29.7 MTPA
Total installed capacity
JSW Steel, the flagship of the JSW Group, is one of the leading and most diversified steel producers in India.
JSW Steel has continuously sustained its market position with the core strengths of agile operations, rich product mix, best-in-class technology, excellence in project execution, sustainable sourcing and consistent focus on employee engagement. With the long-term growth potential for steel consumption in the Indian domestic market, JSW Steel has introduced an additional capital expenditure programme to expand its capacities at its plants, and to modernise and expand capacities of its downstream business.
Its fully integrated operations encompass mining, beneficiation, raw materials processing, steel manufacturing and manufacture of downstream value-added products. With a total installed capacity of 29.7 MTPA in India and overseas, JSW Steel has embarked on a transformative growth path that would take its capacity to 38.2 MTPA by FY 2024-25, 43.5 MTPA by FY 2027-28 (September), and further to 51.5 MTPA by the end of FY 2030-31. The Company has earmarked an estimated I64,434 crore as capex to be spent over FY 2024-25 to FY 2026-27 to complete the capacity expansion to 43.5 MTPA, expand downstream capacity, mining projects, cost savings projects, sustaining Capex, and the modernisation of overseas facilities.
JSW Steel’s domestic roadmap to 50 MTPA is in alignment with India’s sustainable development aspirations. It has multiple projects in the pipeline to achieve this target viz. brownfield potential of 5 MTPA each in Vijayanagar and BPSL; 4 MTPA green steel plant in two phases, a 13 MTPA greenfield plant in Odisha and a greenfield Electric Arc Furnace facility in Andhra Pradesh.
Steelmaking capacity
Total installed capacity

Target capacity

Target capacity

JSW Steel’s manufacturing facilities are strategically located across India – Vijayanagar in Karnataka (12.5 MTPA), Dolvi in Maharashtra (10.0 MTPA), Salem in Tamil Nadu (1.0 MTPA), Jharsuguda (BPSL plant) in Odisha (3.5 MTPA), Raigarh and Raipur plants in Chhattisgarh (1.2 MTPA) - and select overseas locations.
The Company has downstream capacity of ~13.5 MTPA in India. Outside India, JSW Steel has a 1.5 MNTPA EAF-based steelmaking capacity in Ohio, US. Overseas downstream facilities include a 3 MNTPA hot rolling mill in Ohio, a 1.2 MNTPA plate mill and a 0.55 MNTPA pipe mill capacity in Baytown, Texas, US, and a 1.3 MTPA long product capacity in Italy.
In India, downstream facilities comprise the coated products division at Vasind, Tarapur Kalmeshwar Works and Khopoli in Maharashtra, Bawal in Haryana and Rajpura in Punjab, in addition to the downstream facilities at Vijayanagar and BPSL downstream plants at Jharsuguda in Odisha, Chandigarh in Punjab and Kolkata in West Bengal. Its downstream facilities also include the plate and coil division at Anjar in Gujarat.
JSW Steel has one of the largest distributor and retailer networks in India. The Company has also established a strong export presence spanning 100 countries.
JSW Steel has a wide range of product offerings that cater to diversified end markets across geographies. The Company has significantly expanded its product portfolio through a mix of acquisitions, downstream capacity expansions and joint ventures with other leading steel companies. JSW Steel believes that the breadth of its product range gives it the flexibility to adapt its product mix to market demands and enables it to sustain its business and operations through adverse economic conditions.
Robust distribution across India and export presence in 100 countries
Exclusive and non-exclusive retail outlets
Distributors
Branded JSW Shoppe stores in urban areas
JSW Shoppe Connect stores in semi-urban and rural areas
Partners enrolled in JSW Privilege Club

JSW Steel’s strategically located operations, state-of-the-art manufacturing, captive resources, and resilient business model have enabled the Company to establish itself as a leader on the global conversion cost curve. Further, the Company remains focused on strengthening its backward integration to optimise costs and reduce external dependencies. In addition, JSW Steel is leveraging technology, analytics as well as its innovation capabilities to further improve efficiencies.
JSW Steel has secured 24 iron ore mines and 3 coking coal mines in India through open auctions to improve its raw material self-sufficiency. Of the total 24 iron ore mines, 13 iron ore mines in Karnataka and Odisha are operational, with the rest at various stages of exploration and commissioning. The 3 coking coal mines are expected to start mining operations over the next two years. The Company has also built the world’s largest pipe conveyor system, which extends 24 km from the captive mines in Karnataka to the Vijayanagar plant to transport iron ore fines. This is an environment-friendly logistics solution for the transportation of iron ore from the mines to the Vijayanagar plant and results in cost savings by way of reduction in transportation costs.

WSD Aggregate Ranking
Total installed capacity

Target capacity

Conversion cost in FY24*
Source: On the basis of weighted average score out of 10, across 23 different parameters from World Steel Dynamics’ World-Class Steelmaker Rankings as of December 2023.
*-Data for Standalone operations
In India, public sector companies have the provision to extend their leases by another 20 years upon expiry while leases of private sector firms do not have such provisions. Given the impending expiries of low-cost legacy leases until 2030, the premium recorded during recent auctions, and limited clarity on renewal cost jump, mining profitability could come under severe pressure. Against this backdrop, JSW Steel is best positioned as the Company doesn’t have any legacy, low-cost captive mines. Further, the Company won its mining (including coking coal) leases through auctions, and the operationalised captive mines now account for 33% of its iron ore consumption.
In the auction conducted by the Government in April 2015, JSW Steel won the Moitra coking coal block, located in Jharkhand state, which has a total extractable coal reserve of approximately 30 MT. Moitra coking coal block has coking grade coal and is in advanced stage of development and can provide 1 MTPA of coking coal. To further strengthen backward integration, JSW Steel won the Parbatpur and Sitanala coking coal mines in India through auctions, which when commissioned, will provide 1.5 MTPA of coking coal at a lower cost than imports. Further, the Company has been actively scouting for coking coal resources globally, and in May 2024, it announced the acquisition of the Minas de Revuboe mine in Mozambique, which has over 800 million tonnes of high-quality hard coking coal reserves.
JSW Steel is also setting up a 30 MTPA slurry pipeline from the mines to Jatadhar port, including the grinding and filtration plant. Slated for commissioning in FY 2026-27, the slurry pipeline will provide an environment-friendly logistic solution for transportation of iron ore from Odisha mines to the Jatadhar port and reduce logistics costs. The Company is also setting up an 8 MTPA pellet plant in Odisha for further value addition of iron ore, enhancing its cost competitiveness and raw material security. Further, the Company is setting up coke oven facilities at Vijayanagar to cater to the fuel requirements of the expanded capacities. In addition, the Company has set up and planning to install larger blast furnace of 5 MTPA capacity across its expansion projects for economies of scale and efficient steel making operations.

JSW Steel has entered into strategic joint ventures as well as acquired equity interests in various entities which has enabled the Company to add more valueadded products, enhance global footprint, secure raw materials, achieve backward integration and increase technological know-how.
JSW Steel has entered into a 50:50 joint venture with UK-based Severfield UK PLC, which provides structural steel building solutions. Severfield’s manufacturing facility is located at Vijayanagar within the premises of JSW Steel’s plant and has a capacity of 1,00,000 tonnes (165,000 tonnes including associate sub-contractor facilities) per annum. The product portfolio includes engineering, fabrication and erection of structural steel. They also provide cutting-edge flooring technology with composite metal decking through Structural Metal Decks Limited, UK.
JSW Steel also has a joint venture with Marubeni-Itochu Steel (JSW MI Steel Service Centre Private Limited) to set up steel service centres in north and west India for just-in-time solutions for the automotive, white goods and construction sectors. The Company has also pursued unique opportunities in stressed assets in niche markets.
JSW Steel has a wide range of product offerings that cater to diversified end markets across geographies. Its relentless focus on R&D and innovation has led to the development of a diversified portfolio of value-added products. The breadth of the product range provides the Company the flexibility to adapt its product mix to market demands and remain resilient to adverse macroeconomic conditions.
JSW Steel’s portfolio includes hot-rolled, cold-rolled, coated, colour-coated, tinplate, alloy steel and electrical steel products. Its long product range comprises TMT bars, wire rods, rails, grinding balls and special steel bars. These products are widely used in automotive, general engineering machinery projects and construction applications.

Flats: HR Plates, Coils and Sheets | HRPO | CRCA | Electrical Steel | GI/GL/GA | Zn-Mg | PPGI/PPGL | Tinplate


Longs: Alloy Steels
| Wire Rods
| LRPC | TMT Bars





JSW Steel is the leading provider of value-added and special steel products (VASP). The Company manufactures a wide range of value-added flat steel products, such as medium to high carbon steel, high tensile and high strength low-alloy steel grades for the automotive sector, API grade steel for the oil and gas sector, cold rolled close annealed coils, customised galvanised and galvalume products for the solar sector, galvanised products and colour coated products in the flat product segment and rebars, wire rods and structural steel in the long product segment. The Company has one of the largest galvanising and galvalume capacities in India. Further, it has the largest coated capacity in India and one of the largest globally. It has export footprint in more than 100 countries.
Aligned with its focus on innovation and customer-centric solutions, JSW Steel introduced 51 new grades of steel during FY 2023-24, including 21 import substitution grades and 15 grades of advanced high strength steel (AHSS). The Company received 48 new product approvals during the period under review. Further, to enhance special steel offerings, JSW Steel entered into a joint venture with JFE for establishing a cold-rolled grain-oriented (CRGO) mill at Vijayanagar, making it India's first end-to-end CRGO product line.
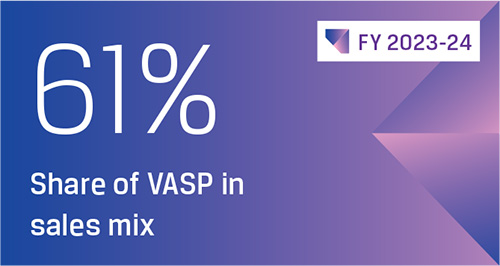

JSW Steel is transforming every aspect of its business by embracing the best available and emergent technologies across functions – Finance, Human Resources, Manufacturing, Mining, Marketing, and Supply Chain. Harnessing the power of Big Data, Advanced Robotics, Hybrid Cloud and Artificial Intelligence, the Company is driving cultural change, augmenting customer experiences, and developing innovative products. Digital initiatives are enabling JSW Steel to improve safety, optimise cost, drive seamless integration of operations, improve product value, and enhance customer delight.
JSW Steel is transforming its mining operations by digitalising mine planning and operations, fuel management system, logistics, and health and safety, which also leads to enhanced productivity and efficiency. Under Project Samarth, the Company’s finance function is undergoing a comprehensive digital transformation with 38 out of 58 initiatives already implemented. Under Project Sampark, JSW Steel is undertaking end-to-end transformation of logistics. The Company has implemented the Digital Logistics Management System (DLMS) at its Vijayanagar and Dolvi plants, for outbound logistics while it is under implementation for in-bound and in-plant logistics.
Project Sampark, when complete, will deliver significant benefits in the form of reduced logistics costs, reduced vehicle turn-around-time (TAT), enhanced workplace safety and complete visibility of vehicle movement inside plants. To further improve operational analytics and decision-making, the Company deployed the Integrated Control Tower (ICT) at the Vijayanagar, Dolvi and Salem plants. The ICT provides real-time analytics and dashboards for plant operations. Further, the Central Command Centre at the JSW Mining Barbil office enables centralised monitoring and control of mining operations.
Sustainability is deeply entrenched into JSW Steel’s business growth strategy. The Company has identified and established 17 sustainability focus areas, setting ambitious targets to continuously monitor progress, and enhance performance every year. The governance and oversight has been entrusted to the Board-level Business Responsibility and Sustainability Committee. JSW Steel is committed to no harm to the environment, people and society.


ENVIRONMENT
Climate Change
Energy
Resources
Water resources
Waste
Waste Water
Air Emissions
Biodiversity
Sustainable Mining
Supply Chain Sustainability

SOCIAL
Indigenous people
Cultural heritage
Employee well-being
Local considerations
Social sustainability

GOVERNANCE
Business ethics
Human rights
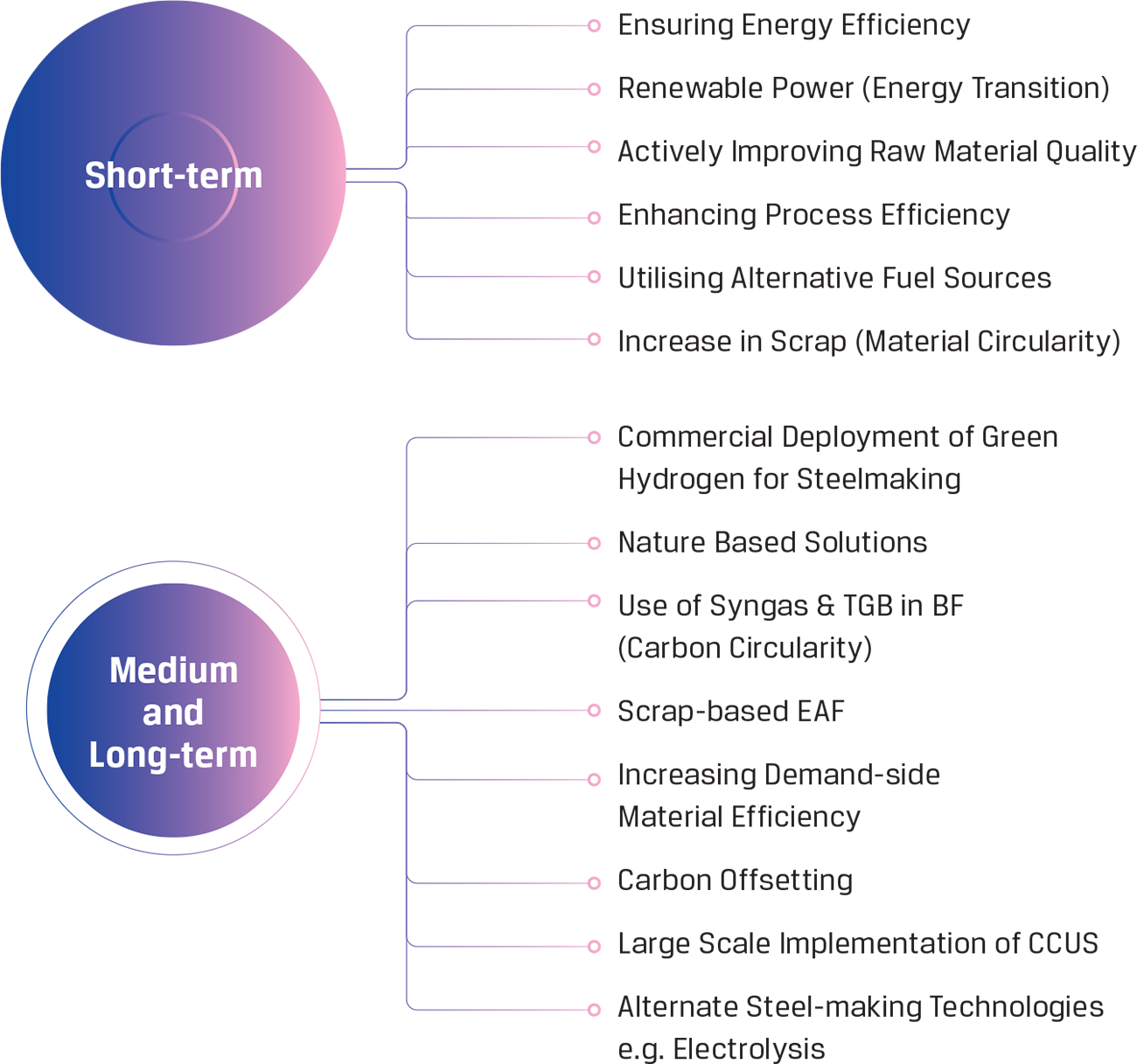
Accelerating decarbonisation and low-carbon steelmaking
In January 2024, the Board approved JSW Steel's commitment to achieving a status of net neutral in its carbon emissions by 2050, significantly ahead of India's Net Zero commitment of 2070. This will be achieved through a range of short-term, medium-term and long-term initiatives. In the short term, the Company is focusing on increasing the share of renewable energy, improving raw material quality, energy and process efficiency, and increasing scrap usage, among others. In the long term, key levers include utilising syngas, adopting green hydrogen, transitioning to scrapbased electric arc furnaces, carbon sequestration through natural and technological solutions, and large-scale adoption of Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS). JSW Steel also published its first Climate Action Report to provide a detailed outline of its progress and future endeavours towards decarbonisation. Read it here.

