Washington D.C. for achieving the target of 25% reduction in energy intensity compared to a baseline set in 2021.
- Awarded Brownfields Grant by Ohio Department of DevelopmentJefferson County Port Authority for continued assessment and remedial activities of site legacy issues through Ohio Voluntary Action Programme.
6.1 Consolidated
FY 2024-25 highlights
Consolidated crude steel production*
 5.1% y-o-y
5.1% y-o-y
Consolidated sales volume#
 6.7% y-o-y
6.7% y-o-y
Crude steel production at Indian operations
 5.6% y-o-y
5.6% y-o-y
* Includes trial run production of 0.33 Mnt
# includes trial run sales of 0.04 Mnt
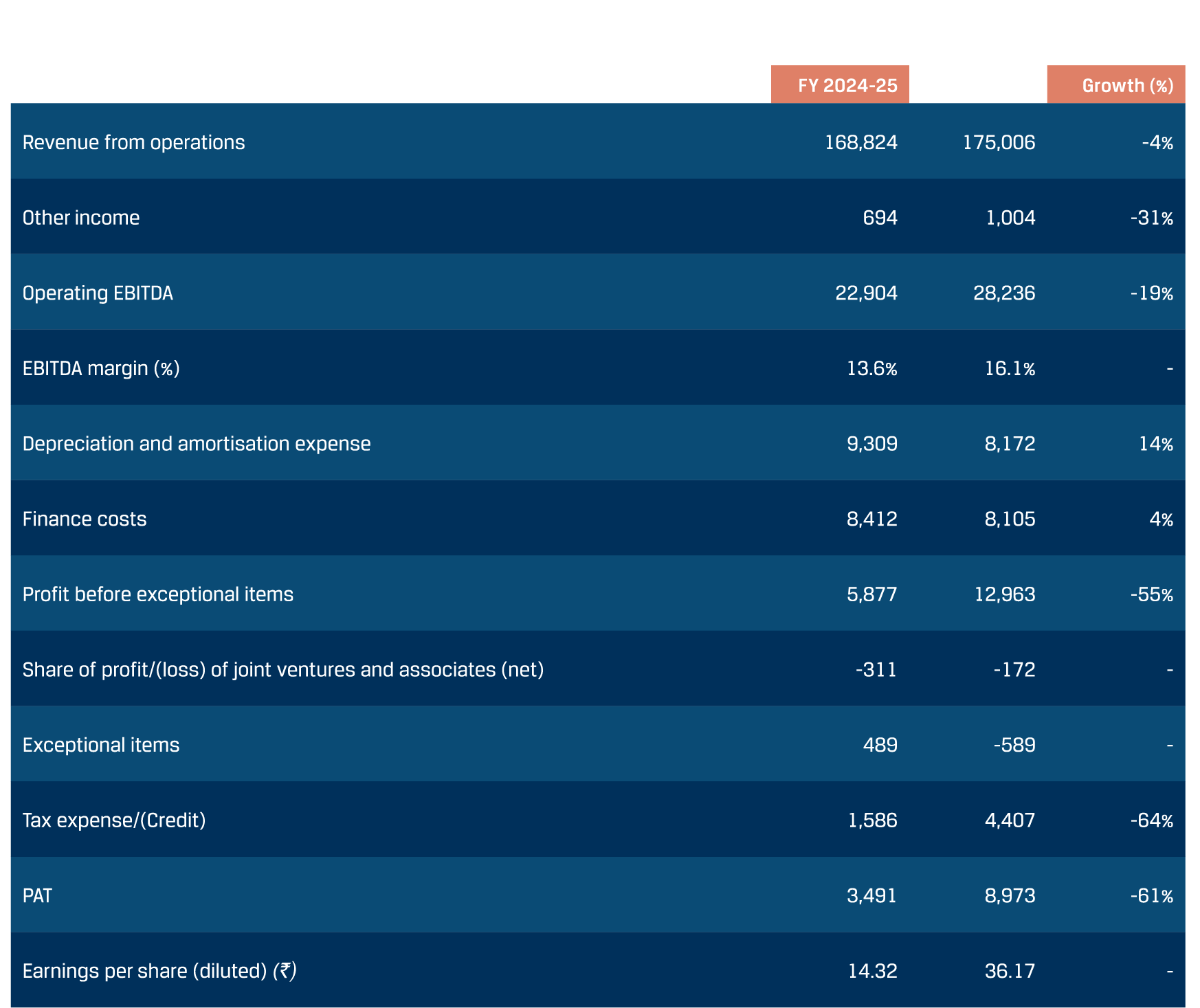
6.1.1 Production and sales
India’s crude steel production rose by 5.3% to 152 MnT in FY 2024-25 and the Steel consumption grew by 11.5% to 152 MnT for FY 2024-25. This was the fourth consecutive year of double-digit steel demand growth in India. The government’s continued capex push should drive domestic demand in FY 2025-26 as well. Steel imports increased by 9.2% y-o-y to 10.5 MnT in FY 2024-25 while steel exports fell by 26.7% to 6.26 MnT. Consequently, India remained a net importer of steel for the second consecutive year.
In FY 2024-25, the Company reported its highest ever annual consolidated crude steel production of 27.79 MnT (27.46 MnT excluding trial run), with an average capacity utilisation of 91% at Indian operations. Crude steel production increased by 5.1% y-o-y upon commissioning of the 4.5 MTPA Blast Furnace, one converter and two casters and allied integrated steel making facility by JSW Vijayanagar Metallics Limited (JVML), a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company, commissioning of the Phase II expansion at Bhushan Power & Steel Limited (BPSL) to 4.5 MTPA and better production volumes from Raigarh unit.
During the year under review, the Company reported its highest ever annual steel sales volume of 26.45 MnT (26.41 MnT excluding Trial Run), up 6.7% y-o-y. The consolidated Indian operations domestic sales stood at 23.58 MnT (23.55 MnT excluding Trial Run), an increase of 14.6% y-o-y, driven by robust domestic demand for steel. The Company achieved its highest year Value-Added Special Products (VASP) sales at 15.40 MnT, an increase of 5.1% y-o-y, and accounted for 62% of the total sales (excluding JVML volumes) for the year. The Company’s branded products’ sales stood at 46% of the total retail sales as against 48% in FY 2024-25. The consolidated Indian operations export of steel products stood at 2.08 MnT, down by 38.6% y-o-y and accounting for 8.1% of the total sales, as against 14.2% in FY 2023-24.
The Company achieved 98% of its production and sales guidance for the year. The EAF-based steel manufacturing facility in Ohio, USA, produced 8,90,182 net tonnes of Slabs during FY 2024-25. Capacity utilisation was 61% during the year. Sales volumes for FY 2024-25 stood at 2,30,897 net tonnes of HRC and 6,31,763 net tonnes of Slabs.
6.1.2 Revenue and EBITDA
In FY 2024-25, the Company’s consolidated revenue from operations decreased by 4% y-o-y to ₹168,824 crore, primarily on account of the higher volume by 8% y-o-y, partially offset by lower sales realisations due to the decline in steel prices. The sales realisation at Indian operations was lower due to subdued domestic pricing on account of lower international steel prices and higher steel imports into India. However, following an investigation and recommendation by the Directorate General of Trade Remedies, the Government of India has imposed a 12% provisional safeguard duty on 21st April 2025 to provide a level playing field to the domestic steel industry. In anticipation of this safeguard duty, the domestic prices improved towards the end of the year.
Consolidated operating EBITDA was ₹22,904 crore, a decrease of 18.9% y-o-y with an EBITDA margin of 13.6%. EBITDA per tonne was ₹8,672 during FY 2024-25, down by 23.9% y-o-y, primarily on account of the decrease in net sales realisation partially offset by decrease in manufacturing cost per tonne.
The domestic subsidiaries posted an operating EBITDA of ₹4,792 crore, as against an operating EBITDA of ₹5,025 crore during the previous year, primarily due to lower EBITDA from Bhushan Power & Steel Limited, partially offset from higher EBITDA at JSW Steel Coated Products Limited and JSW Vijayanagar Metallics Limited. The overseas subsidiaries posted an operating negative EBITDA of ₹43 crore, as against an operating EBITDA of ₹1,203 crore during the previous year, on account of lower profitability from US Baytown operations and US Ohio operations, and JSW Italy operations due to subdued pricing environment.


The total revenue from operations decreased by ₹6,182 crore to ₹168,824 crore in FY 2024-25 from ₹175,006 crore in FY 2023-24.
Revenue from Indian Operations decreased by ₹3,106 crore (2% y-o-y) primarily due to decline in sales realisations by 8% which was partially offset by the increase in domestic dispatch volumes by 7% y-o-y. The domestic volume increase was primarily driven by robust demand from the Government’s infrastructure spend. Export turnover decreased by 45% y-o-y to ₹13,190 crore from ₹23,756 crore in FY 2023-24 on account of a decrease in export volume by 39% along with lower export realisation by 6%. The Indian operations sales revenue was also lower due to lower sales of iron ore and lower sales of pig iron as the same was utilised for steel making.
Export volumes were lower in FY 2024-25 in line with overall Indian Steel export in declining trend y-o-y. China, which accounts for nearly half of the worldsteel industry, recorded a 5% decline in consumption in 2024, mainly due to the structural challenges that its real estate industry was witnessing. This resulted in increased exports from China and decline in international steel prices.
Revenue from Overseas Operations decreased 27% y-o-y to ₹33,604 crore primarily due to lower volumes and decline in steel prices.
6.1.3 Other Operating Income (` in crore)
Other operating revenue for Indian operations was ₹2,127 crore in FY 2024-25 as compared to ₹2,277 crore in FY 2023-24, lower by ₹150 crore. Other operating income decreased largely due to lower export promotion capital goods grant income by ₹95 crore and lower export incentive by ₹51 crore due to lower export volumes.
Other operating income for overseas operations was ₹122 crore in FY 2024-25 as compared to ₹141 crore in FY 2023-24 lower by ₹19 crore. Other operating income is lower primarily due to one-time grant income of ₹32 crore in previous year partially offset by scrap sales.
6.1.4 Other Income (` in crore)
Other income was ₹694 crore in FY 2024-25 as compared to ₹1,004 crore, lower by ₹310 crore. Other income was lower on account of a decrease in interest on bank deposits by ₹240 crore due to lower average amount of cash and bank balances parked in fixed deposits and lower gains on financial investments held in a joint venture, which was merged with the Company in the previous year.
6.1.5 Materials (` in crore)

Overall expenditure on material consumption decreased by 2% y-o-y to ₹99,142 crore on account of the decrease in raw material cost of Indian Operations and the Overseas Operations.
Expenditure on material consumption for Indian operations decreased 1% y-o-y to ₹93,985 crore primarily on account of 14.3% decrease in coal prices in FY 2024-25 due to subdued demand from China primarily on account of higher coking production in China and higher imports from Mongolia. Furthermore, in FY 2024-25 the Iron ore prices declined by 4.1% due focus on regional sourcing of iron ore even though the benchmark domestic iron ore prices increased by 11%.
Mining premium and royalties cost decreased by 9% in FY 2024-25 to ₹9,144 crore from ₹10,011 crore in FY 2023-24, on account of decrease in overall production volumes mainly due to surrendering of Jajang mines in Odisha.
Expenditure on material consumption for overseas operations decreased by 28% y-o-y to ₹28,027 crore primarily on account of decreased volumes and lower input costs.
6.1.6 Employee Benefits Expenses (` in crore)