JSW Steel launched the SEED Program, a decarbonisation initiative which focuses on process and energy efficiencies involving the workforce. Through this initiative, JSW Steel has identified potential abatement opportunities of more than 18 MnT of CO2 emissions by 2030. JSW Steel is the first manufacturer in India to receive the prestigious GreenPro ecolabel for its ‘Automotive Steel’ products. The GreenPro ecolabel, developed by the Confederation of Indian Industry’s (CII) Green Business Centre, recognises the highest standards of environmental sustainability and product performance in the Indian manufacturing sector.

JSW Steel joined the India H2 Alliance (IH2A) to drive the transition to cleaner energy. IH2A is an industry coalition focused on creating a hydrogen value-chain and economy in India. With the participation of government agencies, sustainability think-tanks, and private sector partners, IH2A aims to reduce hydrogen production costs, promote the growth of a local hydrogen supply chain, and support India’s Net Zero carbon goals. As the Steel and Cement Work Group Lead within the India H2 Alliance (IH2A), JSW Steel will collaborate with industry leaders and government entities to establish a shared vision for the commercialisation of hydrogen in the steel and cement industries. By exporting green steel produced with hydrogen, the Company can position India as a global leader in the hydrogen value chain and integrate hydrogen into the industrial supply chain.
Building future-ready workforce; imbibing strong safety culture
JSW Steel’s ability to deliver industry-leading growth, operational excellence and retaining its competitive edge hinges on the dedication and skills of its workforce. Talent management is a pivotal part of the Company's strategic framework. In addition to providing industry-competitive compensation, the Company offers extensive learning and career development opportunities. Celebrating diversity and inclusion, JSW Steel fosters a culture where all employees feel valued and empowered. By leveraging digitalisation, the Company enhances employee capabilities and operational efficiency and productivity, building a future-ready workforce that will continue to shape JSW Steel’s journey in the coming decades.
Further, JSW Steel is committed to building a strong health and safety culture, aligned with the Company’s vision of zero harm. It has been investing in capacity building and has undertaken several initiatives that have started delivering results. The Company conducted a Safety Culture Survey of the workforce, including contract workmen at JSW Raigarh. It has also deployed camera-fitted helmets for monitoring high-risk and critical operations in real time at JSW Dolvi and BPSL, among others.
Making a difference to more than a million lives
JSW Steel's commitment to society is rooted in its ethos of 'Better Everyday'. The Company, through JSW Foundation, has adopted a transformative approach to deliver positive change across its key focus areas of health and nutrition; education; water, environment and sanitation; waste management; agriculture; skill development; sports; and art, culture and heritage. The programmes under the chosen focus areas are designed in such a way that they are scalable, replicable and sustainable, and involve engaging diverse stakeholders, fostering community participation at the grassroots level. In FY 2023-24, these initiatives covered 575 villages across India and made a difference to more than a million lives.


Steel Sustainability Champion by Worldsteel for the sixth consecutive year


India’s Best Workplaces
in Health and Wellness 2023 by
Great Place to Work


Leadership levels in CDP ratings


Dolvi plant received Climate Action Programme (CAP 2.0) award in Energy, Mining and Heavy Manufacturing category from CII and CII-ITC Centre of Excellence for Sustainable Development
The global economy demonstrated strong resilience, navigating multiple headwinds such as the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war, escalating geopolitical tensions in the Middle East, and the cost-of-living crisis in several economies. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) in its World Economic Outlook (WEO) April 2024 estimated global GDP growth at 3.2% for 2023, which was an upward revision of 0.1% point from its January 2024 update, driven by strong private consumption and government spending initiatives, particularly in the US and many emerging market economies. The services sector demonstrated strength, but manufacturing activity remained subdued.
The economic growth was, however, divergent – with the US growing faster than estimated among advanced economies while the UK and Europe barely avoided a recession. India remained a bright spot, globally and among advanced economies. China remained saddled with the continued weakness in its property sector. The absence of a comprehensive policy package for the beleaguered property sector, a prolonged drop in real estate investments, a bleak housing price outlook, and reduced housing demand further weighed on household confidence and spending. Meanwhile, the positive effects of the post-pandemic boost to consumption and fiscal stimulus have started to wane in China.
Although headline inflation has fallen across countries, core and services disinflation has been slow amid the continued tightness in labour markets. In response, major central banks in advanced economies (AEs) kept their policy rates on hold as inflation is yet to align with their targets. A faster-than-expected decline in inflation fuelled expectations of an early reversal in the US monetary policy cycle, leading to a sharp correction in sovereign bond yields in November and December 2023. Yields have, however, hardened since the beginning of 2024 as central bank communications pushed back on market exuberance related to the magnitude and pace of monetary policy easing. Following the correction seen in Q3 2023 (July-September), global equity markets posted strong gains in November-December, primarily in AEs.



The IMF expects global economic growth to remain at the 2023 level of 3.2% in 2024 and 2025 as well, with global headline inflation moderating further from 6.8% in 2023 to 5.9% in 2024 and 4.5% in 2025. It expects advanced economies to achieve their inflation targets ahead of their emerging and developing counterparts. With many countries going into elections in 2024, the economies could receive short-term fiscal boost, and central banks may cut rates at the latter half of the year, should the last leg of the disinflation process get completed.
In advanced economies, growth is anticipated to marginally increase, primarily driven by a recovery in the Euro area following a period of sluggish growth in 2023. In contrast, emerging market and developing economies are poised for stable growth, albeit with regional disparities. Monetary policy expectations vary across major economies, with projections indicating a mix of adjustments. The US Federal Reserve is likely to cut its policy rate, alongside similar moves by the Bank of England and the European Central Bank. Japan is expected to gradually increase policy rates, reflecting growing confidence in achieving sustainable inflation targets. In China, domestic demand remains lacklustre and is likely to remain so unless strong measures and reforms address the root cause. With depressed domestic demand, surplus could arise, which will further impact trade tensions in an already tense geopolitical environment.
In the US, growth is holding up well with resilient labour markets and consumption. The disinflationary process remains on track, albeit with some speed bumps, dampening rate cut expectations. In the Euro area, consumption and manufacturing remain weak but growth appears to be bottoming out and expected rate cut in the near term on soft inflation prints could provide support to recovery. Meanwhile, China demonstrated strong growth in the first quarter of 2024, with positive trend in manufacturing and auto. FAI ex-real estate development was up 9.3%. Japan could witness a modest recovery from the lows of recent quarters, supported by wage hikes and growth in exports.
On the fiscal policy front, the IMF expects governments in advanced economies to tighten fiscal policies in 2024 and beyond. This tightening is evident in projections for the structural fiscal-balance-to-GDP ratio, which is anticipated to rise notably in the US and the Euro area. Emerging markets and developing economies are likely to maintain a broadly neutral policy stance in 2024, with slight tightening anticipated in 2025.
Markets reacted positively to the prospects of central banks exiting tight monetary policy. Financial conditions eased, equity valuations soared, and capital inflows to emerging market economies were buoyant. Further, with the economic impact of the pandemic unlikely to be as high as previously estimated, it bodes well for the overall sentiment. Resilient growth, inflation easing, favourable supply developments, fading energy price shocks, rebound in labour markets, decisive monetary policy actions, and improved monetary frameworks have helped anchor inflation. These are positive developments.
However, challenges remain – core inflation has yet to come down, service inflation remains high, and there is divergence in economic growth across countries. In addition, China needs to be watched closely as domestic demand remains lacklustre. Real interest rates are high, medium-term growth prospects are weak due to lower productivity growth, and huge investments are needed for a green and climate resilient future.
Global GDP growth trend (%)
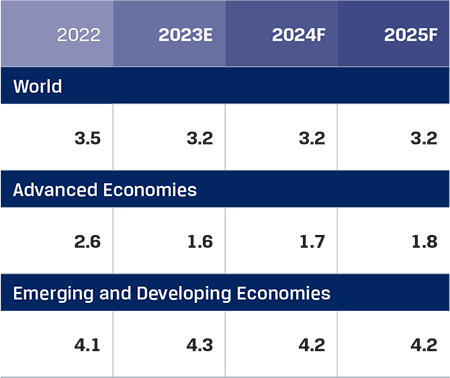
Source: IMF WEO April 2024;
E- Estimates; F - Forecast
Global growth is expected to be steady with moderate improvement in outlook
India remained the fastest growing major economy in the world in FY 2023- 24, with its real GDP estimated to have grown by 8.2%, according to the data released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme implementation (MoSPI), compared to 7.0% in FY 2022- 23. This projection came in above the second advance estimates of 7.6% in February 2024, as the economy recorded 8%+ growth for three consecutive quarters on the back of the Government’s continued spend on infrastructure and housing, robust private consumption and buoyant manufacturing and services sectors.

Total consumption, which accounts for 56% of the GDP, grew 3%, as private consumption remained somewhat tapered and rural demand continued to recover, driven by strength in domestic demand and growing working age population.
Real gross value added (GVA) is estimated to have grown by 7.2%, driven by 9.9% growth in the manufacturing sector, construction at 9.9% and services at 7.5% while agriculture remained weak, at just 1.4%. Manufacturing GVA accelerated, as easing input costs boosted corporate profitability. Industrial activity was also supported by the sustained momentum in mining and electricity generation. Gross fixed capital formation, constituting 34% of the GDP, accelerated to 10.2% from 6.6% in the earlier period, reflecting the Union government’s thrust on infrastructureled capital expenditure and housing.
Sustained capacity utilisation above 75% should help start the private sector investment cycle, further supported by the increase in profitability of corporates and strong bank balance sheets with double-digit growth in credit.

In its Interim Budget for FY 2024-25, the Union government earmarked a record `11.1 lakh crore of capital expenditure, up 11.1% from the year earlier period, in line with its infrastructure development-led push to drive sustained economic growth. Further, the Government announced plans to build two crore more houses under the PM Awas Yojana (PMAY) to account for the increase in the number of families as it inched closer to its target of building three crore houses under the scheme.
India’s overall exports recorded a marginal increase to US$776.68 billion in FY 2023-24, despite global headwinds, according to provisional data released by the Ministry of Commerce, driven by strong services exports, partially offset by a 3.1% fall in merchandise exports, as the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war, the tensions in West Asia, and disturbances in the Red Sea route led to a continued surge in freight rates, along with a spike in insurance costs.
Meanwhile, India's current account deficit improved significantly to 0.7% of GDP, or US$23.2 billion in FY 2023-24, down from 2% in FY 2022-23, according to the RBI, which could be attributed to a decrease in merchandise trade deficit. In fact, the country's current account balance turned a surplus of 0.6% of GDP in Q4 FY 2024, as against deficits in earlier quarters.
India’s retail inflation moderated to a 5-month low of 4.8% in March 2024, but remained above the long-term target of 4% of the RBI. After a series of rate hikes to tame inflation, the RBI remained in a pause mode for seven consecutive Monetary Policy Committee meetings and maintained its ‘accommodation of withdrawal’ stance. Prices of food, which has about 46% weight in the retail inflation basket, continue to be volatile, and a below-normal rainfall could adversely impact the RBI’s inflation targeting.
Gross direct tax collections before adjusting for refunds stood at H23.37 trillion in FY 2023-24, up 18.5% y-o-y with corporate tax revenue expanding over 13% y-o-y and personal income tax collections (including STT) growing 24.3% y-o-y. The figures were in line with the Government’s revised estimates presented during the Interim Budget for FY 2024-25 in February 2024. Gross GST collections increased 11.7% year-on-year to H20.18 trillion. Based on provisional data released by the Ministry of Finance, direct buoyancy of 1.9 indicates that the growth in tax collections continues to outpace the rate of economic expansion and could provide more elbow room for the new government to raise its tax collection targets for FY 2024-25 when it presents the full Budget in July 2024.
Despite 2024 being an election year, the Union government stayed on the path of fiscal consolidation, with India’s fiscal deficit estimates for FY 2023-24 narrowing to 5.8% and further to 5.1% for FY 2024-25, as per Interim Budget estimates. The target reflects the Government’s intent to improve tax collections and lower subsidy, while raising capital spending and funding new welfare schemes. It also keeps India on track to achieve its goal of keeping the deficit below 4.5% of GDP in the next two years.
With the RBI transferring a record `2.11 lakh crore as dividend to the government for FY 2023-24, it would provide adequate manoeuvring space to address any revenue shortfall or direct funds towards increased capex during the full Budget. Further, with the impending inclusion of the country’s sovereign bonds in the JP Morgan and Bloomberg emerging market indices, fiscal prudence and sustainable debt levels hold significant appeal to investors.
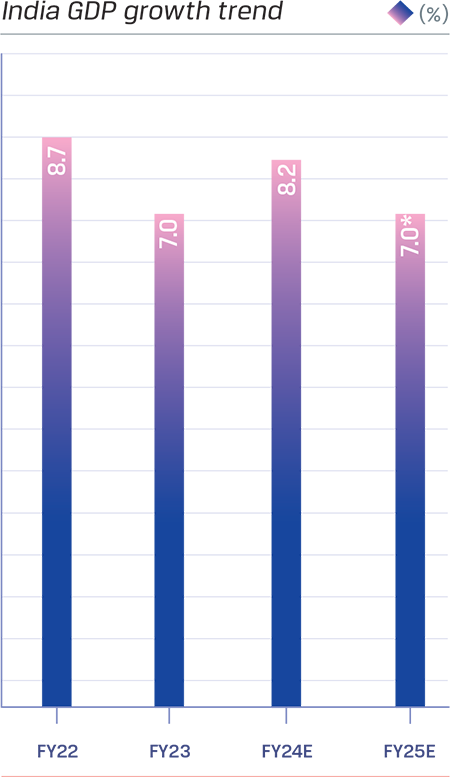
Source: MoSPI Estimates, RBI*
The Indian economy remains on a transformative growth path, demonstrating its inherent strength and resilience. Building on the strong foundations, India appears to be well on track to become the third largest economy over the next three years. Although challenges remain – both external and internal – the robust growth momentum continues to be led by the industrial sector and capital formation. Further, strong outlook for public housing, healthy growth in automobiles, elevated consumer confidence and moderation in inflation will support consumption growth. Expectations of above normal monsoon could boost rural recovery. Further, healthy forex reserves and positive outlook on capitals position India well to sustain its growth momentum.
However, a significant slowdown in global growth could impact India through trade and financial channels, while ongoing global supply disruptions may lead to increased volatility in commodity prices. Adverse weather conditions could rekindle inflationary pressures, prompting tighter monetary actions.
Most multilateral agencies, including the IMF and World Bank, have upgraded India’s growth forecasts for 2024 and 2025, amid caution surrounding geopolitical tensions, disruptions in trade flows, especially due to the volatile situation in the Middle East. The RBI pegs India’s economic growth at 7.2% for FY 2024-25 while expecting inflation to average 4.5%, down from 5.4% in FY 2023-24. India’s central bank expects improving employment conditions and moderating inflation, along with a rebound in agricultural activities, to boost consumption.
FY 2024-25 GDP Forecast (%) Revisions

Source: IMF, World Bank, RBI
Growth momentum likely to continue with positive trends across key sectors and a resilient macro-economic profile
India’s steel demand is likely to witness strong growth, driven by continued investments in infrastructure and urban development, growing manufacturing-led industrialisation and rising aspirational consumption such as consumer durables and automobiles. Infrastructure and construction accounts for 60-65% share, automobiles 9-10% of automobile, general engineering 25-26% and appliances, packaging and others 2-3%.
India is the world’s second largest producer and consumer of steel, but the country’s per capita steel consumption remains significantly below the global average, providing robust growth headroom. Further, during FY 2023-24, elasticity of steel demand to GDP growth was at 1.8, which assumes significance in the context of a contraction in global finished steel demand in CY 2023. The elasticity of steel demand with urbanisation rate is even higher at 3.0. Together, these factors should continue to drive steel demand growth.
After two years of volatility, global steel demand is likely to stabilise but growth is expected to remain weak over the next two years, even as the global economy demonstrates remarkable resilience to several headwinds like Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, escalating geopolitical uncertainties, high inflation and consequent monetary tightening. During the reporting period, higher interest costs, coupled with tighter credit conditions, weighed heavily on manufacturing and housing in most major markets.
Steel demand in China, the largest producer and consumer in the world, remained weak as the country’s property sector outlook, along with construction activities, remained bleak. Further, the country’s ongoing transition from an investment-stimulated to a consumptiondriven economic growth model is expected to limit its contribution to global steel demand growth.
In this scenario, India has emerged as an outlier in the global steel industry, with its young, growing and aspiring population offering its economy the labour and consumer strength to drive growth. Further, large untapped opportunities for growth and development across social, industrial, infrastructure, and defence, coupled with continued policy support and structural reforms, bode well for economic growth. Thus, steel demand could outpace economic growth for a sustained period, as the country is in a ‘nation building’ phase.