Employee benefits expenses for Indian operations were higher by ₹207 crore at ₹4,798 crore in FY 2024-25. The increase was primarily due to annual increments provided to employees, additional manpower cost from Raigarh and Raipur unit for entire twelve months in current year as compared to nine-month in previous year pursuant to merger of JSW Ispat Special Products Limited (JISPL) from July 31, 2023, increase in manpower cost from JSW Vijayanagar Metallics Limited, a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company due to commissioning of the integrated steel making operations including Blast Furnace, one unit of converter and other allied facilities in current year and increase in overall headcount due to capacity additions.
Employee benefits expenses for overseas operations were approximately same as previous year at ₹1,160 crore in FY 2024-25.
6.1.7 Manufacturing and Other Expenses (` in crore)
Manufacturing and other expenses for Indian operations increased 4% y-o-y to ₹39,621 crore primarily due to increase in power & fuel costs by 7% and increase in stores and spares by 4%.
The power and fuel cost increased by ₹1,033 crore a 7% increase to ₹15,851 crore from ₹14,818 crore primarily on account of increase in steam coal prices due to sourcing mix change and power cost incurred at JSW Vijayanagar Metallics Limited on account of commencement of integrated steel operations of 5 MTPA as compared to Hot Strip Mill operations in the previous year and Bhushan Power & Steel Limited due to incremental volumes on commissioning of the phase 2 expansion to 4.5 MTPA from 3.5 MTPA in current year.
Stores and spares consumption increased 5% y-o-y to ₹7,178 crore, primarily on account of overall increase in production volumes by 5.1% y-o-y and additional provisions due to change in provisioning policy of non-moving stores, spares & consumables in FY 2024-25. Carriage and Freight cost decreased marginally by ₹92 crore to ₹8,203 crore primarily due to lower iron-ore exports during the year.
Hedging Cost/Net exchanges loss increased by 16% y-o-y to ₹401 crore primarily on account of mark-to-market unrealised loss on foreign currency loans as the rupee depreciation against the US dollar was 2.1% during FY 2024-25 as against the rupee depreciation of 1.4% in the previous year.
6.1.8 Finance Cost (` in crore)
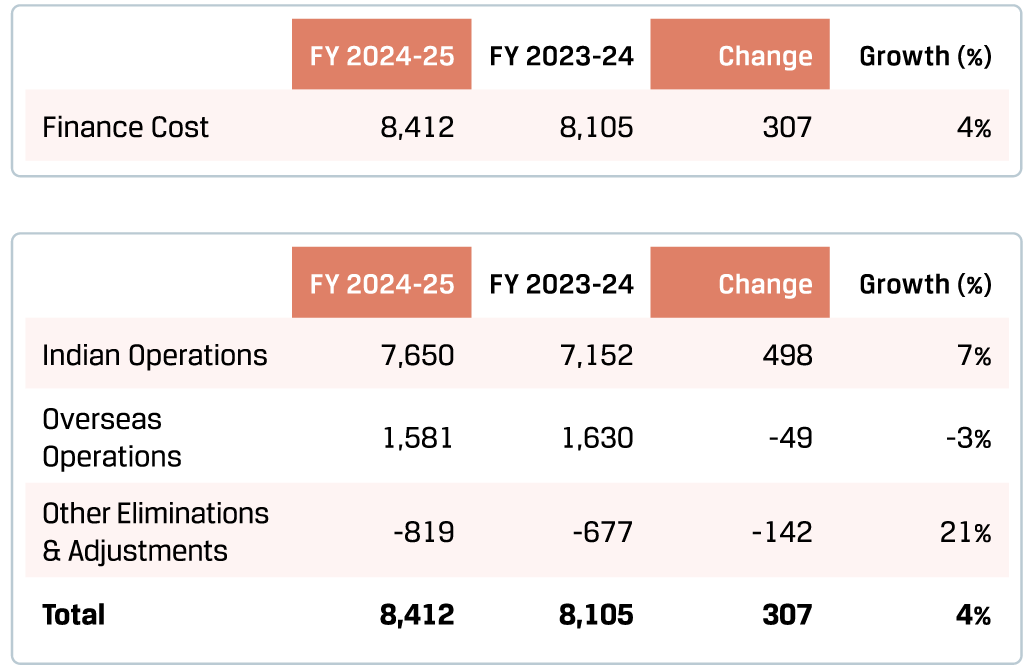
Finance cost at Indian operations increased 7% y-o-y to ₹7,650 crore primarily on account of higher borrowings and interest charge to statement of profit and loss account on account of capitalisation of Property, Plant and Equipments at JVML post commissioning of the integrated steel operations. However, the weighted average interest rate reduced 3 bps to 7.12% as at March 2025 as against 7.15% as at March 2024.The increase in finance cost was also attributable to increase in foreign exchange rate fluctuations treated as part of finance cost as the rupee depreciation against the US dollar was 2.1% during FY 2024-25 as against the rupee depreciation of 1.4% in the previous year partially offset by decrease in cost of acceptances due to lower level of acceptances during the year.
Finance cost at overseas operations declined by 3% to ₹1,581 crore from ₹1,630 crore primarily due to repayment of term loans at US operations and lower working capital interest cost.
6.1.9 Depreciation and Amortisation (` in crore)
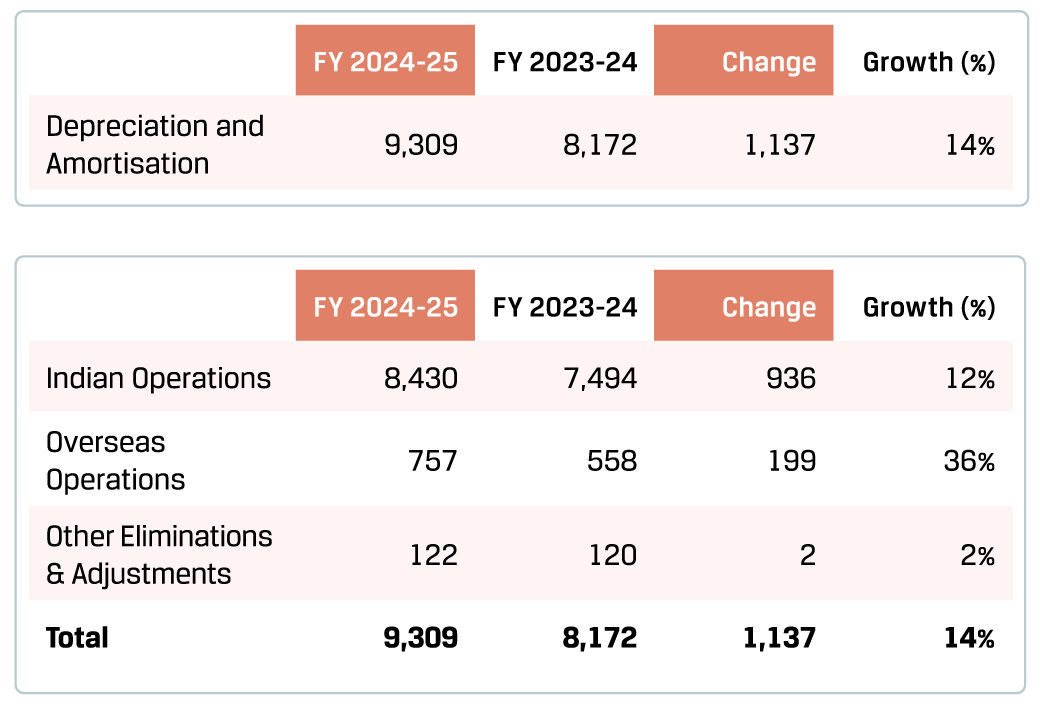
Depreciation and amortisation increased by 14% y-o-y to ₹9,309 crore primarily due to depreciation charge on capitalisation of Property, Plant and Equipments and accelerated depreciation charged on certain assets.
Depreciation charge at Indian operations increased by ₹936 crore, a 12% increase to ₹8,430 crore primarily due to higher depreciation of ₹324 crore on account of capitalisation of Coke Oven 5 Battery B at Vijayanagar, SMS 1 revamping project and balance facilities relating to Dolvi 10 MTPA expansion, mining equipment at Odisha, and other special and sustaining capital expenditure, additional impact on account of merger of JISPL in July 2023 amounting to ₹85 crore, and higher accelerated depreciation on certain assets considering the revision in useful lives and additional depreciation expense of ₹377 crore from JSW Vijayanagar Metallics Limited on account of commencement of 5 MTPA integrated steel making operations due to successful commissioning of the Steel Melting Shop and Blast furnace in current year.
Depreciation charge at overseas operations increased by ₹199 crore, a 36% increase to ₹757 crore due to accelerated depreciation on certain assets considering the revision in useful lives.
6.1.10 Tax Expense/Credit (` in crore)

Tax expense was ₹1,586 crore compared to ₹4,407 crore in FY 2023-24 primarily due to lower profitability on account of lower EBIDTA margins, higher non-cash tax charge in previous year amounting to ₹1,031 crore pertaining to tax regime change of the Company and recognition of deferred tax asset at certain subsidiaries on account of commencement of integrated steel making operations. The effective tax rate is 31.24% for FY 2024-25.
During the year ended 31 March 2024, the Company had elected to exercise the option permitted under Section 115BAA of the Income Tax Act, 1961 to pay corporate income tax at 22% plus surcharge and Cess (aggregating to tax rate of 25.17%) from the financial year 2022-23. Accordingly, the Company had remeasured its current tax and deferred tax charge for the year ended 31 March 2023 basis the new tax regime and recognised a non-cash tax charge of ₹ 1,031 crore pertaining to the previous year’s write off of MAT credit not availed and change in tax rate on deferred tax assets of the Company.
6.1.11 Exceptional Items
There was an exceptional item charge of ₹489 crore during the year comprising of the following items
- ₹44 crore towards stamp duty on slump sale of Salav unit having DRI capacity of 0.9 MTPA along with its auxiliary units to JSW Green Steel Limited, a subsidiary of the Company, by way of a slump sale in line with the Group’s strategy for setting up green steel plant.
- The Company pursuant to a detailed feasibility study concluded that the Banai and Bhalumuda Coal Block is not suitable from the techno-commercial perspective and decided not to go ahead with the investment to develop the Coal Block. The coal block was terminated by Ministry of Coal during the quarter. Accordingly, the bid security forfeiture and related expenditure amounting to ₹103 crore were charged off to the Consolidated Statement of Profit and Loss.
- The Company had submitted a notice for surrender of Jajang iron ore mining lease located in the district of Keonjhar, Odisha due to un-economic operations. Pursuant to the approval of the Final Mine Closure Plan by Indian Bureau of Mines, Ministry of Mines on 9 October 2024, the Company had submitted an application for surrender of Jajang Iron ore Block. Accordingly, the Company had recognised a net provision amounting to ₹342 crore pertaining to the underlying carrying value of assets, inventory (excluding net impact of net realisable value provided for on planned dispatches) and site restoration liability.