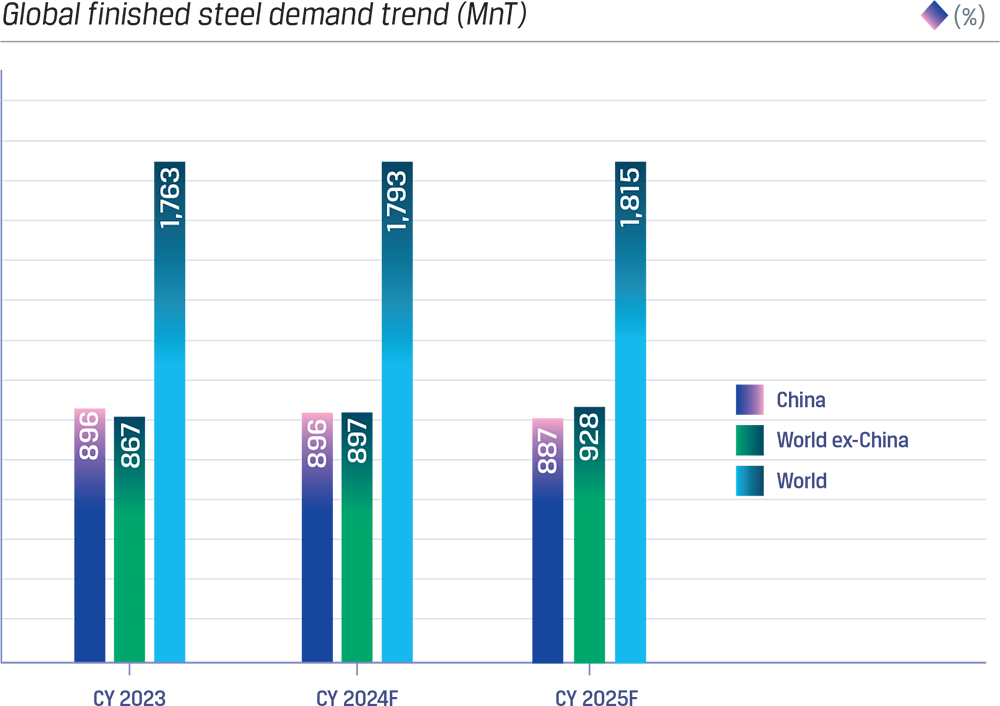
Source: World Steel Association, SRO April 2024
In CY 2023, world crude steel production stood at 1,892 MnT in 2023, largely flat y-o-y, according to the World Steel Association (Worldsteel), as steel producers reduced output in response to weak demand and volatile raw material costs and steel prices. China recorded production of 1,019 MnT, unchanged y-o-y while India’s steel production grew 12.3% to 141 MnT. Japan’s production fell 2.5% to 87 MnT while the US recorded a marginal increase to 81 MnT.
Top 10 steel producing countries in 2023
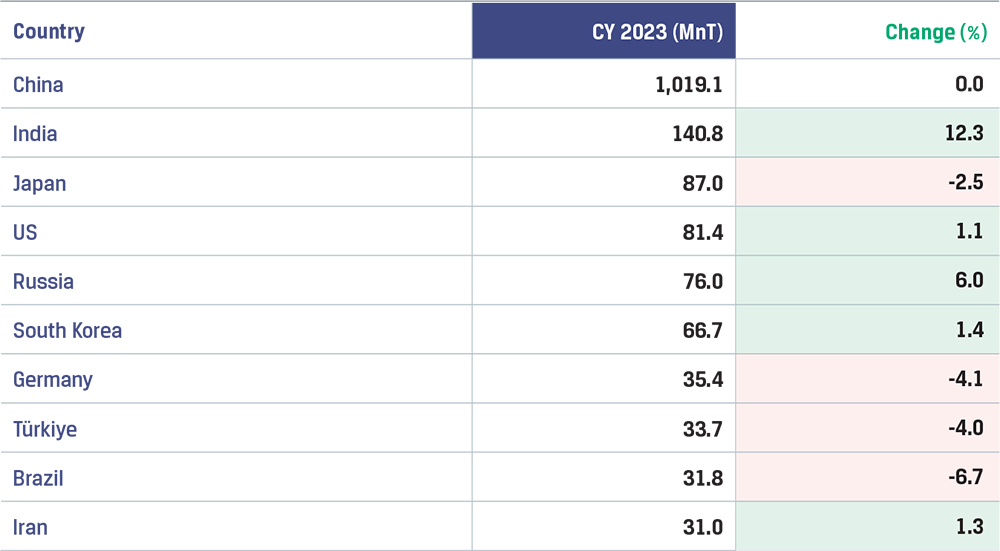
Source: World Steel Association, World Steel in Figures 2024
Global trade flows are expected to remain volatile due to ongoing geopolitical tensions and protectionist policies. Regional conflicts and unrest such as the war between Russia and Ukraine and situation in Israel and elsewhere have been contributing to rising oil prices and further geo-economic fragmentation, affecting normal trade flows.
Global steel prices experienced significant volatility during the year due to a combination of local and global issues. In the early part of FY 2023-24, steel prices in the US and Europe were elevated but they began to decline as China increased its steel exports. In China, continued weakness in the property sector negatively impacted steel prices last year. However, anticipated production cuts in China and healthy demand ex-property sector could potentially support steel prices. The Eurozone’s economy stagnated in 2023, and the outlook for 2024 remains challenging amid weak demand and escalating geopolitical tensions. Nevertheless, expected interest rate cuts in Europe and the US should aid in demand recovery and provide support for steel prices moving forward. In India, domestic demand is expected to remain strong, thereby supporting prices even as imports remain a threat.
Rebar/TMT prices were volatile in all the major markets, due to a mix of seasonal factors, local supply-demand imbalance and policy impact. On a year-on-year basis, rebar prices were weak. China’s steel production rebounded in early January and weighed on domestic prices while steel inventories remained at elevated levels, reflecting weak demand outlook prevailing in the domestic market. India’s domestic rebar prices were impacted by increased supply from secondary players. US and EU domestic rebar prices remained flat.
Trends in Global Rebar Prices (H/T)
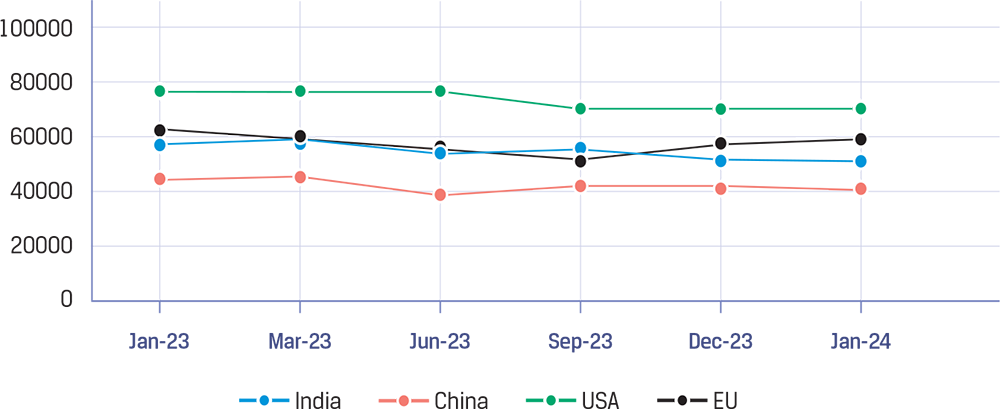
Source: Joint Plant Committee


Similar to rebar, HRC prices were also volatile in 2023 in major markets, due to a mix of seasonal restocking and domestic supply-demand imbalance in major markets. On a year-on-year basis, HRC prices have increased in the US and EU, and have weakened in China, on elevated steel production and subdued demand due to ongoing issues in the property sector. Meanwhile, India HRC prices remained range bound on the back of strong domestic demand offset by higher imports.
Trends in Global Rebar Prices (H/T)

Source: Joint Plant Committee
Prices of 62% iron ore grade ranged between US$95/tonne to US$136/tonne in FY 2023-24. Iron ore prices witnessed positive momentum in early 2023 on elevated steel production in China but started moderating and briefly fell below US$100/tonne in May and remained range bound till June-July 2023. It bounce backed thereafter on the hope of strong stimulus in China which would drive steel demand and production, thereby boosting demand for iron ore. Iron ore prices are again inching lower in middle of 2024 on elevated production from miners in Australia and Brazil and weakening demand outlook.
Hard Coking Coal prices, FOB Australia ranged from US$220/tonne to US$375/tonne during FY 2023-2024. Healthy demand, especially from India, and the absence of production cuts in China along with supply constraints ensured that coking coal prices remained well above US$200/tonne during the year. Accidents and rising safety inspections in China also ensured elevated demand for imported coking coal.
Coking coal prices are likely to remain range bound going forward while iron ore prices could see some decline on potential steel production cuts in China.
Trends in Global Prices of Major Raw Materials for Steel (US$/T)

Source: Fastmarkets Metal Bulletin, Joint Plant Committee

Global finished steel demand is expected to increase by 1.7% (30 MnT) y-o-y in CY 2024. Demand in China is expected to remain flat with the entire growth being driven by World ex China. India, the Euro area, ASEAN and Türkiye are expected to see demand increase of 11 MnT, 4 MnT, 3 MnT and 3 MnT, respectively. Notably, India will contribute 37% of the incremental steel demand in CY 2024. Moderate growth is also expected in the US, Middle East and Africa with 2 MnT each, while for Japan and Korea, it is expected to remain at the same level in CY 2024 versus CY 2023.
In China, steel demand signals a potential shift away from a real estate and infrastructuredriven economic model towards manufacturing and energy transition. India emerges as a key driver of steel demand growth. Similarly, other emerging regions like MENA and ASEAN are anticipated to experience accelerating growth in steel demand after a slowdown in previous years. In the developed world, the EU and UK have faced significant challenges including geopolitical uncertainties, high inflation, partial withdrawal of fiscal support and high energy prices in 2023. After only a technical rebound in 2024, the region’s steel demand is expected to finally show a meaningful recovery with a 5.3% growth in 2025. In contrast, the US demonstrates healthy steel demand fundamentals, poised for a quick return to growth in 2024 after a slowdown in 2023, supported by strong investment activity.
A faster-than-expected disinflation accompanied by monetary policy easing could provide a significant boost to steel-consuming sectors, particularly construction. Further, an acceleration in global decarbonisation efforts or in efforts to strengthen public infrastructure against rising climate change risks are significant positives supporting global steel demand. Further, escalation in geopolitical tensions, high and rising public debt levels triggering fiscal consolidation in major economies, and the last leg of disinflation proving to be longer than expected could weigh heavily on the economic recovery and thus steel demand.
In 2023, the automotive sector bucked the overall weak trend in manufacturing, showing signs of a long-awaited strong recovery on pent-up demand and easing supply chain constraints. However, this strong growth in major auto producing countries is unlikely to sustain into 2024. While global passenger and commercial vehicle sales remained strong, the global automotive industry faced multiple headwinds like slowing growth of EV sales, rising costs, among others.
High interest rates and construction costs continued to weigh on the construction sector, negatively impacting steel demand across most major steel-using regions in 2023. Further, weakness in housing activity in the US, China, Japan and the Euro area is expected to continue into 2024 in most major markets, driven by the lagged impact of monetary tightening, and any meaningful recovery could start to play out only in 2025.

Global manufacturing activity remained weak in 2023 on the back of high costs and uncertainties, tight financing conditions and muted demand, which adversely impacted global steel demand in 2023. According to the Short Range Outlook, leading indicators point to the start of a recovery in global manufacturing activity in 2024. Further, as major economies focus on developing strategic sectors and ensure supply security for strategic components against the backdrop of escalating geopolitical tensions, investments in manufacturing and infrastructure could receive a boost, underpinning global steel demand.
India is the second-largest producer of crude steel in the world. During FY 2023-24, domestic crude steel production rose 13.2% y-o-y to 144.04 MnT, while finished steel consumption increased 13.6% y-o-y to 136.25 MnT, driven by robust domestic demand on the back of the Government’s continued spend on infra and housing, the increasing share of manufacturing in GDP, and strong demand from the automotive segment. However, margins of domestic steelmakers came under pressure due to volatile commodity and energy costs, and the surge in low-cost imports putting more pressure on steel prices.
During FY 2023-24, India turned a net importer of steel as cheaper imports from Asia, especially China, made their way into the domestic market. Overall, steel exports (finished+semis) increased by just 2.5% to 8.54 MnT, due to the weak global demand environment, while steel imports jumped 37% y-o-y to 9.65 MnT. Imports from China increased 93% y-o-y to ~2.7 MnT while that from ASEAN countries and Japan jumped by 75% y-o-y and 52% y-o-y to ~1.7 MnT and ~1.3 MnT, respectively. The rising level of imports poses a significant risk to domestic steel prices and margins. Meanwhile, Europe emerged as the single largest destination for Indian steel exports, accounting for 55% ( ~4.7 MnT) of the total.