6.1.12 Property, Plant and Equipment and Intangibles (` in crore)
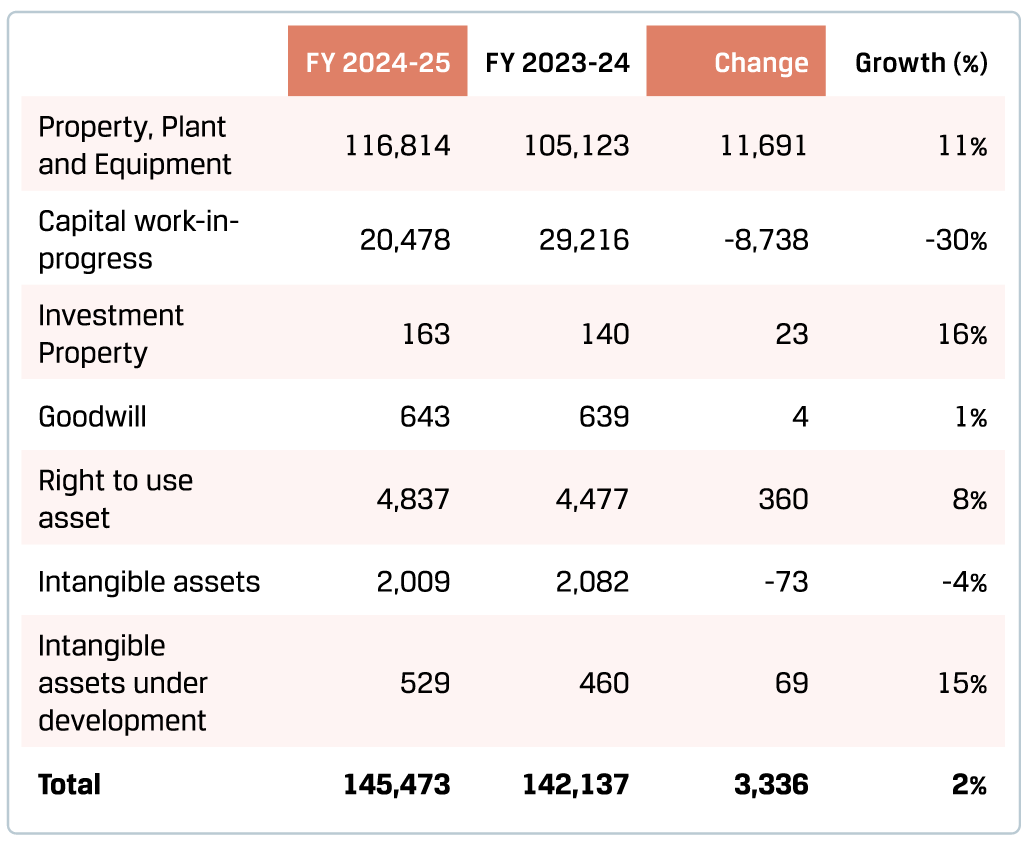
Net block of Property, Plant and Equipment increased by ₹11,691 crore primarily on account of capitalisation of ₹11,965 crore pertaining to Blast Furnace, Steel Melting Shop and allied facilities at JSW Vijayanagar Metallics Limited, capitalisation of ₹2,852 crore at BPSL pertaining to capacity expansion to 4.5 MTPA from 3.5 MTPA, capitalisation of ₹4,704 crore relating to Coke Oven 5 Battery B at Vijayanagar, SMS 1 revamping project and balance facilities relating to Dolvi 10 MTPA expansion, mining equipment at Odisha, and other special and sustaining capital expenditure partially offset by depreciation charge of ₹8,727 crore.
The Right to use asset increased by ₹360 crore to ₹4,837 crore primarily on account of commence of contract relating to Air Separator Unit for procurement of Industrial gases at Vijayanagar.
6.1.13 Investments (` in crore)
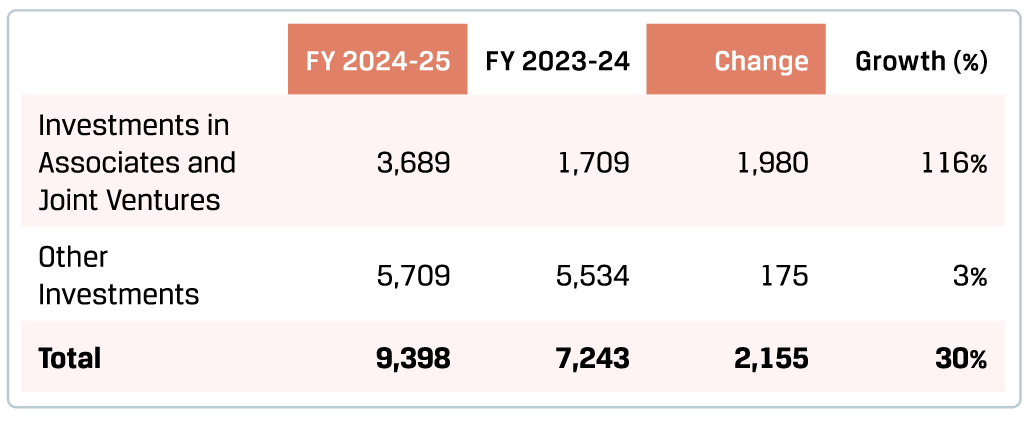
Investments increased to ₹9,398 crore from ₹7,243 crore in FY 2023-24, an increase of ₹2,155 crore due to new investment of ₹1,298 crore in M Res NSW HCC Pty Ltd for sourcing of metallurgical coal from mines in Australia, additional investment of ₹750 crore in JSW JFE Electrical Steel Private Limited for acquisition of Thyssenkrupp Electrical Steel India Private Limited (tkES) a CRGO manufacturer of High grades of CRGO in India, investment s in Associate companies relating to Renewable Energy and additional investment in Bengal Coal Pty Limited for future prospects of coal mines offset by accounting for share of losses using equity method for JV’s and associates.
6.1.14 Loans and Advances (` in crore)
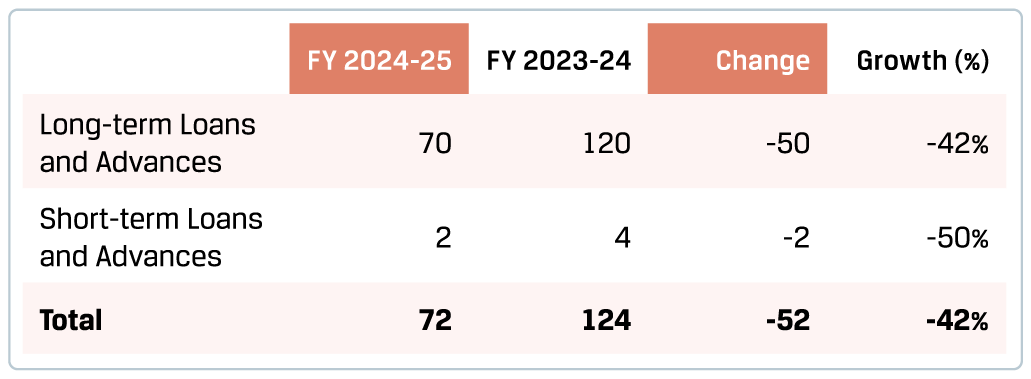
Loans and advances decreased by ₹52 crore primarily due to the repayment of loan given to JSW Projects Limited.
6.1.15 Other Financial Assets (` in crore)
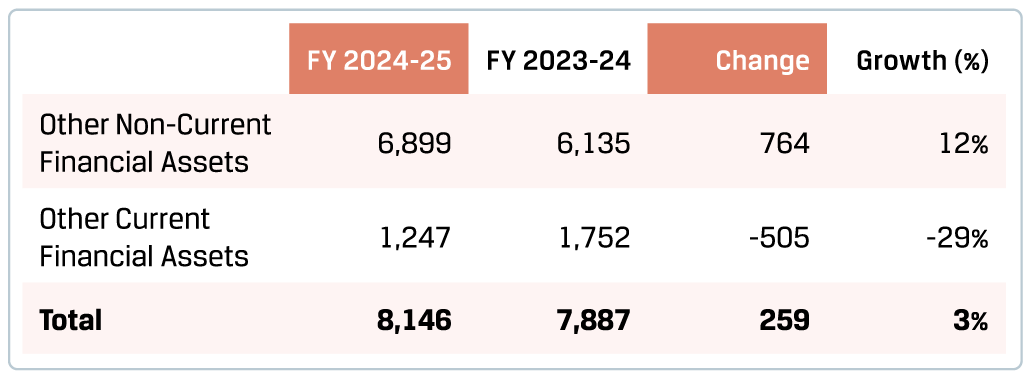
The other financial assets increased by ₹259 crore to ₹8,146 crore on account of increase in the GST incentive receivable from the state of Maharashtra and Karnataka, partially offset by refund of security deposit provided to Sapphire Airlines Private Limited.
6.1.16 Other Non-Financial Assets (` in crore)
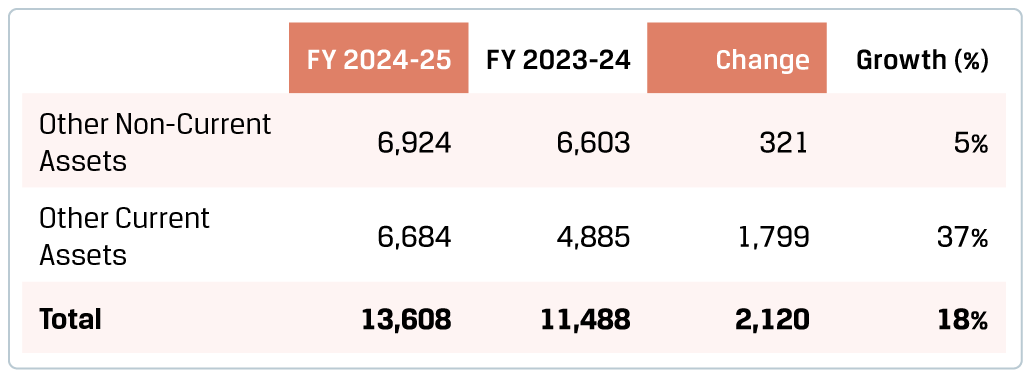
The other Non-financial assets increased by ₹2,120 crore to ₹13,608 crore due to increase in advances made to suppliers for capital projects and amounts paid under protest relating to electricity duty.

6.1.17 Inventories (` in crore)
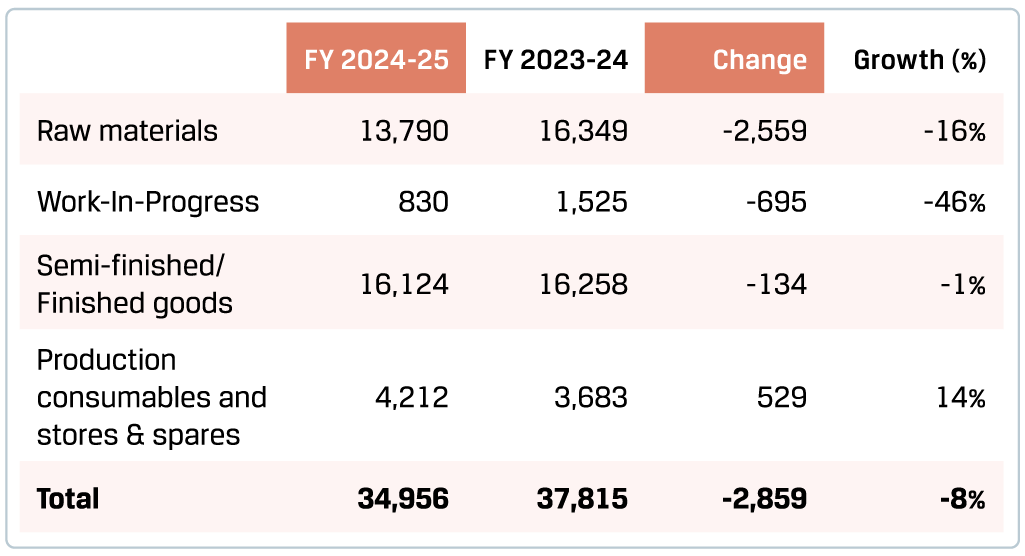
Inventories reduced by ₹2,859 crore to ₹34,956 crore primarily due to decrease in raw material inventories due to decline in coking coal prices and liquidation of 2.21 lakh tonnes of Semi-finished/Finished goods offset by increase in consumables, stores and spares due to commencement of operation at JVML and procurement of critical spares required for maintenance shutdowns planned for the next financial year.
6.1.18 Trade Receivables (` in crore)
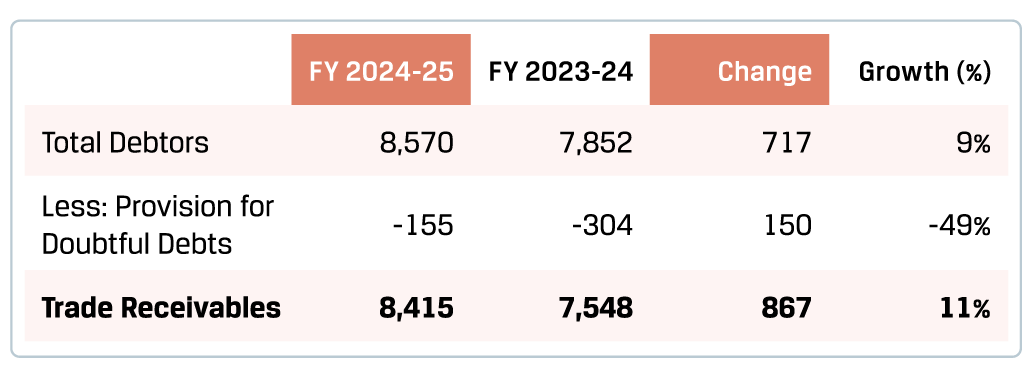
Trade receivables increased by ₹867 crore to ₹8,415 crore due to increase in trade receivable in JSW Vijayanagar Metallics Limited on account of commencement of integrated steel operations. The average collection period was 17 days as compared to 16 days from previous year.
6.1.19 Cash and Bank Balances (` in crore)
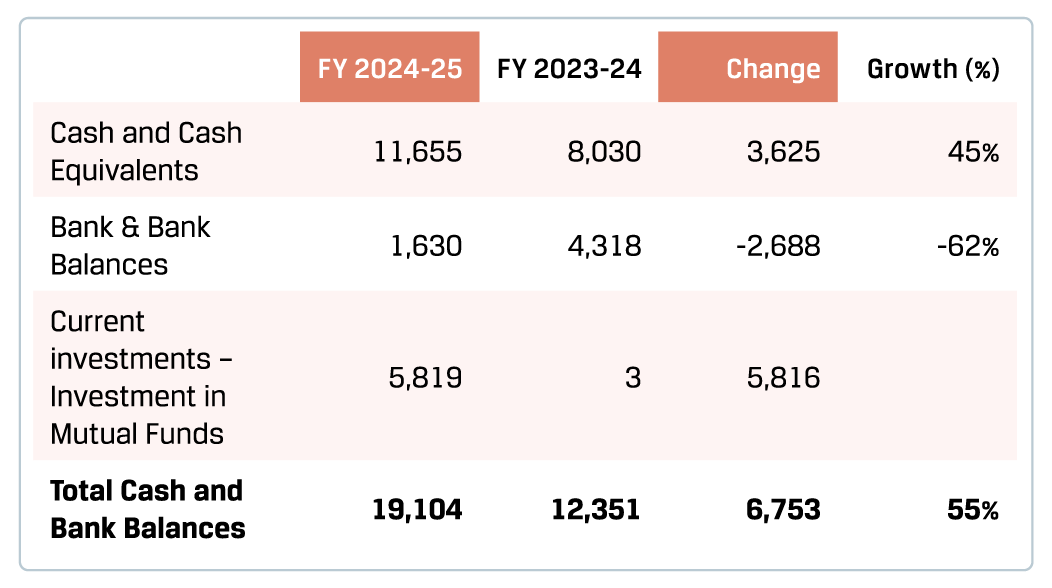
To meet short-term cash commitments and repayment obligations, the Company parks surplus funds in short-term and highly liquid instruments which represent cash and cash equivalents and other bank balances. Total cash and bank balances (including balance in Mutual Fund) increased to ₹19,104 crore from ₹12,351 crore to maintain the strong liquidity position and funds required for repayment of Bond maturing in April 2025 was temporarily parked in fixed deposits and mutual funds.
6.1.20 Borrowings (` in crore)
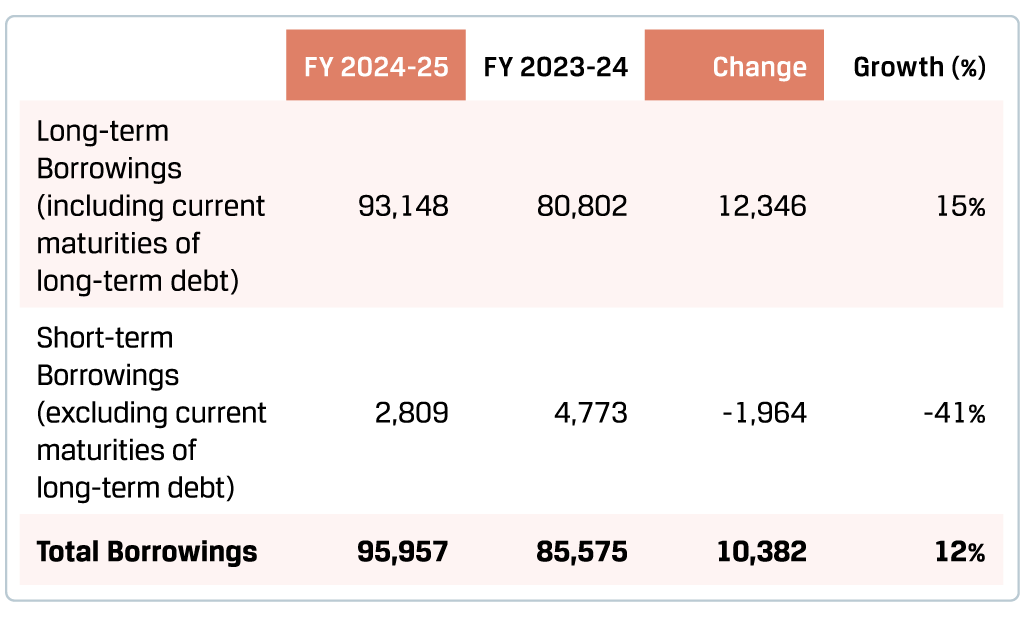
Long-term borrowings (including current maturity of long-term debt) increased primarily due to the new drawing of term loans by ₹11,546 crore (net of repayments) for incurring capital expenditure and general corporate purposes and increase in borrowings due to exchange fluctuation on account of rupee depreciation against US Dollar and Euro.
Short term borrowings decreased by ₹1,964 crore primarily due to decrease in capex acceptances at JSW Vijayanagar Metallics Limited, repayment of commercial paper and lower utilisation of working capital facilities.
6.1.21 Acceptances (` in crore)

Acceptances increased by ₹2,880 crore during FY 2024-25 due to commencement of operations at JSW Vijayanagar Metallics Limited.
6.1.22 Trade Payables (` in crore)

Trade payables decreased by ₹3,693 crore to ₹12,018 crore primarily on account of payments made to operational creditors and decline in raw material prices in FY 2024-25 as compared to FY 2023-24.
6.1.23 Other Financial Liabilities (` in crore)
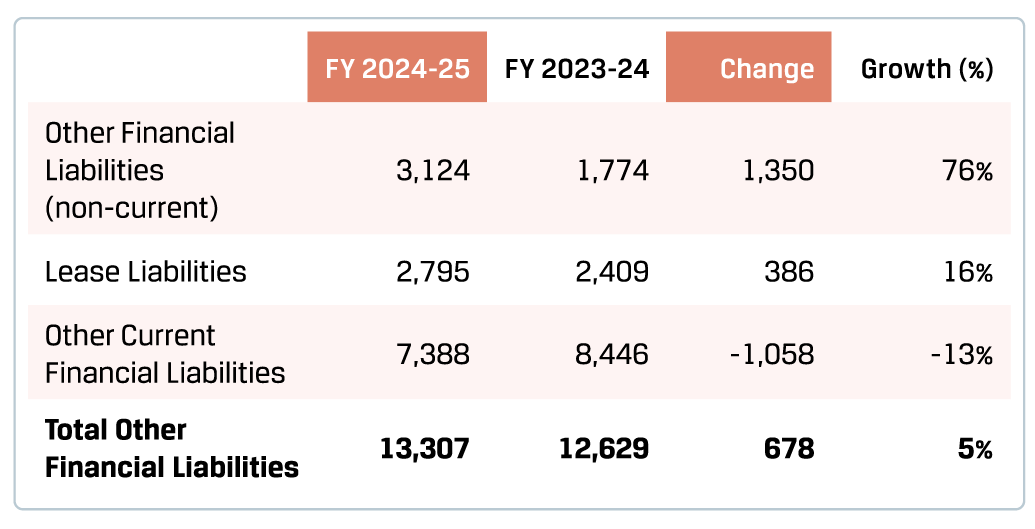
Other financial liabilities increased by ₹1,350 crore to ₹3,124 crore. The increase is primarily on account of consideration of ₹1,286 crore received for sale the under-construction slurry pipeline business and disclosed as other financial liability, since the lease has not yet commenced.
Lease liabilities increased by ₹386 crore to ₹2,795 crore primarily on account of commencement of contract relating to Air Separator Unit at Vijayanagar partially offset by the repayment of principal amount on leases.
Other current financial liabilities decreased by ₹1,058 crore to ₹7,388 crore primarily on account of decrease in payable for capital projects, interest accrued but not due on borrowings, retention money payable for capital expenditure and payable for bid premium and royalty which was partially offset by higher provisions for marketing rebates.
6.1.24 Other Liabilities (` in crore)
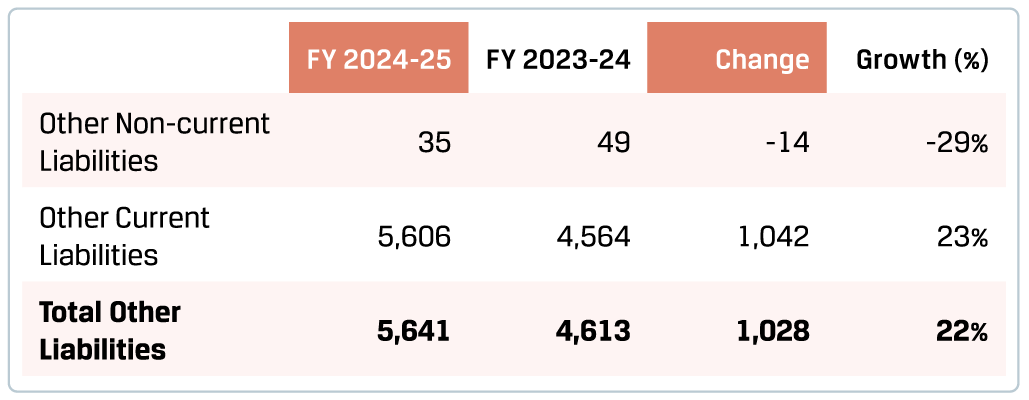
Other liabilities increased by ₹1,028 crore to ₹5,641 crore due to increase in advances received from customers, goods and service tax liabilities and deferred income on export obligations on import of capital goods for projects.
6.1.25 Deferred Tax Liabilities (` in crore)
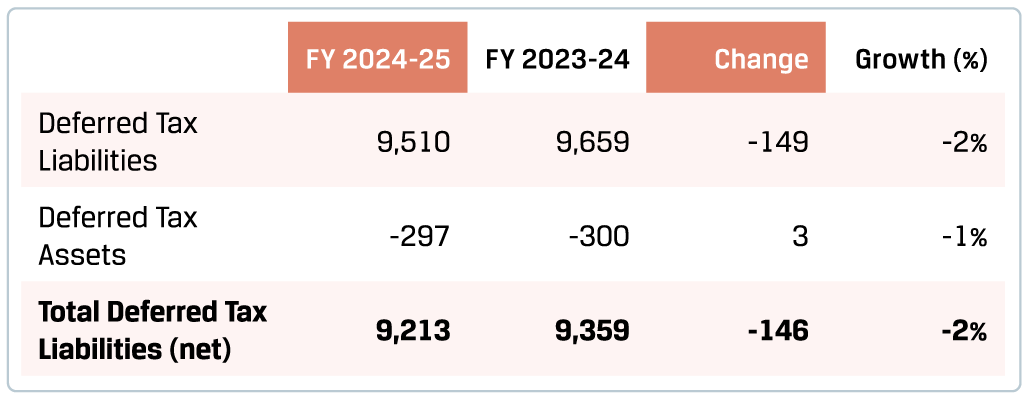
Deferred tax liabilities decreased by ₹146 crore to ₹9,213 crore.
6.1.26 Own Funds
JSW Steel’s equity increased from ₹79,776 crore as on March 31, 2024 to ₹81,666 crore on a consolidated level as on March 31, 2025. Book value per share was at ₹333.95 as on March 31, 2025, as compared to ₹326.22 as on March 31, 2024.
6.1.27 Other Key Financial Indicators
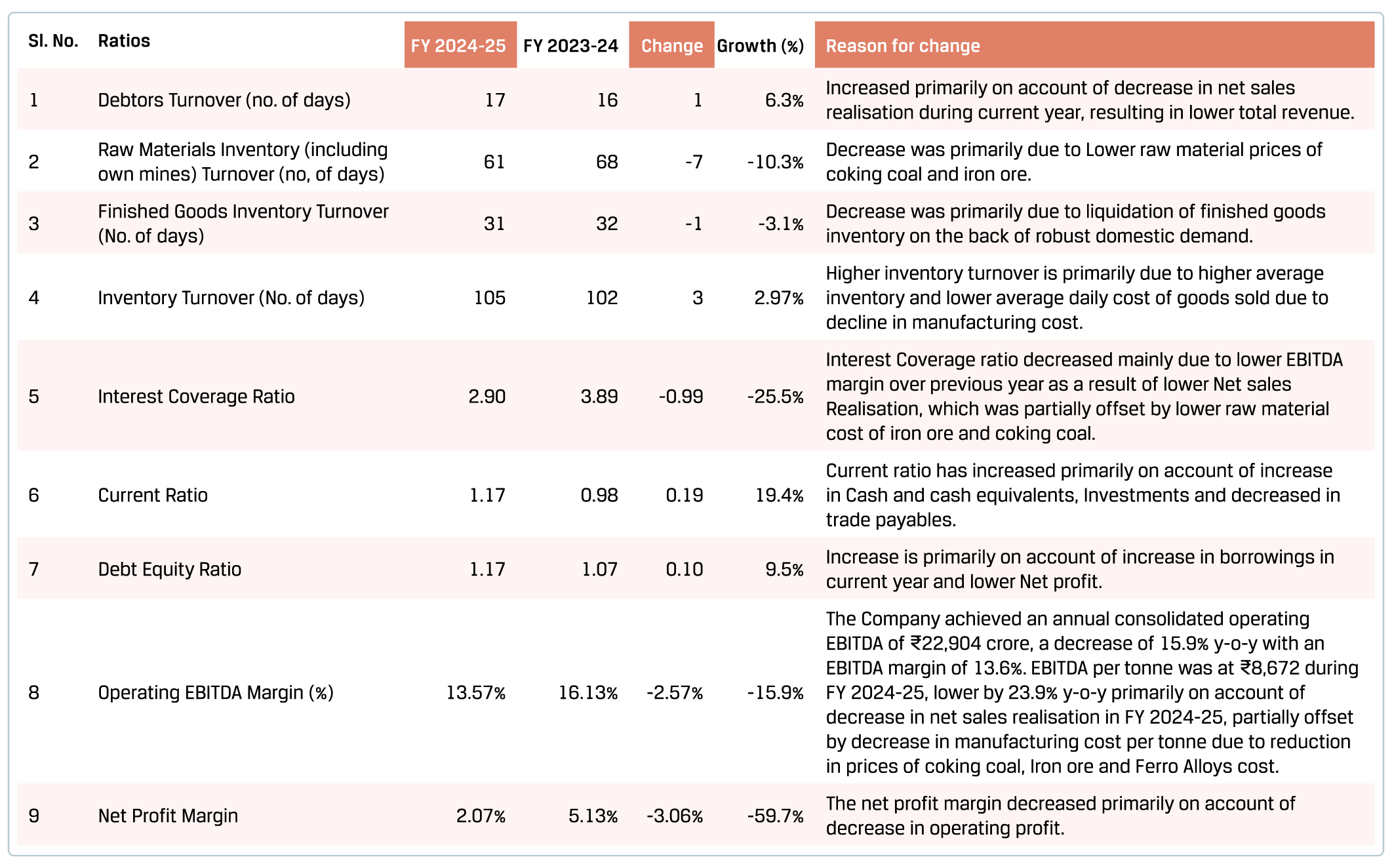
Subsidiaries, Joint Ventures and Associates as on 31 March 2025
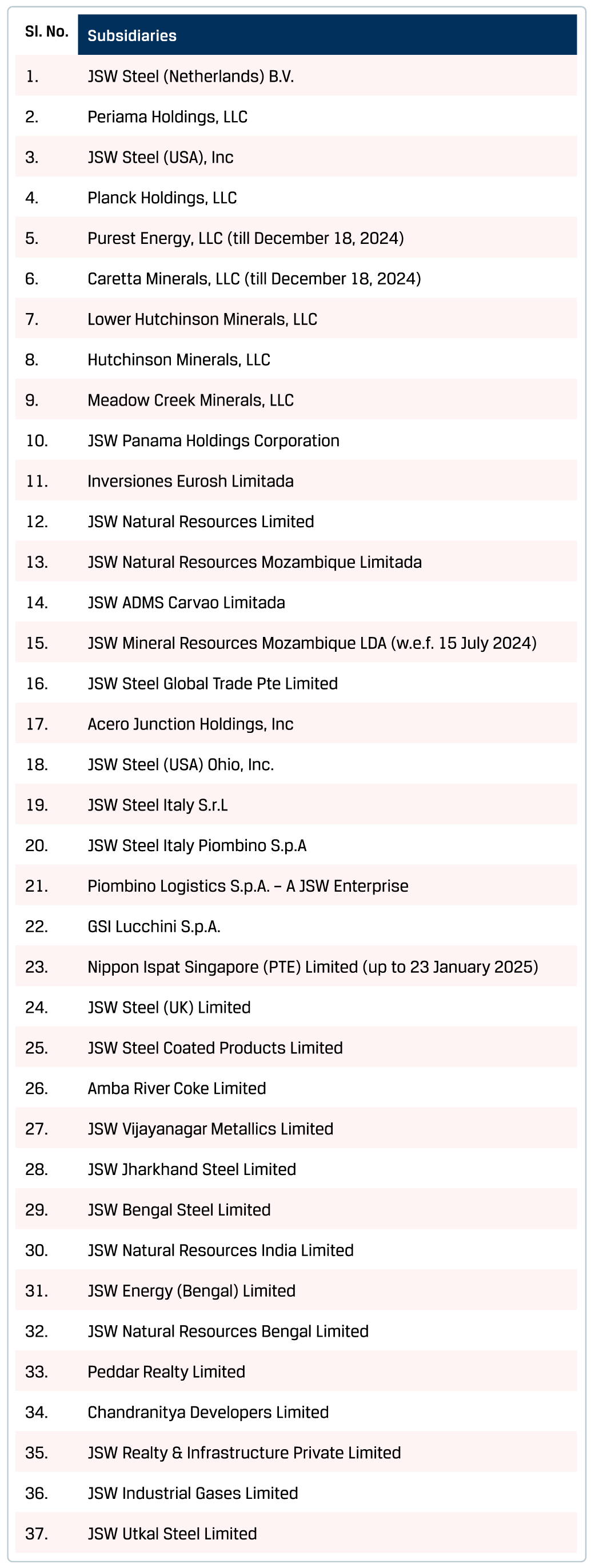