The global steel industry has witnessed a sharp increase of surplus capacity, rising by almost 4x from 180 MTPA in 2000 to as high as 610 MTPA in 2023, which implies the surplus equivalent to global demand growing from 21% in 2000 to 33% in 2023. The combined surplus of China, Japan and Korea grew over 6x, from 80 MTPA in 2000 to 425 MTPA in 2023, accounting for two-thirds of the global surplus capacity. Further, the shift from globalisation to localisation poses significant threat to free and fair trade for India, as well as additional threat of trade diversion from conventional net exporting countries with a declining export space. India, which has been outperforming globally with robust economic and steel demand prospects, needs to have trade measures to arrest surging imports of both steel and steel-intensive manufactured goods, which otherwise could derail the country’s robust steel demand.
Infrastructure and construction
India has been building physical infrastructure over the past decade at a scale and pace never seen before. From roads and highways to airports, dedicated freight corridors to ports and airports, high speed railway to metro networks, this thrust on infrastructure is driving growth in the construction sector, leading to demand for steel. The NHAI pipeline for the next three years remains strong and InvITs are gaining traction with continued interest from foreign players. Further, India’s focus on normalising logistics cost from 14% of GDP to 8-9% in the next few years under the PM Gati Shakti initiative is also likely to boost steel demand.
Further, with focus on urbanisation, India is building megacities and smart cities with robust digital infrastructure, which is leading to an uptick in domestic steel demand. Urban residential real estate cycle continues to be strong with robust, new launches and high affordability, despite higher interest rates. The renewables sector is also witnessing large investments driven by increasing power consumption and the need for green energy transition. The NIP, PLI scheme and defence indigenisation are driving private capex.
Manufacturing
The India government launched the ‘Make in India’ initiative in 2014 to maximise domestic value-addition and put the country on a manufacturing-led growth path, strengthen self-reliance and boost employment opportunities. The initiative envisages an increase in the share of manufacturing from 17% to 25%, employing over 100 million. The steel sector, although not included in the initiative, has a pivotal role in its success, as steel is consumed extensively for manufacturing. Moreover, the drive to increase the share of MSMEs to GDP from 30% to 50% is likely to equally support manufacturing growth, and thus steel demand.
Automotive
In FY 2023-24, the Indian auto sector witnessed healthy demand for passenger vehicles (PV) and commercial vehicles (CV) as chip availability corrected. The outlook for two-wheelers and tractors is improving. Further, the rural economy is expected to recover on better winter crop, elevated reservoir levels and moderating inflation. With large demand incentives for electric vehicles (EV) from both central and state Governments, there is going to be a major shift towards EVs. Infrastructure boost and capex investments by the government augurs well for the HCV and tractor segments going forward. The auto sector also benefits from the PLI boost.
The European Commission has proposed the world’s first ‘carbon border tax’ under the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) on imports of carbon-intensive goods, including cement, iron and steel, aluminium, fertilisers, electricity, and hydrogen. On October 1, 2023, the CBAM entered into application in its transitional phase, where CO2 embedded emissions of products exported to EU are to be reported. CBAM will apply in its definitive regime from 2026, while the current transitional phase lasts between 2023 and 2025. CBAM levies a tax based on the quantum of emissions recorded during the production of such products that enters into the region. India’s steelmaking accounts for ~12% of the country’s total carbon emissions. Indian steel counts Italy, Belgium, Spain and the UK among its top 10 export destinations. While the impact on exports in the long term is still being evaluated, the country has embarked on a journey to transition to green steel. Aligned with India’s commitment to achieving Net Zero by 2070, the steel ministry has laid down a short, medium and longterm transition roadmap that includes the increased adoption of renewable energy and promotion of resource efficiency (until 2030), green hydrogen and carbon capture, utilisation and storage (2023-47) and disruptive technological innovations (2047-70).
India remains a bright spot in the global steel industry and the steel demand in the country is expected to show a healthy growth, driven by strong economic growth of 7.2% projected for FY 2024-25, a record H11.11 lakh capital expenditure for FY 2024-25, buoyant demand from major steel consuming sectors like infrastructure and construction, automotive, capital goods as well as consumer durables. Further, the positive investment climate, on the back of strong corporate profitability as well as robust bank balance sheets, bodes well for private investment cycle to kick off. In addition, the Government’s plan to build additional two crore house under the PM Awas Yojana bodes well for the public housing sector outlook. Further, low inflation expectations for FY 2024-25 at 4.5% versus the FY 2023-24 average of 5.4%, could prompt the country’s central bank to pivot to policy easing, which could further boost demand. With the central government staying on course to its fiscal consolidation path, with fiscal deficit estimated at 5.1% for FY 2024-25 versus 5.6% in FY 2023-24, it provides further headroom for the Government to spend on physical and social infrastructure.
According to the NITI Aayog, India has the potential to become the world’s production centre for green steel and pave the way for its worldwide adoption. The Indian steel industry is leveraging the power of Machine Learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), and smart manufacturing to improve efficiency and strengthen sustainability.
FY 2023-24 Highlights
Highest ever consolidated sales
Growth in supplies to renewable sector
Growth in consolidated sales
Growth in sales to appliance segment
Growth in coated steel sales
Share of Value Added & Specials Longs (Excl. TMT)
Growth in VASP sales as new downstream capacities became operational
Increase in sales of Electrical Steel
Record share of VASP sales in total sales
Share of retail segment in domestic sales
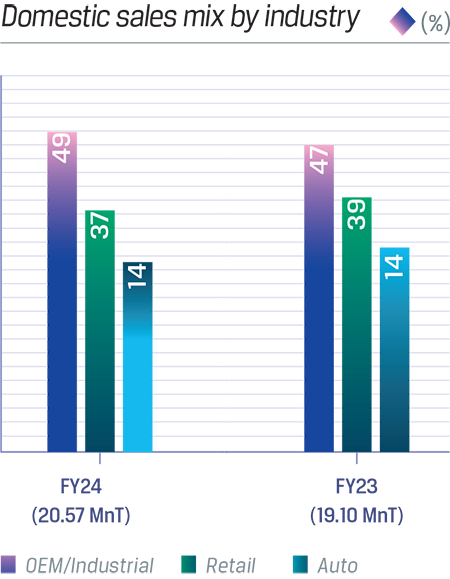
Increase in supplies to Industrial segment
Growth in Branded sales volume
Increase in Specials sales
Share of business in Indian steel market
Increase in Flat steel supplies to automotive segment, while auto industry production grew 9%
JSW India sales as against domestic consumption of 136 MnT

JSW Steel is committed to superior performance, leveraging its cuttingedge, fully integrated manufacturing facilities and a diverse product portfolio that provides high-value additions. Strategically positioned, the Company is well-equipped to capitalise on both existing and emerging opportunities, addressing a broad spectrum of customer needs as both India and the global community emphasise sustainability. With a strong focus on innovation, digitalisation, and sustainability, JSW Steel continues to deliver robust results across various performance indicators. For FY 2023-24, the Company achieved 101% of its production guidance, with average India capacity utilisation at 92%, and 100% of its sales guidance.
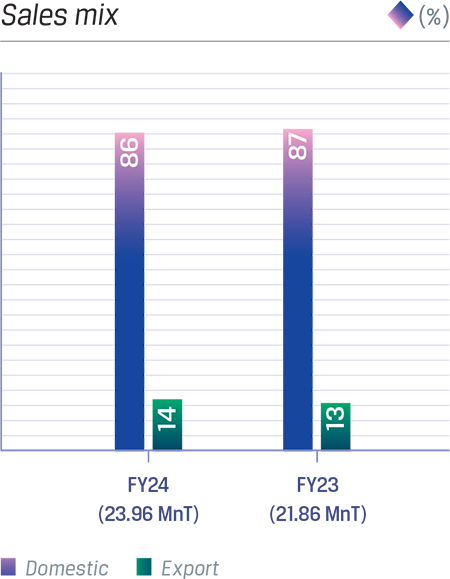
In FY 2023-24, JSW Steel outperformed the general market in steel exports, registering a 23% increase compared to 12% growth seen across India. This achievement drove JSW Steel's share of total national steel exports to 45%. Moreover, the Company's export component within its total sales mix rose to 14%, up from 13% the previous year. Notably, exports of CRM products surged by 36%, while coated products saw a remarkable 52% increase, highlighting JSW Steel's focus on higher-value export segments.
Share of domestic sales is 86% in the total sales mix. Volumes grew by 8%.
JSW Steel is actively supplying high-strength TMT Bars, HR Plates, and LRPC for the MumbaiAhmedabad High-Speed Rail (MAHSR) project. The MAHSR route, spanning over 500 km, is currently under construction. Looking ahead, we are anticipating the upcoming Varanasi-Delhi bullet train project, which will cover an estimated distance of 865 km. A detailed project report for this venture has already been submitted. Committed to providing top-tier steel, JSW Steel remains dedicated to supporting India’s ambitious infrastructure projects.

Hyundai Motors awarded JSW Steel the 'Excellence in Customer Delight' award at their Annual Vendor Meet FY 2023-24.
Maruti Suzuki India Ltd. (MSIL) felicitated JSW Steel with the 'Special Support Award' at the Maruti Supplier Conference 2024.
Suzuki Motorcycles India Pvt. Ltd. awarded the JSW BPSL plant the 'Best Supplier Award' for CPS Implementation at their Annual Supplier Conference 2024.

Schaeffler India recognised JSW Steel's Longs unit (Salem) in the 'Value' category on Supplier Day 2024.

Toyota Boshoku presented JSW Steel with an 'Appreciation for Support' Award for initiating localisation of AHSS Steel.
In the wind power and solar power industries, JSW Steel has emerged as a prominent and favoured supplier. Key components of windmills such as towers, generators, nacelles, gearboxes, blades, and rotor hubs are all manufactured using steel. The wind power industry added 3.25 GW capacity in FY 2023- 24, with JSW HR plates being utilised in 65% of the towers, supporting the installation of 2.07 GW capacity. Our Anjar plate mill produces specialised HR plates for these tubular towers, vital for their structure. In the solar power sector, the industry saw a 15 GW increase in capacity, where our key products like Galvalume (brand Galvos) and Magsure experienced a 93% growth in sales, contributing to the solar infrastructure. JSW Steel's innovative materials continue to support and enhance the sustainable energy infrastructure in India.
JSW Steel collaborates closely with automotive manufacturers to enhance safety, reduce weight, and improve fuel efficiency in vehicles. JSW's Advanced High-Strength Steel (AHSS), known for its exceptional tensile strength and malleability, empowers OEMs to attain superior safety ratings. Key safety components, including those crucial for crash protection, are crafted from AHSS. Additionally, the Company has engineered steel specifically for suspension parts, ensuring high strength and optimal fatigue resistance. In FY 2023-24, JSW Steel has secured several key grade approvals in the automotive sector. Notable achievements include supplying hot rolled steel for Dolvi-Kalyani Maxion Wheels and Urja Metallics, and providing specialised coated steel for Hyundai and Kia Motors.
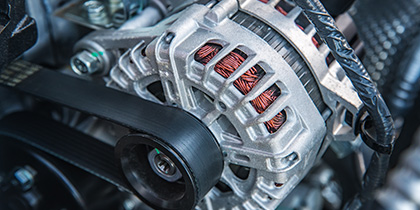
JSW Steel has placed a strategic emphasis on enhancing its share of VASP in the overall sales mix and has made significant investments in driving product innovation. The Company achieved its highest ever VASP sales volume, up 19% y-o-y, and increased its share of VASP sales in the overall mix to 61% during FY 2023-24, as compared to 56% in FY 2022-23
Product mix change

Flats, comprising Hot Rolled, Cold Rolled, Colour Coated, Galvanised, Galvalume and Avante Steel doors contributed 75% to the top line in FY 2023-24, an 11% growth over the previous year.

JSW Steel is renowned for the top-notch quality and reliability of its hot-rolled products. Employing advanced machinery and manufacturing techniques, Hot Roll coils are produced at Hot Strip Mills located in Vijayanagar, BPSL, and Dolvi. These hot-rolled offerings find applications across various sectors such as structural and general engineering, tubing, piping, and LPG cylinder manufacturing. They serve as vital components in industries spanning Industrial & Engineering, Automotive, Energy, and Capital Goods. In FY 2023-24, hot-rolled products constituted 38% of the Company's overall product portfolio.
![]() WATER PIPELINE:
WATER PIPELINE:
Contributed to ~2,428 km water pipeline constructions
![]() OIL & GAS:
OIL & GAS:
Contributed to ~1,531 km
pipeline constructions


The Vijayanagar plant boasts India's widest cold rolling mill, specialising in the manufacturing of CR closed annealed sheets and coils. These products are widely utilised in automotive, consumer durables, industrial & engineering, and electrical panel industries. Cold Rolled products made up 16% of the total product mix in FY 2023-24.


The cold rolled close annealed (CRCA) segment constitutes a significant portion of the total flat product sales. In FY 2023- 24, heightened demand from the PV segment drove CRCA category sales to their highest levels ever. JSW Steel has seized an early advantage by partnering with leading automobile manufacturers to pioneer innovative steel grades. Among these advancements are HSLA and AHSS, specialised steel grades engineered for enhanced impact resistance and lightweight construction. These novel grades empower auto OEMs to meet consumer preferences for eco-friendly vehicles by incorporating lightweight steel, thereby improving fuel efficiency and contributing to carbon neutrality goals.


Our range of Electrical Steel products remains instrumental in enhancing the energy efficiency of various electrical equipment, including motors, pumps, fans, domestic appliances, white goods, power generators, and small transformers. Customised CRNO grades have been developed to meet the specific needs of rapidly expanding sectors such as Two Wheeler EV and Air Conditioner Compressors. Moreover, we have upheld our status as a preferred supplier in the Wind Energy and Railway Traction Motor segments by consistently providing energy-efficient electrical steel solutions.


Coated steel is an anti-corrosive, value-added material, with galvanised steel accounting for more than half of the demand. Galvalume and colour-coated steel are rapidly growing segments, with applications across multiple industries. There is significant potential for growth as India’s per capita consumption of coated steel stands at approximately 7 kg, compared to 50-60 kg in the US and Europe. Rural consumption is expected to be a key growth driver. Demand for coated steel is projected to grow at a CAGR of about 10% to surpass 11 MTPA by FY 2024-25, which is approximately 1.5 times faster than that of overall steel (about 7%) and domestic GDP growth (7-7.5%).
JSW Coated Steel currently supplies multiple brands with GI (Vishwas), GL (Silveron), and colour-coated products (Everglow, Colouron+, Pragati+), as well as OEM products (Radiance).

JSW’s colour-coated steel is corrosion-resistant and used in manufacturing valueadded products that address construction, warehousing, and roofing requirements. JSW colour-coated products hold a strong position in the current market landscape, securing a leading market share of 44%, with overall domestic sales reaching 1.37 MnT. JSWSCPL is the only company to offer brands across multiple price ladder segments, including Everglow in the super-premium, Colouron in the premium, Pragati in the popular, and the recently launched Indradhanush in the mass market segment. The market for colour-coated products has increased by 12% y-o-y based on JSW’s production and products. JSW Steel has partnered with JSW Paints to launch new coating variants, including Anti-Dust, Hi-Gloss, and Cool Roof. The Cool Roof paint system is a sustainable product that offers better heat reflectivity to reduce the temperature inside buildings and alleviate the heat load on AC systems. The AntiDust variant has been designed for public infrastructure projects to maintain a long-lasting and attractive appearance in challenging environments. The Company is dedicated to maintaining its strong position in the appliance business by providing a range of new colours and coating combinations to its customers. Furthermore, it continues to supply colour-coated products for several prestigious national and international projects.
JSW Steel is expanding its product portfolio in line with the expansion plans of its clients through the Early Vendor Involvement process. It is collaborating with multinational customers to supply materials to their global operations while also developing grades that support the 'Make in India' initiative, boost domestic demand, and aid import substitution. The Company is working closely with its customers to source high-quality materials for their diverse end-use applications and has undertaken specific localisation projects to assist them.
JSW Steel has qualified for the PLI scheme for specialty steel. The Company has been approved for six categories. This includes six projects which are already underway at a committed cost of `5,350 crore.