6.2 Standalone
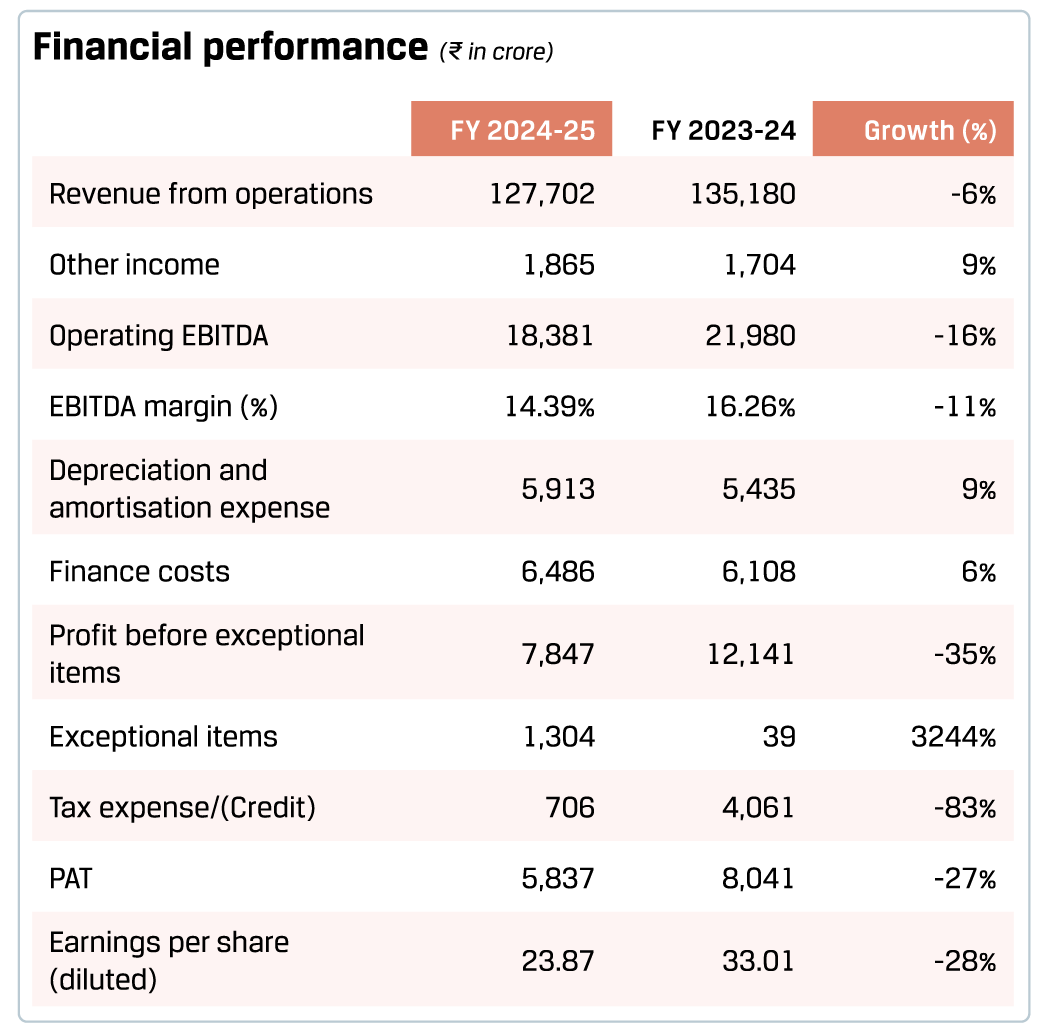
FY 2024-25 highlights
Crude steel production
 1% y-o-y
1% y-o-y
Sales volume
 2.5% y-o-y
2.5% y-o-y
Domestic sales
 8% y-o-y
8% y-o-y
6.2.1 Production and sales
In FY 2024-25, JSW Steel reported its highest ever crude steel production at 22.47 MnT with an average capacity utilisation of 92%. The Crude steel production increased by 1% y-o-y.
The Company reported its highest ever steel sales volume at 21.74 MnT, which grew by 2.5% y-o-y. Domestic sales stood at 20.50 MnT, an increase of 8.1% y-o-y. The domestic steel demand grew by 11.5% y-o-y to 152 MnT driven by the government’s thrust on infrastructure, housing construction, the growing share of manufacturing in GDP, and increased demand from the auto sector.
The Company exported 1.24 MnT of steel, down 44.8% y-o-y and accounted for 5.7% of the total sales, as against 10.6% in FY 2023-24.
6.2.2 Revenue and EBITDA
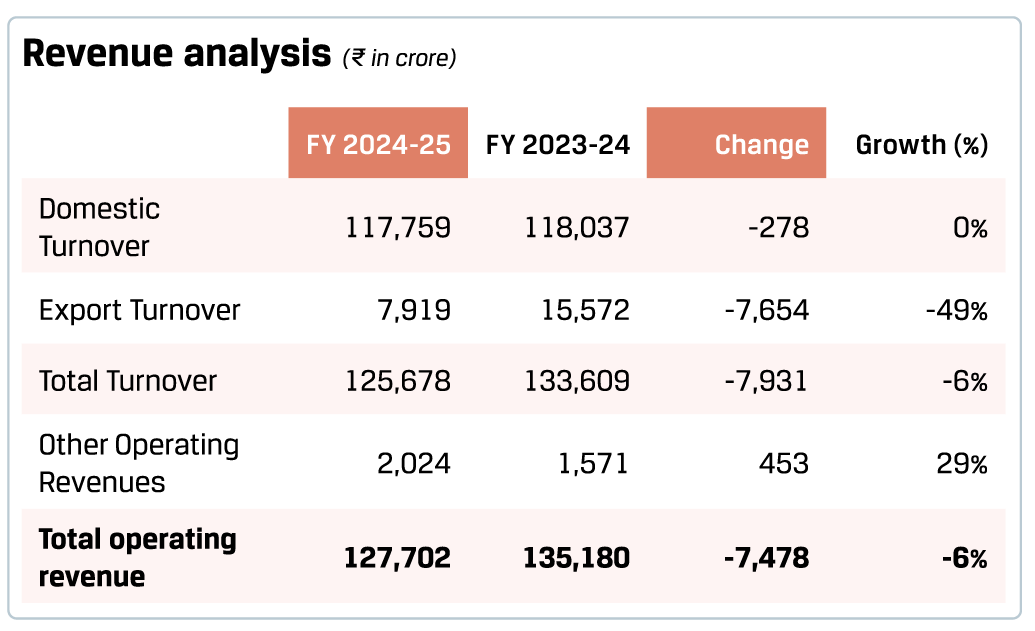
Revenue from operations declined 6% y-o-y to ₹127,702 crore, primarily due to decline in sales realisation by 9% both in domestic and export sales, which was partially offset by a 2.5% increase in sales volumes. The sales realisation at Indian operations was lower due to subdued domestic pricing on account of lower international steel prices and higher steel imports into India. Operating margin for FY 2024-25 stood at 14.39% as against 16.26% in FY 2023-24 mainly due to decline in average sales realisations which was partially offset by lower raw material prices of iron ore and coking coal.
Overall consumption of iron ore from the Karnataka and Odisha captive mines to the steel manufacturing plant locations constituted 37% of the Company’s iron ore requirements of the Company in FY 2024-25.
The Company achieved an annual Operating EBITDA of ₹18,381 crore, a decrease of 16.3% y-o-y with an EBITDA margin of 14.4%. EBITDA per tonne was at ₹8,453 during FY 2024-25, lower by 18.4% y-o-y primarily on account of decrease in net sales realisation in FY 2024-25, partially offset by decrease in iron ore and coal prices.
Operating EBITDA
Net Profit
India was a net steel importer during FY 2024-25 with elevated imports (up 37% y-o-y), especially from China; this remains a challenge for the domestic steel industry. However, domestic steel demand remained healthy, driven by growth in overall consumption and the Government’s spend in the infrastructure sector.
Domestic turnover remained flat in FY 2024-25 as against FY 2023-24, though there was an increase in volume by 8% which was offset by lower realisations. The domestic sales volume increase was primarily due to better domestic demand driven by the Government’s infrastructure spend.
Export turnover decreased 49% y-o-y to ₹7,919 crore from ₹15,572 crore in FY 2023-24, on account of a decrease in export volumes along with lower export realisations. The export volumes were lower in FY 2024-25 in line with overall Indian Steel export in declining trend y-o-y. China, which accounts for nearly half of the world steel industry, recorded a 5% decline in consumption in 2024, mainly due to the structural challenges that its real estate industry was witnessing. This resulted in increased exports from China and decline in international steel prices.
6.2.3 Other Operating Income (` in crore)

The other operating income increased by ₹453 crore to ₹2,024 crore in FY 2024-25 as compared to ₹1,571 crore in FY 2023-24. Other operating income was higher largely due to a higher job work income of ₹528 crore partially offset by lower Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) grant income by ₹95 crore due to lower export volumes.
6.2.4 Other Income (` in crore)

The other income increased by ₹161 crore to ₹1,865 crore primarily due to the higher dividend income of ₹90 crore from group companies and higher interest income from loans extended to subsidiaries amounting to ₹285 crore partially offset by decrease in interest income due to lower average amount of cash and bank balances parked in fixed deposits and lower gains on financial investments held in a joint venture, which was merged with the Company amounting to ₹211 crore.
6.2.5 Materials (` in crore)
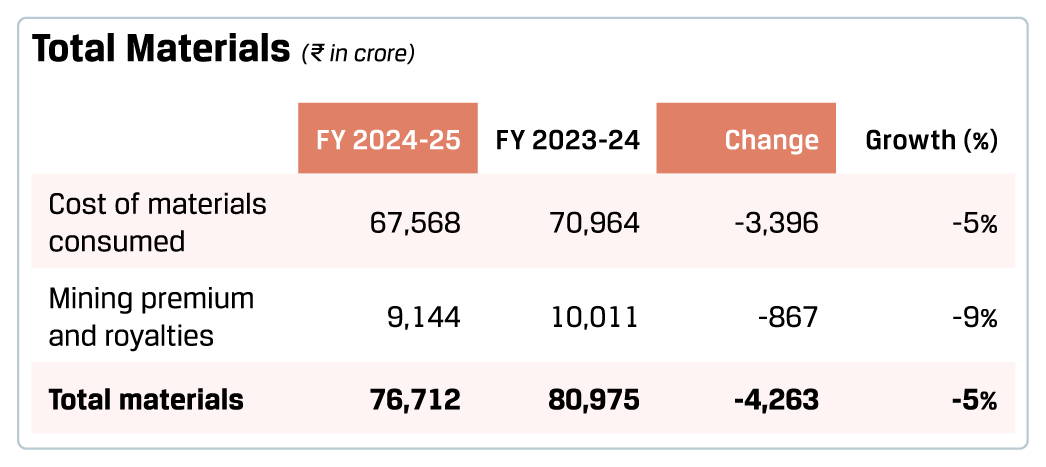
Expenditure on material consumption decreased by 5% y-o-y to ₹67,568 crore primarily on account of decrease in coking coal prices due to subdued demand from China primarily on account of higher coking production and higher imports from Mangolia. Furthermore, in FY 2024-25 other raw materials like the Iron ore prices declined by 4.1% due to focus on regional sourcing of iron ore even though the benchmark domestic iron ore prices increased by 11%. However, the cost of other raw materials like Zinc and limestone increased which was offset by lower Ferro Alloys cost.
Mining premium and royalties cost decreased by ₹867 crore (9%) in FY 2024-25 to ₹9,144 crore from ₹10,011 crore in FY 2023-24, on account of a decrease in overall volume of production mainly due to the surrendering of Jajang mines in Odisha.
6.2.6 Employee Benefits Expenses (` in crore)
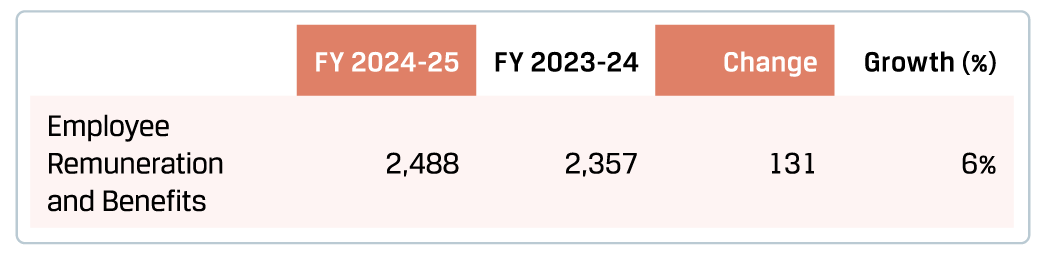
Employee benefits expenses were higher by ₹131 crore a 6% increase y-o-y at ₹2,488 crore in FY 2024-25, primarily due to annual increments and marginal increase in employee head count. The overall headcount increased to 15,793 as on March 31, 2025 from 15,493 as on March 31, 2024.
6.2.7 Manufacturing and Other Expenses (` in crore)

Manufacturing and other expenses increased by ₹253 crore, a 1% increase y-o-y to ₹30,121 crore primarily due to increase in power and fuel cost offset by lower other expenditure.
The power and fuel cost increased by ₹561 crore, an increase of 5% y-o-y to ₹12,136 crore due to higher production volumes, higher steam coal rates due to change in sourcing mix and increase in natural gas prices.
Stores and spares cost increased by ₹155 crore, an increase of 3% y-o-y to ₹5,261 crore, primarily on account of the overall increase in production by 1% y-o-y.
The ocean freight expenditure decreased by ₹124 crore a decrease of 12% y-o-y to ₹876 crore primarily on account of decline in export sales volume by 45%. The domestic freight expense decreased by ₹425 crore, a decrease of 7% y-o-y to ₹5,919 crore due to higher sales in the western and southern markets thereby lowering the freight costs and lower iron ore sales.
Other miscellaneous expenditure decreased by ₹73 crore, a decrease of 3% y-o-y to ₹2,368 crore primarily on account of reversal of provision for onerous contracts relating to iron ore sales offset by increase in water charges and outsourced manpower expenses.
6.2.8 Finance Cost (` in crore)

Finance cost increased by ₹378 crore, an increase of 6% y-o-y to ₹6,486 crore primarily on account of additional borrowings during FY 2023-24 due to borrowings for capital expenditure projects. The increase in finance cost was also attributable to increase in foreign exchange rate fluctuations treated as part of finance cost as the rupee depreciation against the US dollar was 2.1% during FY 2024-25 as against the rupee depreciation of 1.4% in the previous year partially offset by decrease in cost of acceptances due to lower level of acceptances and lower working capital interest cost on account of lower utilisation of working capital facilities.
6.2.9 Depreciation and Amortisation (` in crore)

Depreciation and amortisation increased ₹478 crore, an increase of 9% y-o-y to ₹5,913 crore primarily due to higher depreciation of ₹324 crore on account of capitalisation of Coke Oven 5 Battery B at Vijayanagar, SMS 1 revamping project and balance facilities relating to the Dolvi 10 MTPA expansion, mining equipment at Odisha, and other special and sustaining capital expenditure, additional impact on account of the merger of JISPL in July 2023 amounting to ₹85 crore, and higher accelerated depreciation on certain assets considering the revision in useful lives.
6.2.10 Tax Expense/Credit (` in crore)