Galvanised and Galvalume products make up 13% of the total product mix. JSW Steel is the country's largest producer of Galvalume products that are preferred for roofing and cladding end uses due to their superior corrosion resistance and heat reflectivity as well as longer lifespan with the same coating weight. As demand for the solar segment continues to surge, new grades are being developed to meet emerging needs and broaden the sector's customer base.
The JSW Galvos brand is designed to address the typical challenges that solar panel installations face, such as harsh outdoor conditions and being embedded in the ground. Galvos is specially equipped to withstand challenging alkaline and corrosive environments, in conjunction with an epoxy/PU layer, and has been performing well in this segment. Last year, to address the needs of solar trackers, HSLA grades were developed for making torque tubes for Indian and export markets, a first in the industry. These HSLA grades have been approved by major global solar players for use in their installations in India and abroad. JSW Steel is collaborating with global developers to offer these solutions worldwide.
GI & GL products constituted 41% market share of domestic market and JSW increased domestic sales by 12% y-o-y. The alloy-coated galvanised and galvalume products are versatile and characterised by high corrosion resistance and heat reflectivity.

This is a galvanised steel made with a Zinc, Magnesium, and Aluminium alloy, providing five times the corrosion resistance of traditional galvanised iron under extreme weather conditions. Manufactured at JSW's Vijayanagar and Vasind Coated plants, Magsure is utilised in a variety of sectors, including solar structures, cooling towers, and water storage, among others. Key attributes of JSW Magsure include superior corrosion resistance, enhanced workability, high chemical resistance, and environmental friendliness, making it an ideal choice for demanding applications.

Tinplate is a highly sustainable packaging material with endless potential, as it can be recycled indefinitely, making it more environmentally friendly than many other competing materials. It is also one of the most valuable downstream products in the flat steel segment. Global demand for tinplate is expected to rise as the world looks for sustainable packaging materials. Domestic demand has been steadily improving due to increasing urbanisation, changes in food habits favouring packaged food, and a growing variety of food retail options. JSW’s growth in Tinplate as a premium product is 29% year-on-year and is largely replacing imports, with its present market share in the domestic market at 39%.
Tinplate, being a packaging medium, is one of the highest value-adding downstream products in the flat steel segment. JSW envisages this category growing steadily and has expanded capacities to capture more variants within the prime grades for BIS certified tinplate. Currently, 30-35% of India’s total tinplate demand is met from imports.
Long products serve as essential components for major infrastructure endeavours, playing vital roles in road construction, metro and rail infrastructure development, bridge construction, and the establishment of power and nuclear plants. JSW Steel achieved sales of 4.9 MnT of long products in FY 2023-24, marking a 5% year-on-year growth.

TMT (OEM)
Crafted from virgin iron ore for unparalleled purity, JSW Steel’s TMT bars boast exceptional strength and flexibility. Utilising state-of-the-art technology - renowned for producing top-tier HYQST (High Yield Quenched and Self Tempered) bars via the METCS (Morgan Enhanced Temperature Control System) process - ensures superior quality. Its attributes, such as weldability, corrosion resistance, and malleability, render it the preferred choice for consumers.
The emerging demand for TMT in India stems from the Government's focus on infrastructure development initiatives. Long products are indispensable raw materials for a multitude of large-scale projects encompassing road construction, metro and rail infrastructure expansion, bridge building, and power generation, including nuclear plants.
JSW Steel is actively supplying its TMT long products to over 500 ongoing projects spanning various sectors. Among these, road projects constitute more than 20%, and metro rail initiatives approximately 10%, with the remainder distributed across a spectrum of several other projects.
Key infrastructure projects underway

Wire Rods
Produced with cutting-edge technology to ensure superior quality, wire rods are engineered to fulfil diverse application needs. Fabricated at facilities in Vijayanagar, Salem and BPSL, wire rods constitute 5% of the Company's product spectrum. They serve various industries, including automotive, general engineering, spring applications, welding, machining, and bearings.
The surge in demand for wire rods parallels the growth of India's automotive and industrial manufacturing sectors.

Low Relaxation Prestressed Concrete Steel Strands
JSW Steel has introduced a groundbreaking product for the construction industry, the 'LRPC' - Low Relaxation Prestressed Concrete Steel Strands, from its Vijayanagar - Neotrex plant with a capacity of 144 Kt per annum. LRPC structures reduce project costs through decreased concrete and labour time, enabling longer spans, sleeker structures, increased safety, and more usable space. This product has quickly gained traction, achieving 40% of plant capacity utilisation in its first year, 28% market share by Q4 FY 2024, and securing involvement in major projects like the Mumbai-Ahmedabad Bullet Train and NHAI road projects across India.

Alloy Steel
JSW Special Alloy Steel is manufactured at Salem Works, which stands as India's largest primary integrated special alloy steel plant. Sales of alloy longs surged by 11% in FY 2023-24, constituting 4% of the product mix. Further, new grades have been formulated to cater to diverse applications spanning automotive, textile machinery, general engineering, and more.
Throughout the year, the Salem plant secured nine product approvals across various sectors, including automotive, oil & gas, bearings, mining, wind energy, and general engineering. Salem's strategic location offers a competitive edge, benefiting from lower transportation expenses and expedited deliveries facilitated by its well-connected network of highways and stockyards across India.
Furthermore, Boron Wire Rod grades have been successfully developed and commercialised at the Vijayanagar plant, thereby enriching the product portfolio. With the Government's PLI scheme is geared toward promoting domestic production of specialty steel items, JSW anticipates heightened product development and accelerated prototyping in this segment, as applications are currently being accepted.
JSW Shoppe is a unique franchise model that serves as a cornerstone of our retail strategy, functioning as an exclusive outlet model that provides customers direct access to the Company's comprehensive range of products. This enhances customer experience by ensuring product availability, quality assurance, and brand consistency across all touchpoints.
JSW Steel has effectively utilised branding initiatives to embed a strong brand recall among its target audiences. By employing branding strategies that align with community values and customer needs, it has established a significant and positive presence in the minds of consumers. For instance, regional campaigns during local festivals have reinforced brand recognition and affinity, connecting culturally and emotionally with customers.

During FY 2023-24, JSW Steel launched several high-impact advertising campaigns. Notable among them were the #RoofToDream campaign and the targeted regional campaigns during Pongal and Onam that achieved commendable reach and impressions across digital platforms. These campaigns were carefully designed to resonate with specific demographics, leveraging cultural nuances to enhance engagement and brand connection.
JSW Steel’s integrated media strategy involves a mix of traditional and digital channels to maximise reach and engagement. It includes television, print, outdoor, and online platforms, ensuring comprehensive coverage that spans diverse consumer segments. This sophisticated media mix has allowed the Company to maintain a consistent brand message, increase customer touchpoints, and drive more effective market penetration.

Solar module mounting structure (Magsure–Coated)
Designed for the renewable energy sector, offering enhanced durability and resistance for long-term solar installations.

Long Members for CVs
Hot-rolled steel for structural components in commercial vehicles, ensuring optimum strength & weldability

Oil & gas valves
(Long & Special Alloy)
Alloy steel for manufacturing valves in the oil and gas industry, ensuring superior strength and corrosion resistance.
JSW Steel introduced 'The JSW Experience Centre', a digitally advanced facility designed to showcase its array of products and services. This state-of-the-art centre features the JSW Legacy Wall, which illustrates the Company's evolution and influence in the steel industry. The Product Wall offers an interactive display of JSW Steel's diverse products, while the Digital Portal includes kiosks for exploring products and downloading brochures via QR codes. The centre embodies JSW’s core values—Courage, Agility, Collaboration, Compassion, and Commitment—enhancing brand engagement and facilitating informed purchasing decisions.

Reinforcement and crash parts for PVs
Cold-rolled steel for automotive structural and crash parts, providing excellent combination of strength and formability.

Ammunition shell casing for artillery guns
Special alloy steel for ammunition shell casings, meeting stringent defence specifications with high resistance to impact and stress.

Railway wagon
Hot-rolled steel for railway wagons, providing necessary strength and durability for demanding railway transportation conditions.

JSW Steel engages customers by highlighting the distinct advantages of its products through targeted marketing campaigns and interactive retail experiences.

Highlighted during local festivals with campaigns that connected product features with regional cultural traits.
Promoted through the Roof to Dream initiative, showcasing its utility in school roofing projects across India.

Featured in campaigns highlighting its customised solutions, with a focus on the fast construction benefits it offers, particularly targeting urban markets like Mumbai, Pune, and Bengaluru.

Displayed at industry expos and supported by a unique marketing collateral, which helped position the product among builders, architects, and interior designers.

JSW Steel strives to establish a powerful connection with its retail network and influencers, prioritising an exceptional purchasing experience for its consumers. With over 17,500 exclusive and non-exclusive retail outlets, 469 distributors and 2,059 branded stores, and a widespread presence across more than 530 districts in India, the Company's retailing and distribution network is one of the largest in the country. It also has a partner programme, JSW Privilege Club, which has 90,000+ members. This extensive network enables JSW Steel to cater to its customers' varied demands and provide them with a seamless procurement process.
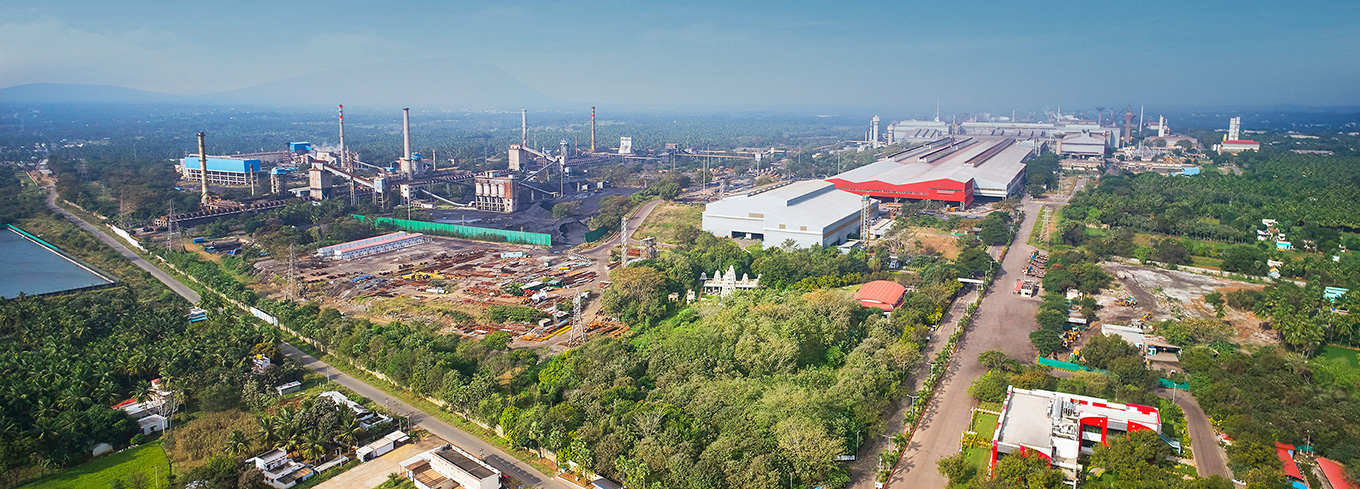

JSW Vijayanagar Works, situated in Karnataka, is India’s largest single-location integrated steel-producing facility with a 12.5 MTPA capacity. What started as a small plant 25 years back is today an epitome of state-of-the-art technology and operational excellence in steelmaking and exemplifies JSW Steel's commitment to innovation and sustainability.
FY 2023-24 highlights
Digitalisation projects completed
Safety digital initiatives optimised with Man-Machine Interface (MMI)
Iron ore consumption from captive Karnataka mines
Reduction in water consumption achieved by reutilisation of wastewater
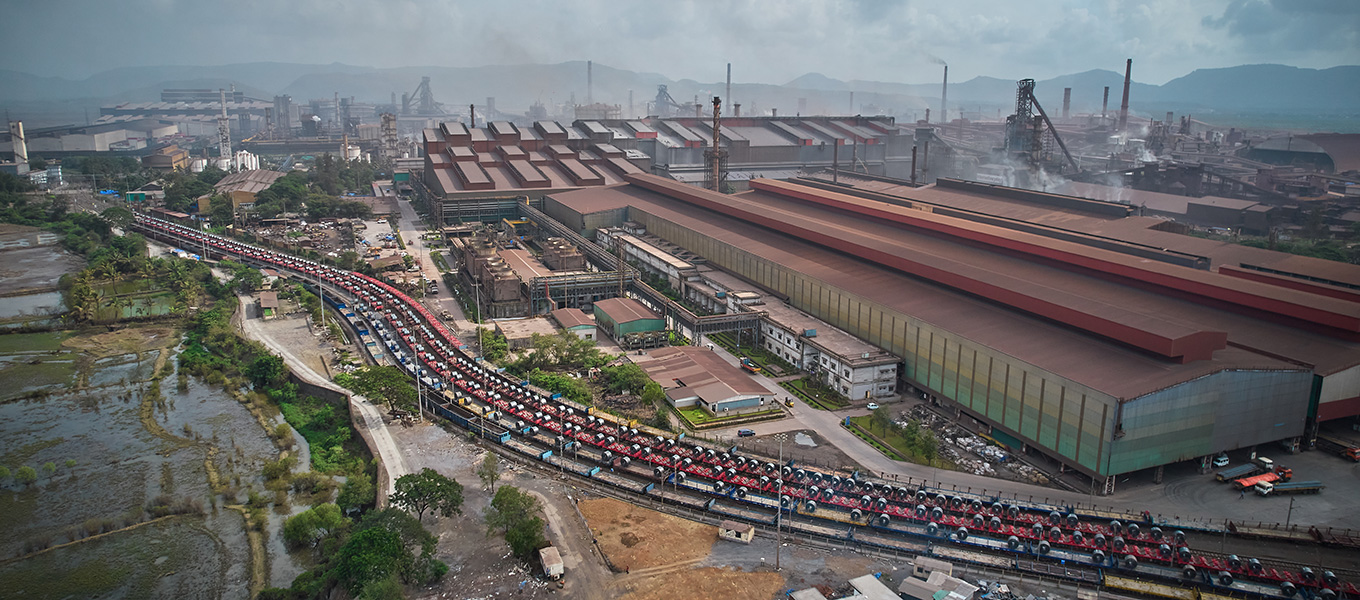


JSW Dolvi Works is a 10 MTPA integrated steel plant located on the west coast of India. Acquired by JSW Steel in 2010, the plant's capacity was increased from 3.3 MTPA to 10 MTPA currently through brownfield expansions. Dolvi Works primarily focuses on flat steel production, with an 8.5 MTPA capacity for flat products and the rest 1.5 MTPA for long products. It is the first plant in India to use the Conarc technology for steelmaking and compact strip production, as well as implement a dry Gas Cleaning Plant (GCP) and Energy Recovery System (ERS) in SMS.
FY 2023-24 highlights
Reduction in specific freshwater consumption
Implementation of cutting-edge digital solutions including Advanced Process Control (APC), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT) and digital twins, positioning JSW Dolvi as a leader in digital maturity
Received multiple national and international safety awards, including recognition from the British Safety Council and FICCI for excellence in safety systems
Utilisation of steel slag for road construction - recycling and sustainable use of byproducts



JSW Steel's Salem Works is India's largest specialty steel plant, with a production capacity of 1 MTPA. It is one of the country's largest plants for special alloy steel long products, catering to diverse industries with its advanced production capabilities.
FY 2023-24 highlights
Zero Lost Time injury (LTI).
Collaborated with BITS Pilani on upskilling employees on SMART Manufacturing concepts with a tailor-made mentorship programme.
Highest-ever captive power generation.
Lowest cobble in BRM, a benchmark for Indian high-speed mills.
Implemented a Centralised Digital Emergency Management system to improve emergency handling process.
Installed mobile type dedusting in Coke Oven Pusher Car to control the visible emission and fugitive emission.
Launched digitalised skill assessment platform for contractual workforce in September 2023.
LEAP (Learn, Engage, Accelerate and Progress) programme for Diploma Apprentice Trainees conducted.