Effective tax rate in FY 2024-25
Tax expense was ₹706 crore compared to ₹4,061 crore in FY 2023-24, primarily due to lower profitability on account of lower EBIDTA, receipt of dividend and profit earned on sale of a unit for which tax deduction / exemption have been claimed as per Income tax laws. Further, the Company trued up the tax balances with the tax records which has resulted in reversal of tax liabilities amounting to ₹218 crore. Thus, the effective tax rate came in at 10.8% for FY 2024-25 primary due to receipt of dividend for which deductions have been claimed as per Income tax laws.
6.2.11 Exceptional Items (` in crore)
The exceptional items charge amounting to ₹1,304 crore comprised of the following
- Profit of ₹1,449 crore on the sale of Salav unit having DRI capacity of 0.9 MTPA along with its auxiliary units to JSW Green Steel Limited by way of slump sale, in line with the Company’s strategy for setting up a green steel plant.
- Recognition of income amounting to ₹1,454 crore on buyback of shares by Piombino Steel Limited, a subsidiary in India.
- Impairment provision of ₹3,762 crore towards investments and loans provided to subsidiary in the US and Mauritius based on recoverability assessment carried out for respective underlying businesses.
- The Company pursuant to a detailed feasibility study concluded that the Banai and Bhalumuda Coal Block was not suitable from the techno-commercial perspective and decided not to go ahead with the investment to develop the coal block. The coal block was terminated by the Ministry of Coal. Accordingly, the bid security forfeiture and related expenditure amounting to ₹103 crore were charged off to the statement of Profit and Loss.
- The Company had submitted a notice for the surrender of the Jajang iron ore mining lease located in the district of Keonjhar, Odisha due to un-economic operations. Pursuant to the approval of the Final Mine Closure Plan by the Indian Bureau of Mines (IBM), the Ministry of Mines on October 9, 2024, the Company submitted an application for surrendering the Jajang Iron Ore Block. Accordingly, the Company recognised a net provision amounting to ₹342 crore on September 30, 2025, pertaining to the underlying carrying value of assets, inventory (excluding net impact of net realisable value provided for on planned dispatches) and site restoration liability. An implementation certificate of the Final Mine Closure Plan was issued by IBM on April 7, 2025, which, as a process of surrender, was submitted to the Government of Odisha on April 10, 2025.
6.2.12 Property, Plant and Equipment and Intangibles (` in crore)
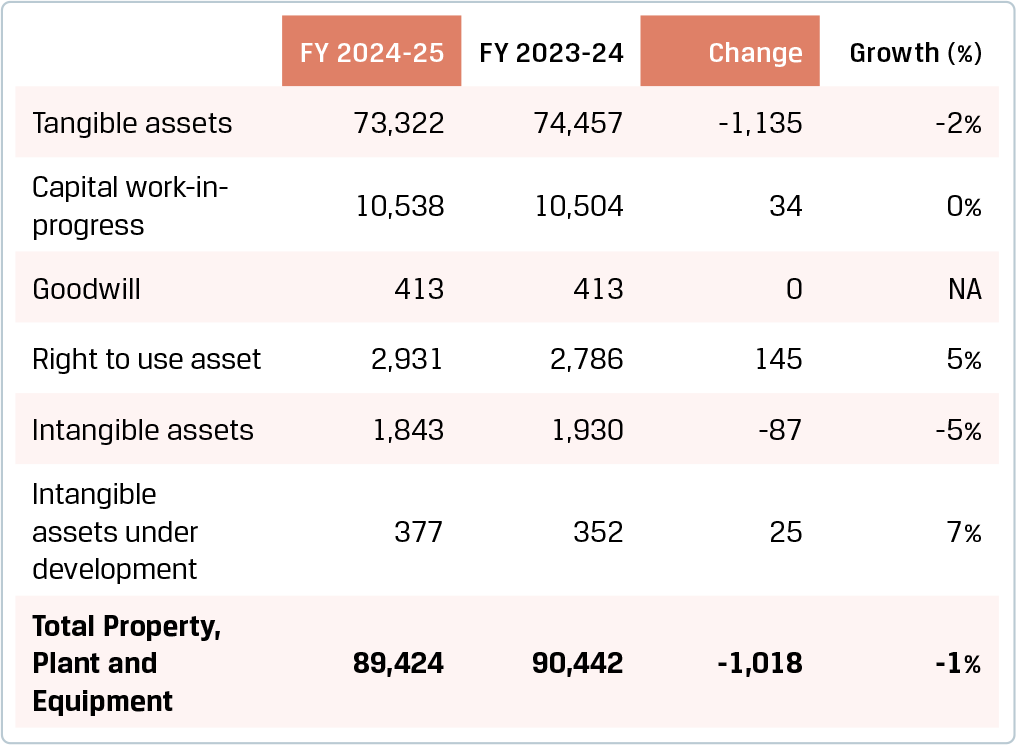
Net block of Property, Plant and Equipment decreased by ₹1,135 crore to ₹73,322 crore primarily on account of depreciation cost of ₹5,357 crore and sale of Salav unit to JSW Green Steel Limited by way of a slump sale partially offset by capitalisation of assets amounting to ₹4,704 crore relating to Battery D of Coke Oven 5 of capacity 0.75 MTPA at Vijayanagar, SMS 1 revamping project and balance facilities relating to the Dolvi 10 MTPA expansion, mining equipment at Odisha, special projects and sustenance capex across all the plant locations.
The Right to use asset increased by ₹145 crore to ₹2,931 crore primarily on account of commence of contract relating to Air Separator Unit at Vijayanagar offset by transfer of leasehold land to freehold land.
6.2.13 Investments (` in crore)
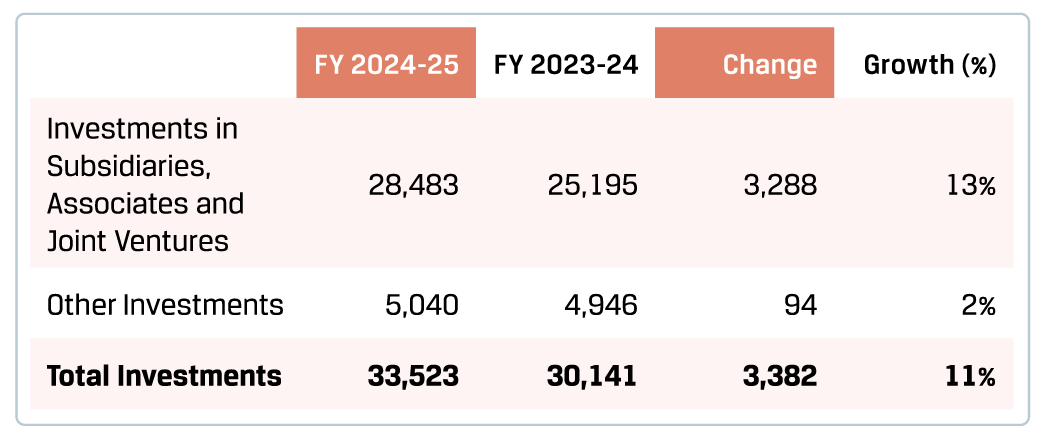
Investments in subsidiaries, associates and joint ventures increased by ₹3,288 crore to ₹28,483 crore primarily due to an additional equity investment of ₹2,233 crore in JSW Green Steel Limited considering the management's intention to invest in Green Steel facility, investment of ₹755 crore in JSW JFE Electrical Steel Private Limited for acquisition of Thyssenkrupp Electrical Steel India Private Limited (tkES) a CRGO manufacturer of High grades of CRGO in India and additional investments of ₹400 crore in JSW Utkal Steel Limited to set Pellet plant and other allied facilities at Jatadhar Odisha offset by decrease in investment on account of buy back of equity shares by a subsidiary in India.
The other investments increased by ₹94 crore to ₹5,040 crore primarily due to an increase in fair value of the equity stake of JSW Energy Limited due to increase in share prices.
6.2.14 Loans and Advances (` in crore)
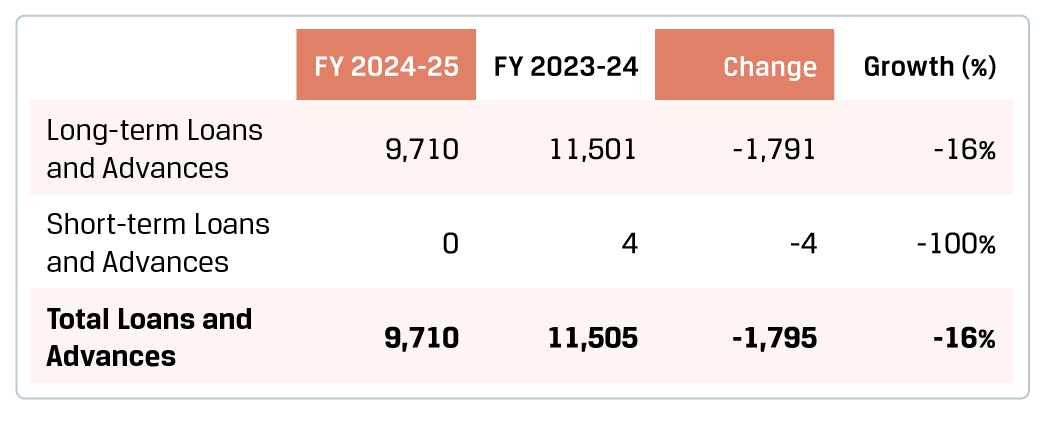
Long-term Loans and advances decreased by ₹1,791 crore to ₹9,710 crore primarily due to additional provisions recognised for loans extended to overseas subsidiaries of Periama Holdings and Acero Junction Holdings amounting to ₹3,762 crore, partially offset by loans extended to overseas subsidiaries for acquisition of Illawara coal mines, loan extended to subsidiaries for catering to the interest and principal repayment obligations and loans extended to Indian subsidiaries to support their operations.
6.2.15 Other Financial Assets (` in crore)
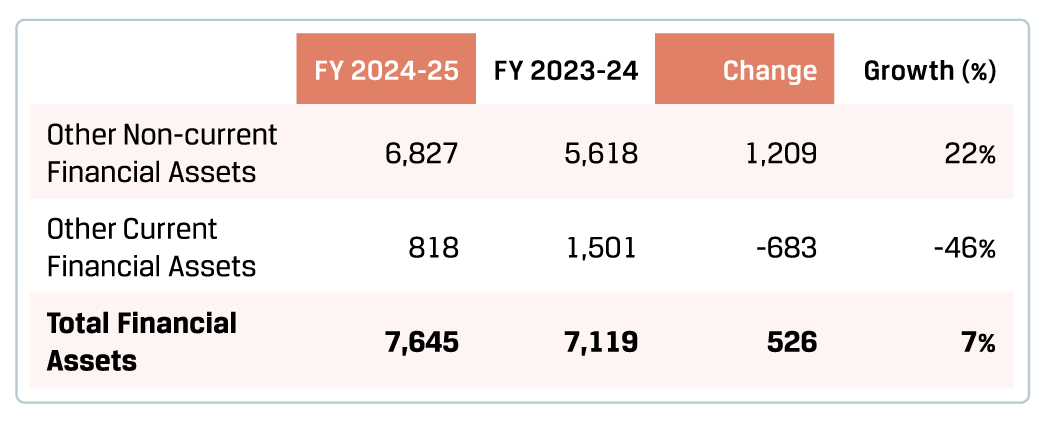
The total financial assets increased by ₹526 crore to ₹7,645 crore on account of increase in the GST incentive receivable from the state of Maharashtra and Karnataka by ₹481 crore, and the increase in accrued interest income on loans extended to certain overseas subsidiaries amounting to ₹557 crore partially offset by the refund of security deposit of ₹448 crore by Sapphire Airlines Private Limited.
6.2.16 Other Non-Financial Assets (` in crore)
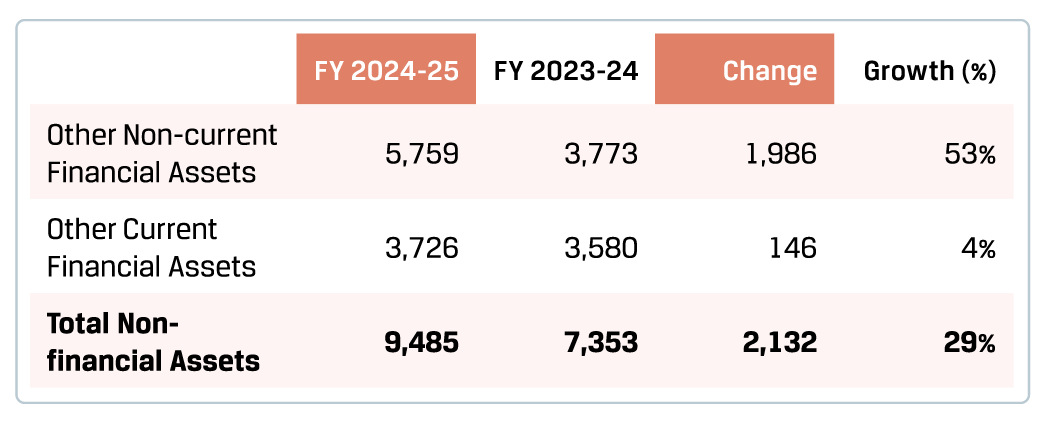
Other non-current assets increased by ₹1,986 crore to ₹5,759 crore primarily due to an increase in the advances made to suppliers for capital projects and amounts paid under protest relating to electricity duty.
Other current assets increased by ₹146 crore to ₹3,726 crore on account of an increase in GST input tax credit available for set-off, partially off-set by a reduction in advances to suppliers and a reduction in security deposits.
6.2.17 Inventories (` in crore)
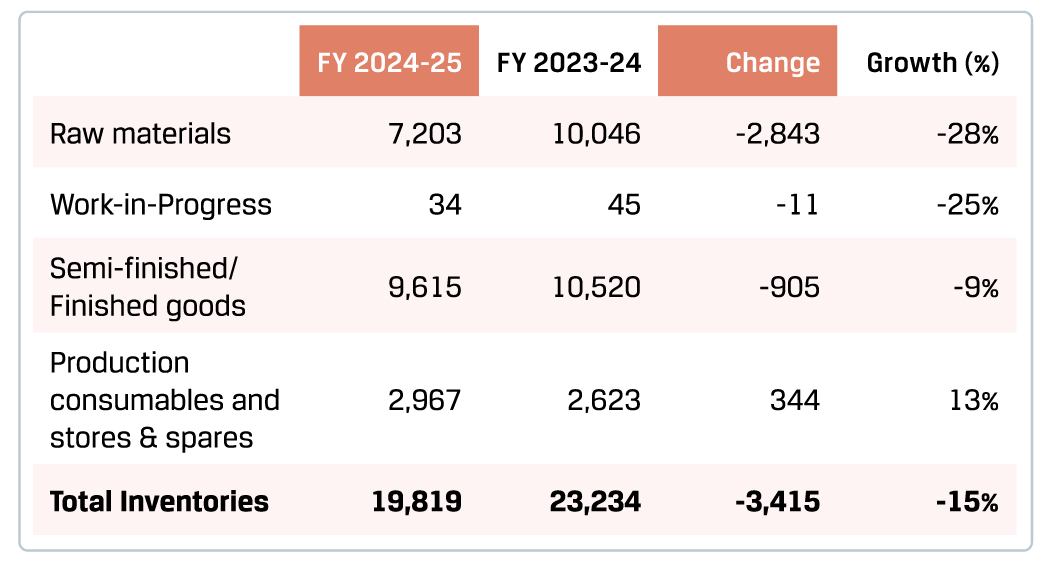
The decrease in value of inventories was primarily due to the reduction in raw material inventories and decrease in semi-finished/finished good inventory partially offset by increase in inventories of consumables, stores and spares.
The decrease in raw material inventories is primarily due to decline in coking coal prices.
Liquidation of 1.5 lakh tonnes of Semi-finished/Finished goods due to robust domestic steel demand led to decrease in semi-finished/finished good inventory.
The inventory of consumables, stores and spares increased due to procurement of critical spares required for maintenance shutdowns planned for the next financial year.
6.2.18 Trade Receivables (` in crore)
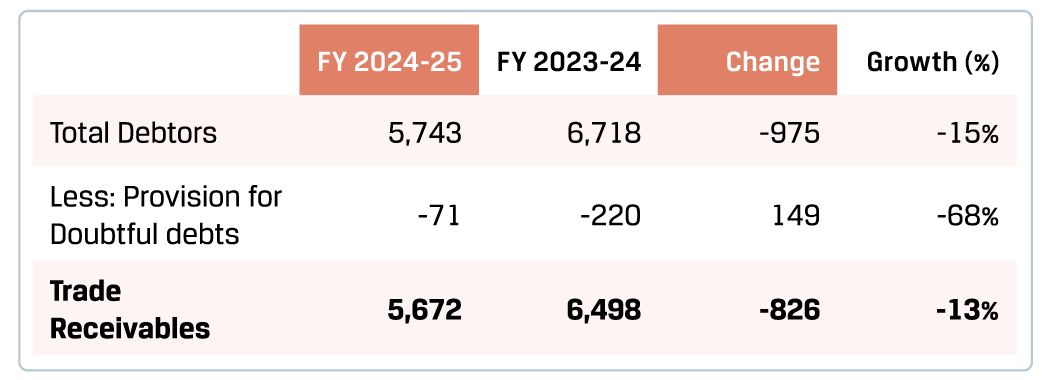
Trade receivables decreased by ₹826 crore to ₹5,672 crore due to decrease in net sales realisation as compared to FY 2023-24. Further, the average collection period as on March 31, 2025 marginally increased on account of decrease in net sales realisation during current year, resulting in lower total revenue.
6.2.19 Cash and Bank Balances (` in crore)
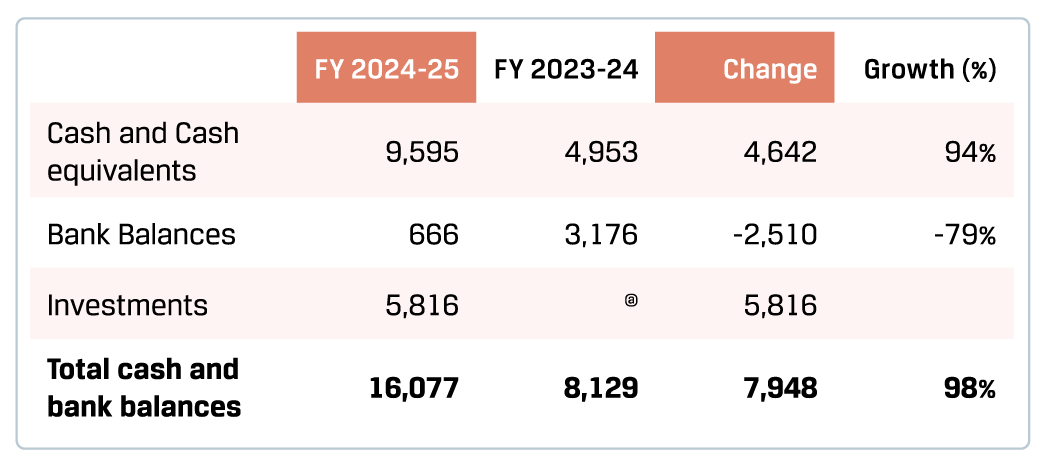
To meet short-term cash commitments and repayment obligations, the Company parks surplus funds in short-term and highly liquid instruments which represent cash and cash equivalents and other bank balances. Total cash and bank balances (including balance in Mutual fund) increased to ₹16,077 crore from ₹8,129 crore primarily to maintain a strong liquidity position. Further the cash and bank balances were higher as the funds required for repayment of Bond maturing in April 2025 was temporarily parked in fixed deposits and mutual funds.
6.2.20 Borrowings (` in crore)
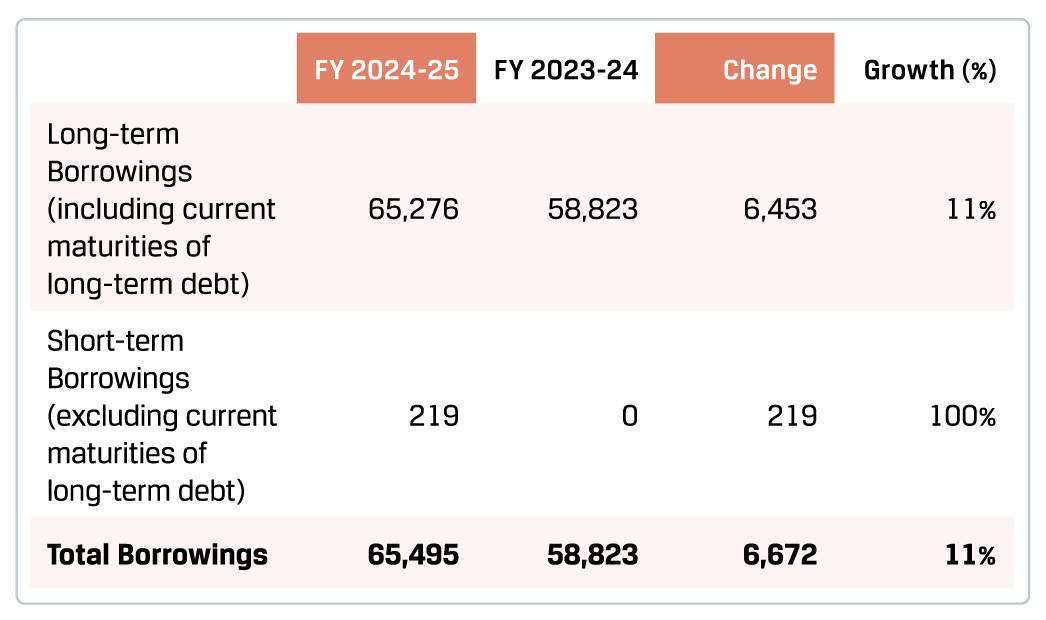
Long-term borrowings (including current maturity of long-term debt) increased primarily due to the net drawal of term loans amounting to ₹5,998 crore for incurring capital expenditure and general corporate purposes. Short-term borrowings reflect utilisation of working capital facilities at the end of the financial year.
6.2.21 Acceptances (` in crore)

Acceptances marginally increased by ₹115 crore during FY 2024-25 primarily on account of higher acceptances towards domestic procurement of Iron Ore, which was partially offset by lower acceptances of coking coal due to decline in prices.
6.2.22 Trade Payables (` in crore)