JSW Steel Raigarh Works is an integrated steel production facility, with a crude steel capacity of 0.95 MTPA. It is known for its excellence in manufacturing special alloy steel long and flat products
FY 2023-24 highlights
Achieved 5 million+ safe man hours
Highest ever monthly production achieved in March 2024 for Blast Furnace, DRI and SMS Units
71 Surveillance cameras installed throughout plant premises for safety enhancement
Installation of 75 numbers of Vertical Life Line on Monkey Ladders
Blast furnace top equipment (Bank of valves and BLT gear box) replaced for the first time, enhancing furnace performance and reliability
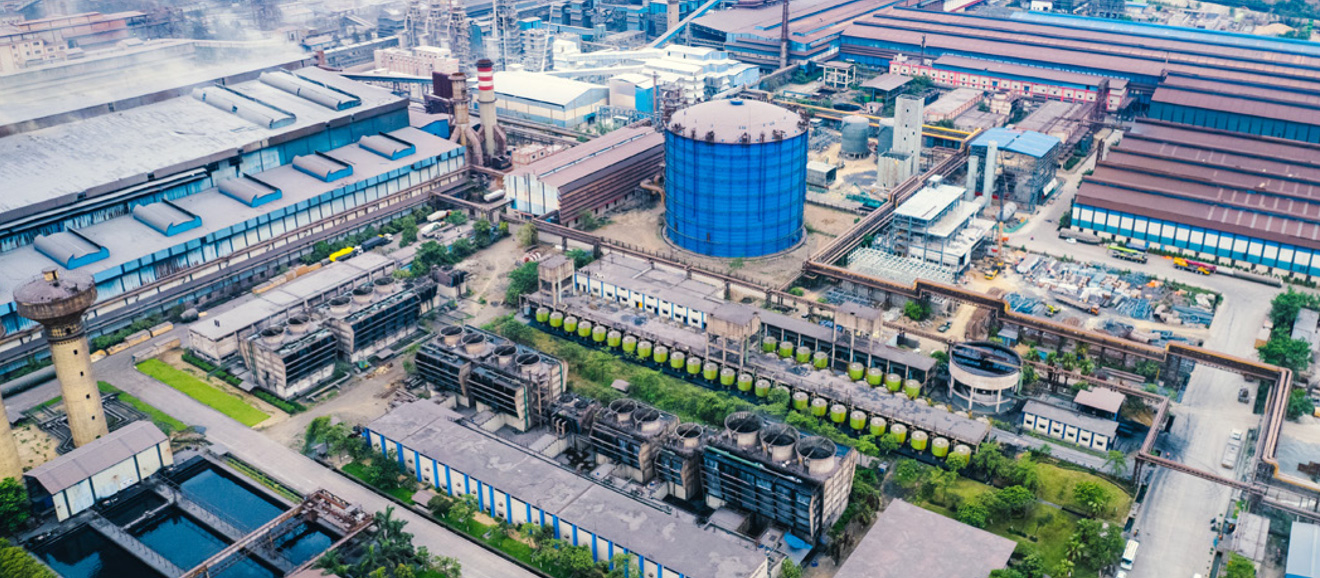



BPSL, acquired by JSW Steel through the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (IBC) in March 2021 located at Sambalpur, Odisha, is an integrated steel producer with 3.5 MTPA capacity at present, which is being expanded to 5 MTPA. It also has downstream capacity of 1.8 MTPA at Sambalpur, Kolkata and Chandigarh. BPSL is one of the largest alloy steel producers in India with a 1.2 MTPA capacity.

Projects in progress:
1.1 Water:
1.2 Air:
1.3 Waste:
1.4 CO2 Emission/Energy conservation
1.5 Measurement and Monitoring:



JSWSCPL is India’s largest manufacturer and exporter of Coated Steel products with a total capacity of 5.3 MTPA and colour coated capacity of 2.4 MTPA. It has pan-India presence with 8 plants including one coming up at Jammu & Kashmir. The products manufactured include Galvanised, Galvalume, CRCA, Colour Coated Products and Tin Mill products.
JSWSCPL has been a leader in product innovation, launching 7 brands across premium and other segments to cater to different customer segments. Branded sales constituted around 30% of total sales. JSWSCPL aspires to be the leading global downstream consumer-centric steel brand. It is the largest player with over 30% domestic market share.
FY 2023-24 highlights
Digitalisation projects completed
Provided safety cameras for fork lift reversing safety with red light flash on three sides. Seat belt lock and biometry for fork lift operator safety and to avoid misuse of fork lift by others
Face Recognition System (FRS) provided for all the associates, attendance recording and discipline


The global economy performed well despite the headwinds of elevated interest rates and adverse geopolitical events. The economic activity was resilient due to growth in employment and incomes held steady supporting demand, including greater Government spending and household consumption. According to the IMF, global GDP growth for 2023 is estimated at 3.2%. Inflationary pressure is easing across major economies albeit with some speedbumps. This is likely to allow central banks to commence rate cuts in 2024, although the extent of cuts has been diluted compared to earlier forecasts.
Geopolitical risks have risen, and need to be watched, especially for their impact on global trade and energy prices. India’s economic growth momentum continues, driven by the industrial sector and robust capital formation. Steel demand grew 13.6% in FY 2023-24. Strong government spends on infrastructure and an anticipated private capex recovery are contributing to the momentum. An expected rural recovery, aided by above-normal monsoons during 2024, provides further tailwinds to economic growth. India’s overall macroeconomic profile remained strong during the year, buoyed by healthy forex reserves and positive capital inflows, despite escalating geopolitical risks.
FY 2023-24 highlights
Crude steel production
 7% y-o-y
7% y-o-y
Sales volume
 8% y-o-y
8% y-o-y
Domestic sales
 6% y-o-y
6% y-o-y
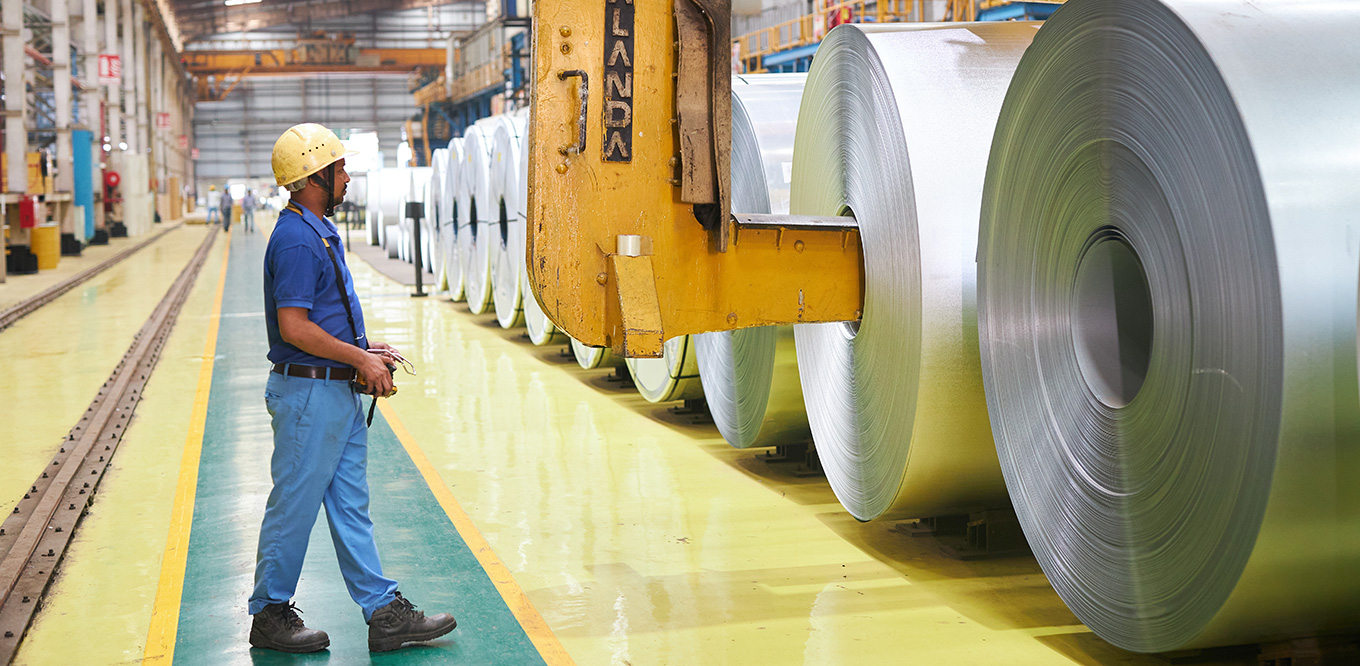

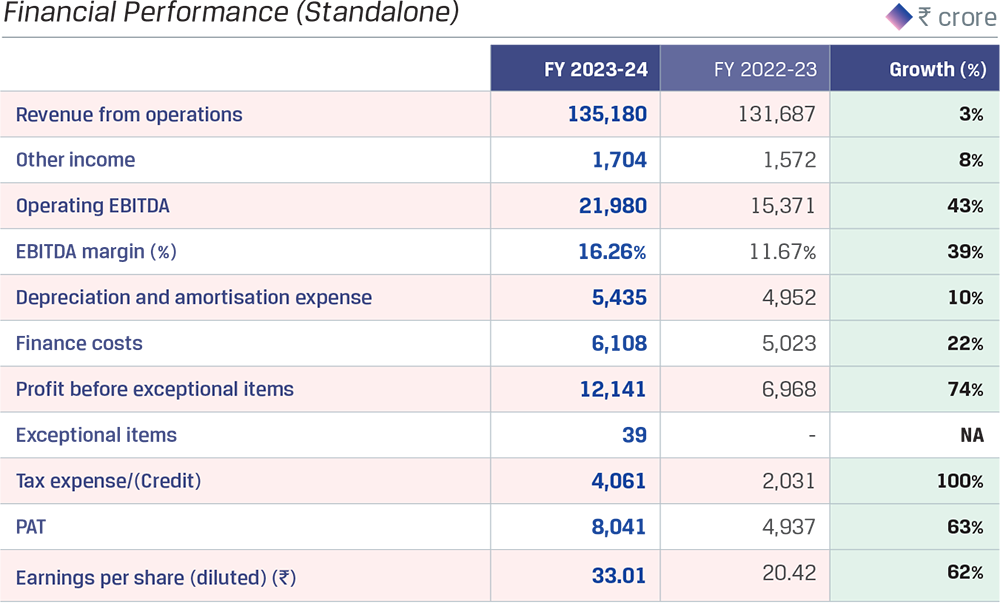
In FY 2023-24, JSW Steel reported its highest ever crude steel production at 22.26 MnT*, with an average capacity utilisation level of 92%, vs. 91% in FY 2022-23.Crude steel production increased by 7% y-o-y primarily due to the ramp-up of the Dolvi Phase II expansion of 5 MTPA, which was commissioned in FY 2021-22, and additional production volumes from Raigarh unit pursuant to merger of JSW Ispat Special Products Limited (JISPL) from July 31, 2023.
During FY 2023-24, JSW Steel reported its highest ever steel sales volume at 21.22 MnT, which grew by 8% y-o-y. The Company exported 2.25 MnT of steel, up 27% y-o-y and accounted for 11% of the total sales, as against 9% in FY 2022- 23. Domestic sales stood at 18.97 MnT, an increase of 6% y-o-y. The domestic steel demand grew by 14% y-o-y to 136.25 MnT primarily due to the Government’s thrust on infrastructure, housing construction, the increasing share of manufacturing in GDP, and increased demand from the auto sector. Sales of Value Added and Special Products (VASP) accounted for 61% of the total sales volume for the year. The Company’s branded products’ sales stood at 41% of the total retail sales, up from 39% in FY 2022-23.
*The merger of the Joint Venture, Creixent Special Steels Limited along with its subsidiary JSW Ispat Special Products Limited (JISPL) with the Company became effective on July 31, 2023. The production volumes have not been restated for the earlier periods.
Revenue from operations grew 3% y-o-y to `135,180 crore, primarily due to an increase in volumes, which grew by 8% partly offset by lower sales realisations, down 5% y-o-y on account of the decline in steel prices attributed to lower international steel prices and increased imports at predatory pricing. The Company registered better operating margins in the first three quarters of FY 2023-24 as against FY 2022-23 primarily due to a reduction in costs, mainly on account of cost of coal consumed and power and fuel costs. However, the Q4 margins were impacted by lower realisations and higher coking coal cost that peaked towards Q3 FY 2024. The realisation during FY 2023-24 remained fairly stable but lower compared to FY 2022-23.
Overall despatches from the Karnataka and Odisha captive mines to the plant locations constituted 41% of iron ore requirements of the Company in FY 2023-24, which was also 41% during FY 2022-23. The unprecedented increase in international coking coal prices and iron ore prices in the second half of the previous financial year and other raw material prices due to geopolitical issues had resulted in increase in total cost in FY 2022-23.
The Company achieved an annual Operating EBITDA of I21,980 crore, an increase of 43% y-o-y, with an EBITDA margin of 16.3%. EBITDA per tonne was at I10,357 during FY 2023-24, higher by 33% y-o-y primarily on account of lower coking coal prices, which were elevated in the previous year, lower power and fuel costs partially offset by decline in sales realisations and higher iron ore prices. The domestic iron ore prices were higher due to elevated international iron ore prices leading to increase in exports of iron ore /pellets, resulting in pressure on domestic supply.

FY 2023-24 highlights
Operating EBITDA
Net Profit
Revenue analysis (` in crore)
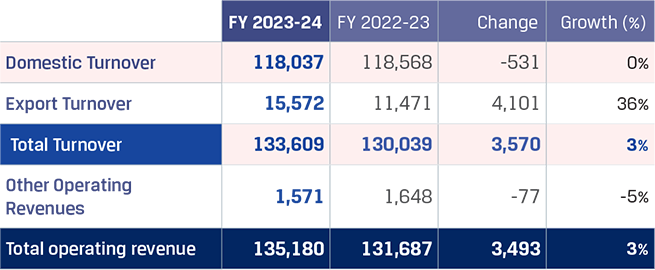
India was a net steel importer during FY 2023-24 with elevated imports (up 37% y-o-y), especially from China; this remains a challenge for the domestic steel industry. However, domestic steel demand remained healthy, driven by growth in overall consumption and the Government’s spend in the infrastructure sector.
Domestic turnover remained flat in FY 2023-24 as against FY 2022-23, though there was an increase in volume by 6% which was offset by 7% lower realisations. The domestic sales volume increase was primarily due to better domestic demand driven by the Government’s infrastructure spending. Export turnover increased 36% y-o-y to `15,572 crore from `11,471 crore in FY 2022-23, on account of a 27% increase in export volumes offset by lower export realisations which declined by 10%. The export volumes were lower in FY 2022-23 due to imposition of export duty on steel from May 2022 to November 2022.
Overall other operating revenue was `1,571 crore in FY 2023-24 as compared to `1,648 crore in FY 2022-23. Other operating income was lower by `77 crore, largely due to a lower export incentive income as the Company exported under the Advance Authorisation Scheme as against availing duty drawback income in the previous year and decrease in Government grant income due to lower realisations. However, this decrease in other operating income was partially offset by higher Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) grant income and job work income.
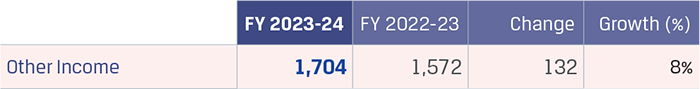
Other income was higher by `132 crore mainly due to the receipt of NCD redemption premium on investments made in Piombino Steel Limited, a subsidiary of the Company, increase in interest income was due to higher cash and bank balances, which was partly offset by a lower dividend income from group companies and lower interest income from loans extended to subsidiaries.
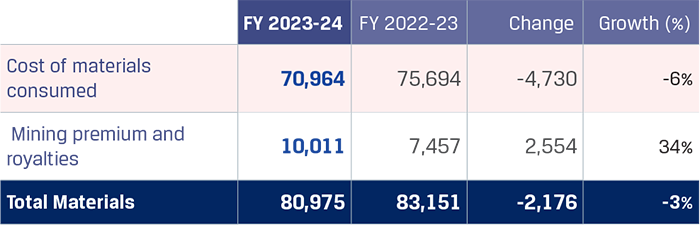
Expenditure on material consumption decreased 6% y-o-y to `70,964 crore primarily on account of a 22% decrease in coking coal prices in FY 2023-24, as the coking coal prices were higher due to supply chain disruptions and the Russia-Ukraine conflict in FY 2022-23. This decrease on raw material cost was partially offset by an increase in iron ore cost and increased consumption of raw materials due to increase in production volumes by 7%.
Mining premium and royalties cost increased by 34% in FY 2023- 24 to `10,011 crore from `7,457 crore in FY 2022-23, on account of increase in iron ore IBM prices consequent to elevated international iron ore prices leading to increase in exports of iron ore /pellets, resulting in pressure on domestic supply.

Employee benefits expenses were higher by `382 crore at `2,357 crore in FY 2023-24. The increase was primarily due to annual increments provided to employees, additional manpower cost from Raigarh unit pursuant to merger of JSW Ispat Special Products Limited (JISPL) from July 31, 2023, increase in overall headcount due to capacity additions and increase in managerial remuneration consequent to increase in profits. The overall headcount increased to 15,493 as on March 31, 2024 from 13,884 as on March 31, 2023.
Manufacturing and other expenses decreased 4% y-o-y to `29,868 crore primarily due to decrease in power & fuel costs by 16% partially offset by increase in other manufacturing costs on account of increase in production volumes by 7% and higher ocean freight and domestic freight cost due to increase in sales volumes by 8%.
The power and fuel cost decreased 16% y-o-y to `11,575 crore primarily on account of decline in steam coal prices, decline in natural gas prices and partial replacement of thermal power with renewable power available at lower costs. The steam coal prices and natural gas prices were higher in FY 2022-23 owing to energy crises following the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
Stores and spares consumption increased 6% y-o-y to `5,100 crore, primarily on account of overall increase in production by 7% y-o-y.
The ocean freight expenditure increased 29% y-o-y to `1,001 crore primarily on account of increase in exports of steel products by 27%. The domestic freight expenses increased by 23% y-o-y to `6,345 crore due to increase in domestic sales volume despatches by 6% and increase in iron ore despatches.
Hedging Cost/Net exchanges loss decreased by 81% y-o-y to `292 crore as the rupee depreciation against the US dollar was 1.4% during FY 2023-24 as against the rupee depreciation of 8.5% in the previous year.
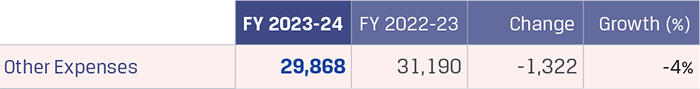

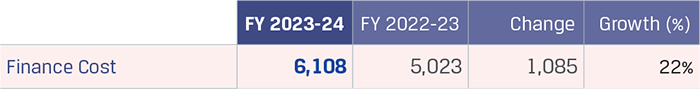
Finance cost increased 22% y-o-y to `6,108 crore primarily on account of higher borrowings and an increase in benchmark rates of domestic and foreign currency borrowings as central banks across the world increased interest rates to contain inflation. The increase in finance cost was also attributable to increase in borrowings pursuant to merger of JSW Ispat Special Products Limited (JISPL) from July 31, 2023 and increase in interest cost on acceptances as the SOFR rates increased during the year.
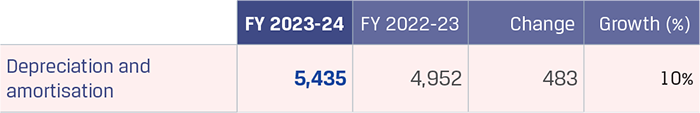
Depreciation and amortisation increased 10 % y-o-y to `5,435 crore primarily due to increase in depreciation cost on account of merger of JISPL, higher normal depreciation on account of capitalisation of Coke Oven 5 Battery B at Vijayanagar, balance facilities relating to Dolvi 10 MTPA expansion, mining equipment at Odisha, and other special and sustaining capital expenditure and higher accelerated depreciation on certain assets considering the revision in useful lives of assets.
Tax expense was `4,061 crore compared to `2,031 crore in FY 2022-23, primarily due to higher profitability and a non-cash tax charge of `1,031 crore pertaining to the previous years on account of tax regime change. During the year ended March 31, 2024, the Company had elected to exercise the option permitted under Section 115BAA of the Income Tax Act, 1961 to pay corporate income tax at 22% plus surcharge and cess (aggregating to tax rate of 25.17%) from the financial year 2022-23. Accordingly, the Company had re-measured its current tax and deferred tax charge for the year ended March 31, 2023 basis the new tax regime and recognised a non-cash tax charge of `1,031 crore pertaining to the previous year mainly representing write off of MAT credit not availed and change in tax rate on deferred tax assets of the Company. In view of this exercise of the option to transition to the new regime, the Company has recognised provision for current tax and deferred tax for the year ended March 31, 2024 at the tax rate of 25.17% with necessary tax adjustments. The effective tax rate was 25.04% for FY 2023-24.
Effective tax rate