Trade payables decreased by ₹3,829 crore to ₹8,913 crore primarily on account of payments made to operational creditors and reduction in raw material prices.
6.2.23 Other Financial Liabilities (` in crore)
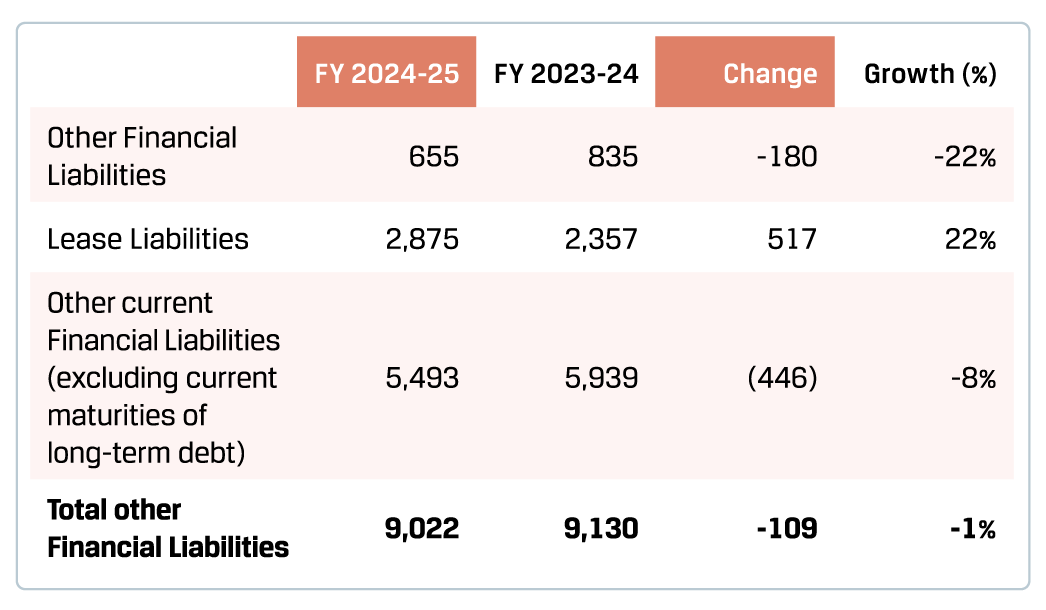
Other financial liabilities decreased by ₹180 crore to ₹655 crore mainly due to the decrease in retention money payable for capital expenditure.
Lease liabilities increased by ₹517 crore to ₹2,874 crore primarily on account of addition in lease liabilities for railway wagons taken on lease, increase in lease liabilities pursuant to contracts entered for Air Separation Unit and cargo handling at ports, partially offset by the repayment of principal amount on leases.
Other current financial liabilities decreased by ₹446 crore to ₹5,493 crore primarily on lower Bid premium and Royalty due to decrease in overall volume of Iron ore production mainly due to surrendering of Jajang mines in Odisha in FY 2024-25 as compared to FY 2023-24, decrease in interest accrued but not due on borrowings, decrease in retention money payable for capital expenditure partially offset by higher provisions for marketing rebates.

6.2.24 Other Liabilities (` in crore)
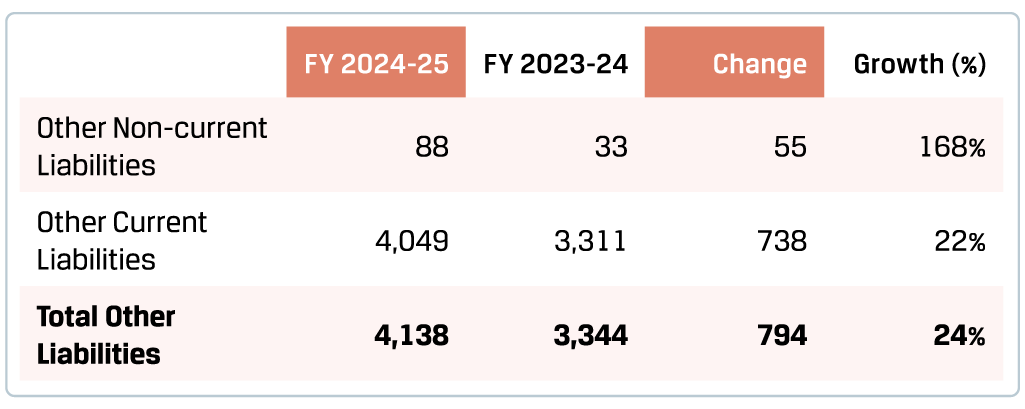
Other current liabilities increased by ₹738 crore to ₹4,049 crore due to increase in advances received from customers and statutory liabilities.
6.2.25 Deferred Tax Liabilities (` in crore)

Deferred tax liabilities decreased by ₹792 crore to ₹8,528 crore, primarily on account of creation of deferred tax asset on provision relating to investments and loans extended to subsidiaries.
6.2.26 Capital Employed
Total capital employed increased 6% y-o-y to ₹1,24,181 crore in FY 2024-25 primarily due to capitalisation of Property, Plant & Equipment and increase in net current assets. Return on average capital employed for FY 2024-25 was 10.5%, as against 14.4% in FY 2023-24 due to lower EBIDTA margin at 14.4% in FY 2024-25 as against 16.3% in the previous year.
6.2.27 Own Funds
JSW Steel’s equity increased from ₹75,283 crore to ₹79,839 crore as on March 31, 2025. Book value per share was at ₹326.48 as on March 31, 2025, as compared to ₹307.85 as on March 31, 2024.

6.2.28 Other Key Financial Indicators
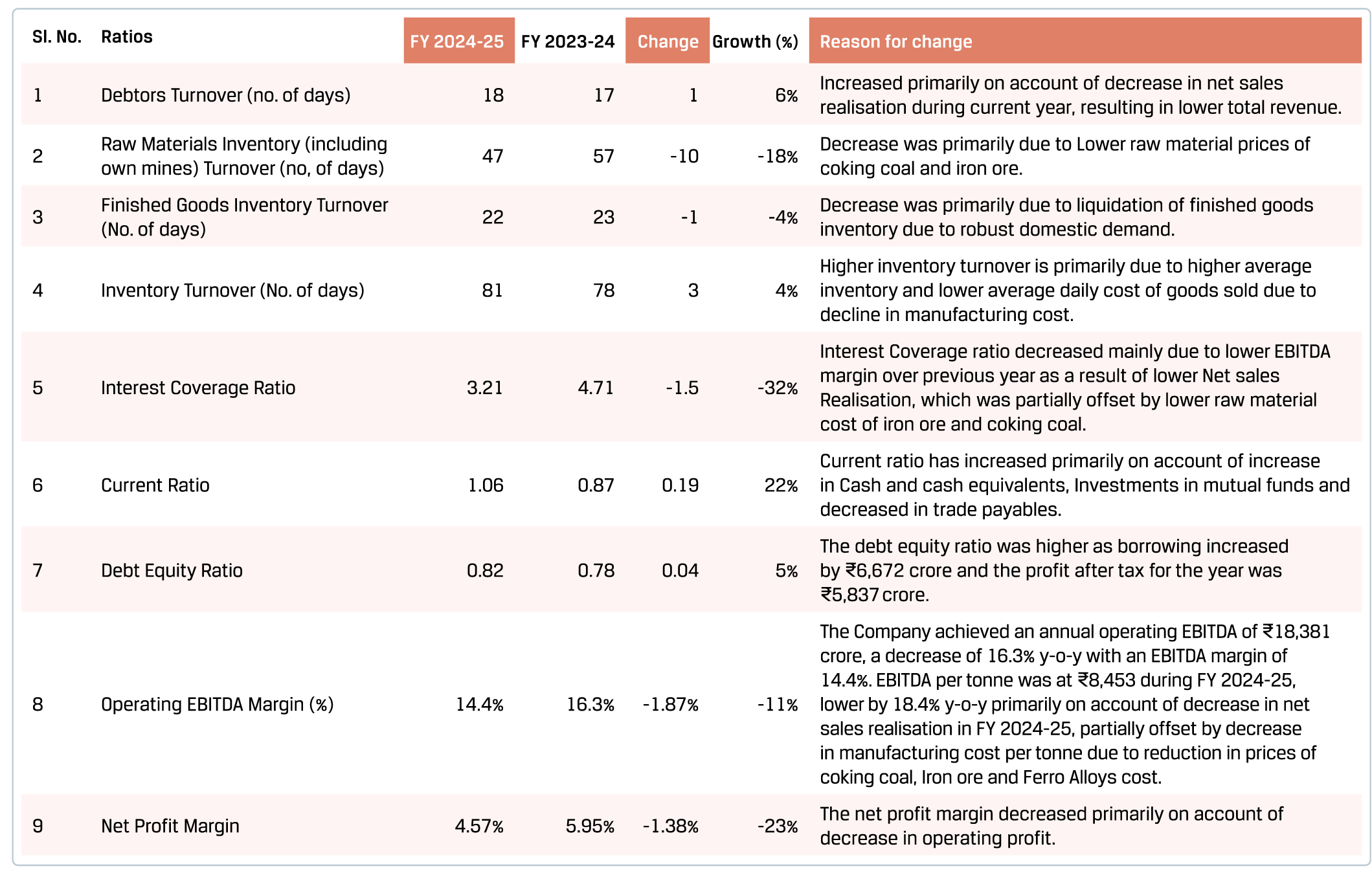
7.0 Digitalisation
JSW Steel’s digital transformation strategy harnesses the power of Industry 4.0 technologies to enhance operational efficiency, quality, safety and sustainability. By integrating cutting-edge digital solutions such as IoT sensors in mining and machine learning in manufacturing, it optimises processes in real time. Key initiatives like digital twins, predictive analytics and AI-driven systems drive proactive maintenance and improve decision-making. These advancements develop a culture of innovation, streamline operations and set new industry benchmarks. Through this transformation, it is reshaping traditional practices, contributing to a more sustainable and efficient future in steel production.
Read more8.0 Human resources
JSW Steel recognises that its ambition to become a more efficient and leading steel producer relies on the commitment and expertise of its workforce. Talent management is integral to the Company's strategy, offering a supportive work environment with competitive compensation packages. Employees benefit from extensive learning and career development opportunities, while a strong emphasis on diversity and inclusion creates a culture of empowerment. Leveraging digitalisation further enhances employee capabilities and operational efficiency. With robust health and safety measures in place, the Company ensures the well-being of its workforce, driving them to consistently achieve peak performance.
Read more9.0 Corporate social responsibility
At JSW Steel, our guiding principle, ‘Better Everyday’ extends beyond our commitment to Corporate Social Responsibility. We believe in actively addressing social inequalities, striving to create a more equitable and prosperous India. Our approach is deeply empathetic, rooted in genuine stakeholder engagement, grassroots participation, and local involvement, ensuring our initiatives resonate deeply within communities. We focus on impactful programmes across vital sectors: enhancing education to unlock potential, fostering livelihoods and skill development for economic independence, improving health and nutrition for a thriving populace, and strengthening community development through essential infrastructure and sustainable practices. Beyond these, we champion sports promotion and preservation of India's rich art and heritage. Through these scalable and sustainable efforts, JSW Steel is dedicated to making a meaningful impact, ensuring positive change across the country.
Read moreCSR focus areas
Health and nutrition
Improving rural healthcare through outreach, building a healthier nation with comprehensive programmes.
Beneficiaries
Water, environment and sanitation
Supporting sustainable water solutions, including solar bore wells and rainwater harvesting, aligned with United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals.
Beneficiaries
Skills and livelihoods
Empower communities by providing vocational training, micro-entrepreneurship and supporting women’s self-help groups.
Beneficiaries
Art, culture and heritage
Champion India's art, culture and heritage through restoration initiatives, preserving traditions and societal evolution.
Restoring Mughal Garden in Kashmir, supported Hampi archaeological museum in Karnataka and David Sasson Library in Mumbai
Education
Creating safe, inspiring learning environments, ensuring lifelong passion for education through strategic collaborations.
Beneficiaries
Waste management
Promoting waste management, raising awareness and encourage waste upcycling and alternative livelihoods in communities.
Agriculture and allied livelihoods
Collaborate with farmers, enhancing skills, productivity and market access to promote sustainable incomes.
Sports promotion
Nurture India's sporting talent through school initiatives, offering training in various disciplines to develop champions.
Beneficiaries

10.0 Risk management
JSW Steel’s Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework offers a robust and structured approach to identify, prioritise, manage, monitor and report on both current and emerging risks. Adhering to the globally recognised Committee of Sponsoring Organisations (COSO) framework, it integrates internal controls seamlessly into business processes. The Company employs a balanced risk management strategy, incorporating both bottom-up and top-down approaches.
Local plants and corporate functions identify and assess risks, implementing effective mitigation strategies, while the Risk Management Group (Senior Leadership Team) and the Risk Management Committee (RMC) oversee long-term strategic and macro risks.
The RMC, chaired by an Independent Director, ensures risks are prudently managed, focusing on executing strategies and mitigating unintended risks such as performance and process risks. Through robust policies, internal controls and regular audits, the Company proactively mitigates risks, protect shareholder interests, achieve business objectives and enable sustainable growth.
Read more