Exceptional Items Includes
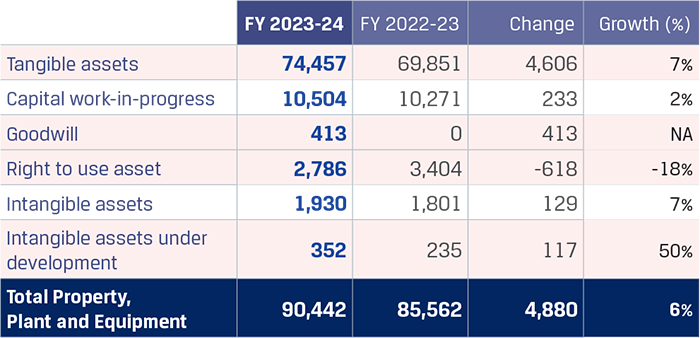
Net block of Property, Plant and Equipment increased by `4,606 crore primarily on account of acquisition of Raigarh assets amounting to `3,502 crore pursuant to the JISPL merger becoming effective on July 31, 2023, capitalisation of assets amounting to `6,094 crore relating to Battery B of coke oven 5 of capacity 0.75 MTPA at Vijayanagar, Dolvi Phase II raw material handling system, special projects and sustenance capex across all the plant locations partially offset by depreciation charge for the year.
The right to use asset decreased by `618 crore to `2,736 crore primarily on account of acquisition of the DRI plant, CDQ facilities and power plant under the Build Own Operate and Transfer agreement during the year.
Pursuant to the merger of JISPL with the Company, the purchase consideration paid has been allocated in accordance with the Ind AS 103 'Business Combinations' on the basis of fair value of the acquired assets and liabilities. Accordingly, the Company has recognised goodwill of `413 crore on account of this acquisition.
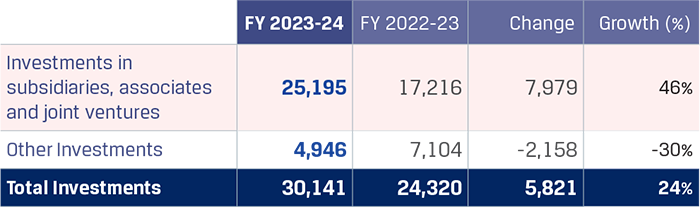
Investments in subsidiaries, associates and joint ventures increased to `25,195 crore primarily due to additional investment of `5,735 crore in equity investments in JSW Vijayanagar Metallics Limited for setting up the 5 MTPA steel project at Vijayanagar, acquisition of Mivaan Steel Limited pursuant to the merger of JISPL effective July 31, 2023, investments made in JSW Paints Private Limited and additional investment of `707 crore in JSW Utkal Steel Limited to set up a 30 MTPA slurry pipeline in Odisha and Pellet plant at Jatadhar Odisha. The decrease in the other investments to `4,946 crore is on account of redemption of Non-convertible Bonds issued by Piombino Steel Limited, a subsidiary of the Company, partially offset by increase in the fair value of equity stake of JSW Energy Limited due to increase in share prices.
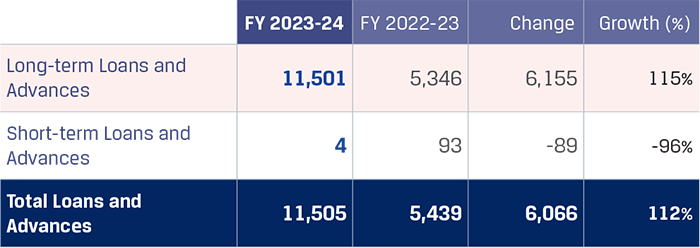
Loans and advances increased primarily due to loan extended to JSW Vijayanagar Metallics Limited amounting to `1,276 crore for setting up the 5 MTPA steel project at Vijayanagar, additional loan extended to Piombino Steel Limited, amounting to `3,144 crore for redeeming the Non-convertible Bonds issued by them and loans extended to overseas subsidiaries to cater to the interest and principal repayment obligations.
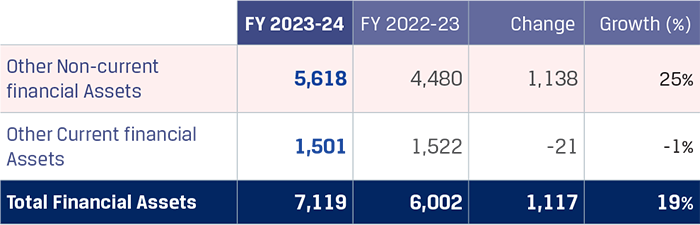
The other non-current financial assets increased to `5,618 crore on account of increase in the GST incentive receivable from the state of Maharashtra and Karnataka, and the increase in accrued interest income on loans extended to certain overseas subsidiaries.
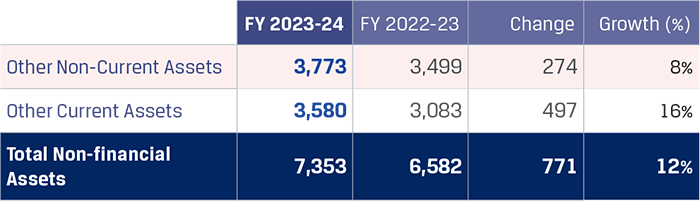
The other non-current assets increased by `274 crore to `3,773 crore primarily on account of accumulation of GST input tax credit and increase in prepaid amounts, which was partially offset by a decrease in the capital advances made to suppliers for capital projects on account of completion of supply of goods or services.
The other current assets increased by `497 crore to `3,580 crore on account of increase in GST input tax credit available for set off by reduction in advances to suppliers and reduction in security deposits.
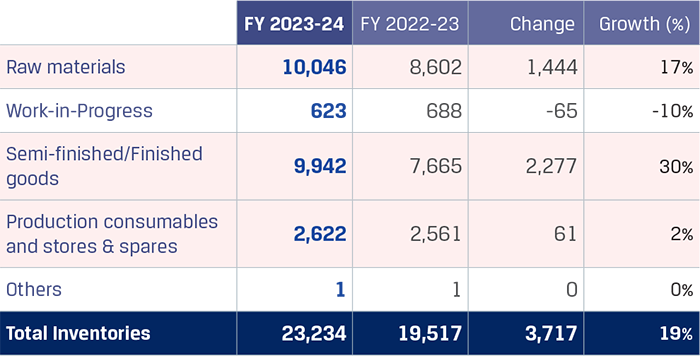
The increase in inventory was primarily due to an increase in iron ore fines and coking coal inventory by `1,444 crore as iron ore fines inventory increased by 7.21 lakh tonnes with iron ore prices increasing by 19% in FY 2023-24. The coal inventory also increased by 7.22 lakh tonnes and coal prices fell by 12% in FY 2022-23. Limestone and other raw materials cost witnessed a marginal increase.
Work-in-progress and semi-finished/finished goods increased by `2,277 crore primarily due to an increase in steel inventory by 4.69 lakh tonnes and captive mines’ iron ore inventory by 19.63 lakh tonnes.
Average raw materials inventory (including own mines’ iron ore) holding as on March 31, 2024 increased to 57 days from 48 days as on March 31, 2023 primarily due to the increase in both iron ore and coking coal inventory.
Average finished goods inventory holding increased to 31 days as on March 31, 2024 from 23 days as on March 31, 2023 primarily due to the increase in finished goods inventory on account of higher volumes and inventory increase during Q3 FY 2024 due to increased imports.
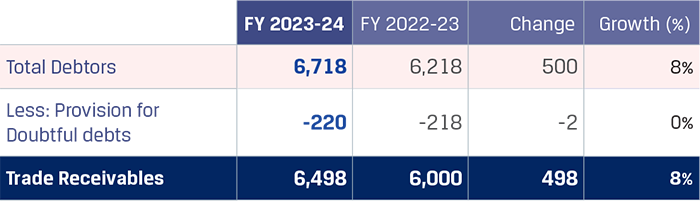
Trade receivables increased by `498 crore to `6,498 crore due to higher sales volumes during the year. However, the average collection period as on March 31, 2024, was maintained at 17 days.
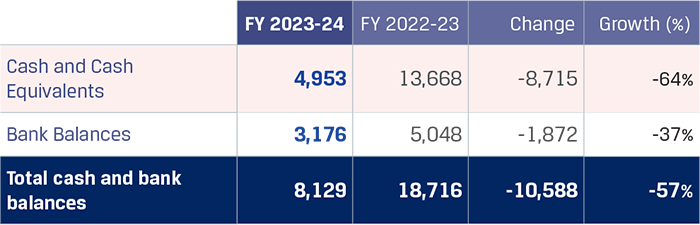
To meet short-term cash commitments and repayment obligations, the Company parks surplus funds in short-term and highly liquid instruments which represent cash and cash equivalents and other bank balances. Total cash and bank balances decreased to `8,129 crore from `18,716 crore primarily on account of lower cash and bank balances due to a reduction in term deposit accounts with maturity less than 3 months at inception and a reduction in maturity more than 3 months but less than 12 months at inception as the cash and bank balances were utilised for capex and working capital requirements.
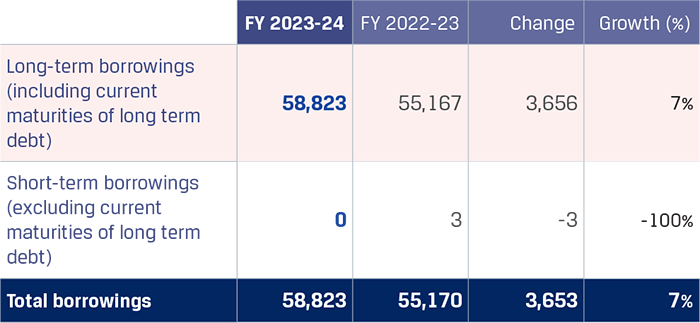
Long-term borrowings (including current maturity of long-term debt) increased primarily due to the net drawing of secured term loans by `1,651 crore, net increase in unsecured term loans by `2,288 crore for incurring capital expenditure and general corporate purposes which was offset by the net redemption of debentures by `840 crore. Deferred government loans increased by `316 crore.
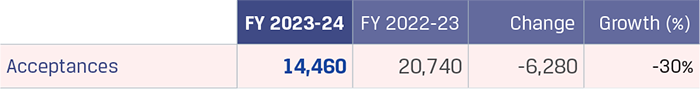
Acceptances decreased by `6,280 crore to `14,460 crore during FY 2023-24 due to decline in coking coal prices and repayment of acceptances.
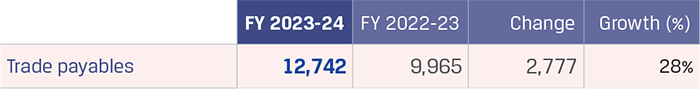
Trade payables increased by `2,777 crore to `12,742 crore primarily due to increase in creditors for goods.
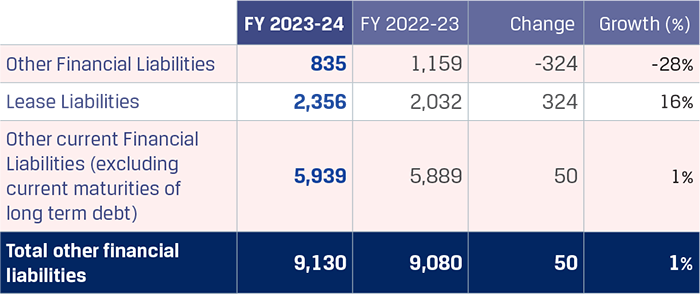
Other current financial liabilities decreased by `324 crore to `835 crore mainly due to the decrease in allowances for financial guarantees consequent to reversal of impairment provision of financial guarantees provided to a subsidiary in the Netherlands mainly on account of significant improvement in the business of its Italian subsidiaries.
Lease liabilities increased by `324 crore to `2,356 crore primarily on account of addition in lease liabilities for railway wagons taken on lease, increase in lease liabilities pursuant to contracts entered for cargo handling at ports and lease assets acquired as a result of the JISPL merger, partially offset by the repayment of principal amount on leases.
Other current financial liabilities increased by `50 crore to `5,939 crore primarily on account of increase in interest accrued but not due on borrowings, higher provisions for marketing rebates which was partially offset by the decrease in retention money payable for capital expenditure.
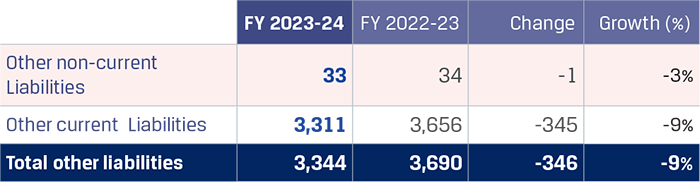
Other current liabilities decreased by `345 crore to `3,311 crore due to decrease in advances from customers as the advances received under the five-year Advance Payment and Supply Agreement (APSA) were settled by way of export of steel products and increase in statutory liabilities due to provisions made for Goa Green cess and other statutory payments.
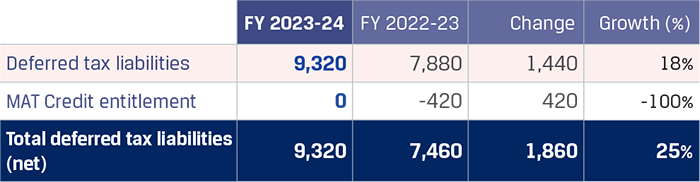
Deferred tax liabilities increased by `1,440 crore to `9,320 crore, primarily on account of additional liability recognised due to adoption of new tax regime wherein deferred tax assets / liabilities are re-stated from 34.94% to 25.17% and utilisation of tax losses acquired pursuant to merger with JISPL. MAT credit was written off due to transition to the new tax regime.
Total capital employed increased 8% y-o-y to `1,17,235 crore in FY 2023-24 primarily due to capitalisation of Property, Plant & Equipment and increase in net current assets. Return on average capital employed for FY 2023-24 was 14 %, as against 10% in FY 2022-23 due to higher earnings.
JSW Steel’s net worth increased from `63,659 crore to `75,283 crore as on March 31, 2024. Book value per share was at `307.75 as on March 31, 2024, as compared to `263.36 as on March 31, 2023.
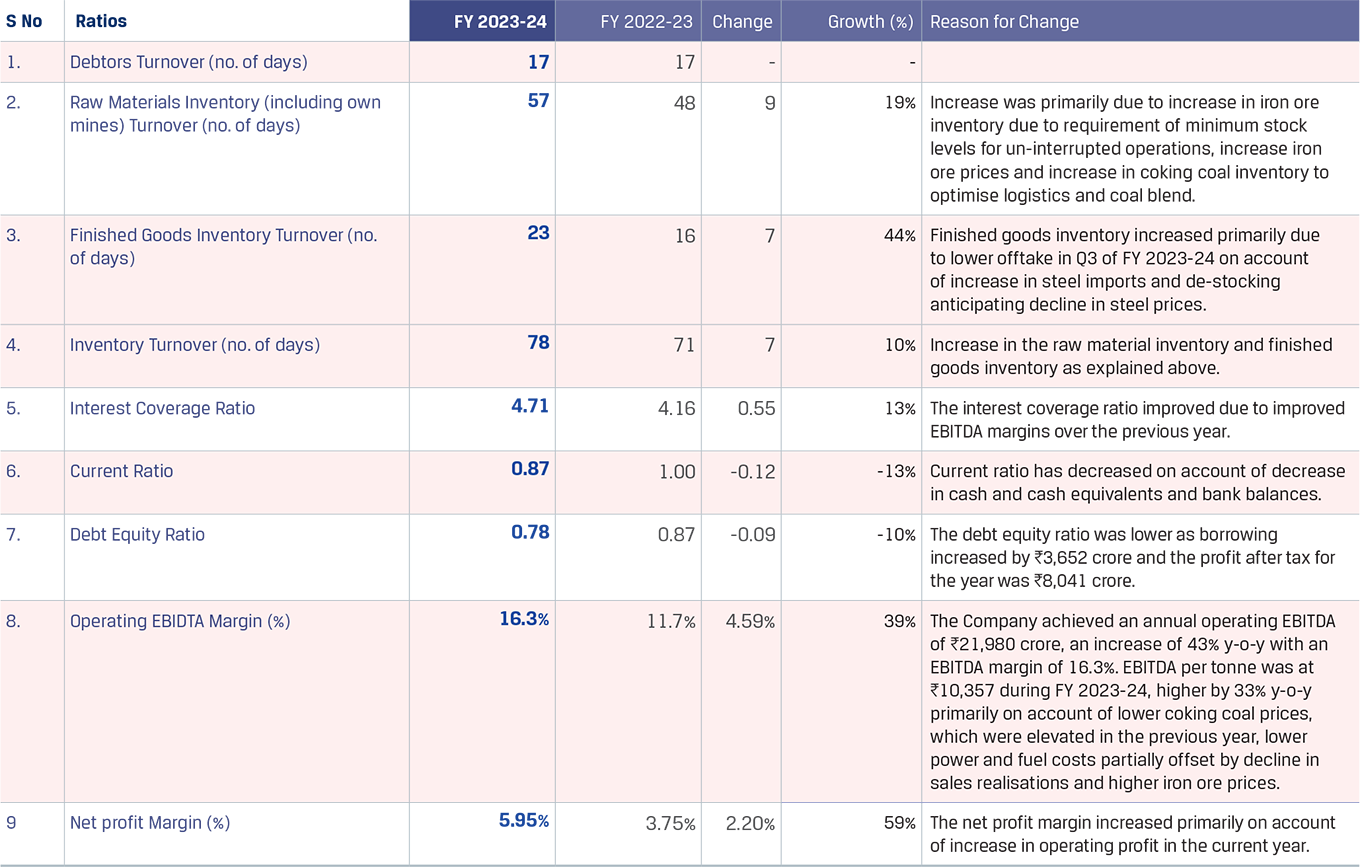
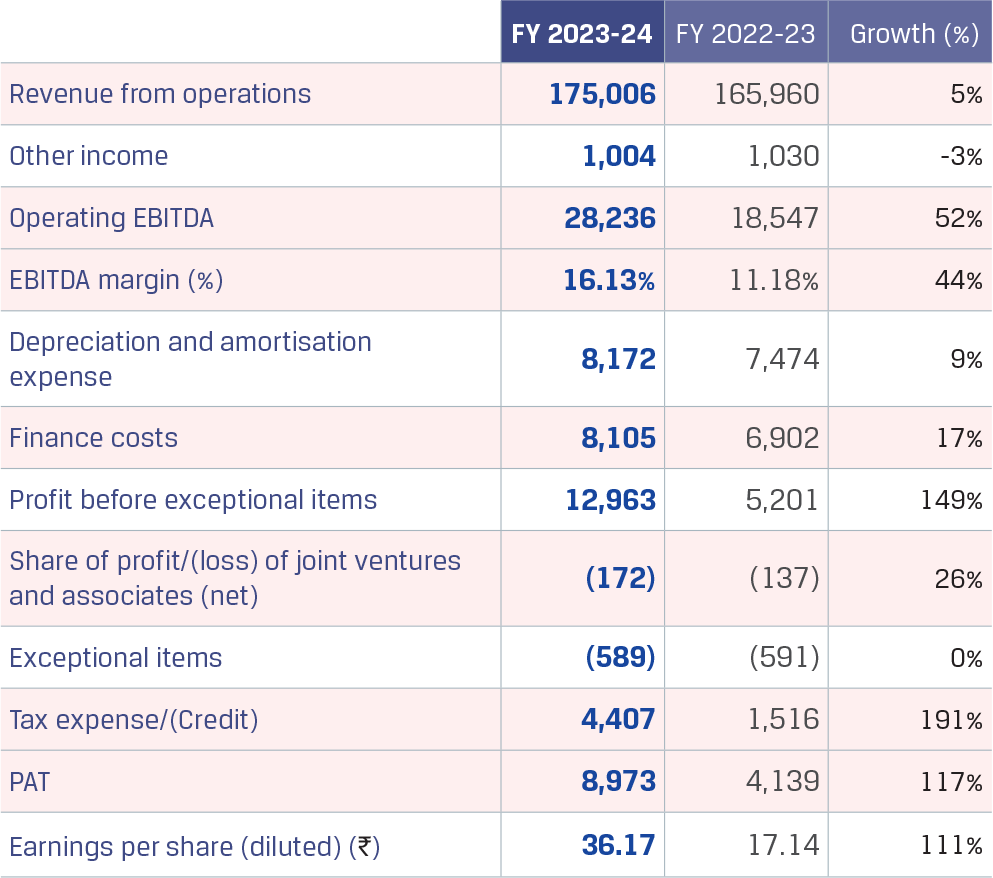
In FY 2023-24, the Company reported its highest ever annual consolidated crude steel production of 26.43 MnT, with an average capacity utilisation of 92% at Indian operations. Crude steel production increased by 9% y-o-y primarily due to the ramp-up of the Dolvi Phase II expansion of 5 MTPA which was commissioned in FY 2021-22, additional production volumes from Raigarh unit and Mivaan Steel Limited pursuant to merger of JSW Ispat Special Products Limited (JISPL) from July 31, 2023, increased production from Bhushan Power and Steel Limited (BPSL) pursuant to ramp up of capacity post commissioning of the Phase 1 expansion to 3.5 MNTPA and improvement in capacity utilisation at JSW Ohio due to improved steel demand in the US.
During the year under review, the Company reported its highest ever annual steel sales volume of 24.78 MnT, up by 11% y-o-y. The consolidated India operations export of steel products stood at 3.4 MnT, up by 23% y-o-y and accounting for 14% of the total sales, as against 13% in FY 2022-23. The exports of steel products were higher in FY 2022-23 as there was no export duty levy during the year as compared to export duty levy of 15% between May 2022 and November 2022. The consolidated India operations domestic sales stood at 20.57 MnT an increase of 8% y-o-y, driven by domestic demand for steel. The Company achieved its highest year Value-Added Special Products (VASP) sales at 14.65 MnT, an increase of 19% y-o-y, and accounted for 61% of the total sales volume for the year.
The EAF-based steel manufacturing facility in Ohio, US, produced 9,62,697 net tonnes of Slabs during FY 2023-24. Capacity utilisation was 66% during the year. Sales volumes for FY 2023-24 stood at 2,58,492 net tonnes of HRC and 6,47,371 net tonnes of Slabs.
FY 2023-24 highlights
Crude steel production Consolidated
 9% Y-o-Y
9% Y-o-Y
Sales volume Consolidated
 11% y-o-y
11% y-o-y
Crude steel production Indian Operations
 8% y-o-y
8% y-o-y
Sales volume Indian Operations
 10% y-o-y
10% y-o-y
Operating EBITDA
Net Profit

In FY 2023-24, the Company’s consolidated revenue from operations grew by 6% y-o-y to `175,006 crore, primarily on account of the increase in dispatches by 11%, partly offset by lower sales realisations due to decline in international steel prices.
Consolidated operating EBITDA was `28,236 crore, an increase of 52% y-o-y with an EBITDA margin of 16.1%. EBITDA per tonne was `11,394 crore during FY 2023-24, higher by 38% y-o-y, primarily on account of the decline in coking coal prices and power and fuel costs, partially offset by lower sales realisations.
The domestic subsidiaries posted an operating EBITDA of `5,025 crore, as against an operating EBITDA of `2,791 crore during the previous year, primarily due to higher EBITDA from JSW Steel Coated Products Limited and Bhushan Power & Steel Limited (BPSL) compared to previous year and additional EBIDTA on account of Mivaan Steel Limited becoming subsidiary of the Company w.e.f. from July 31, 2023 by virtue of amalgamation of JISPL. The overseas subsidiaries posted an operating EBITDA of `1,203 crore, as against an operating EBITDA of `554 crore during the previous year, on account of higher profitability from US Baytown operations and JSW Italy operations, and lower losses from the US Ohio operations.
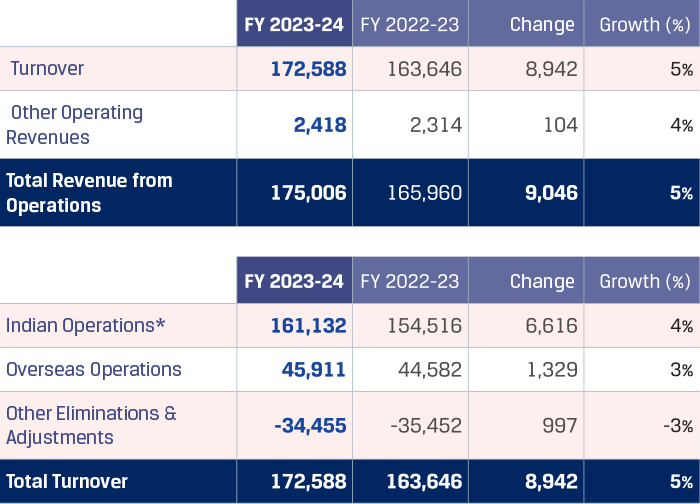
*Net off eliminations of transactions within domestic/Indian entities
The total turnover increased by `8,942 crore to `172,588 crore in FY 2023-24 from `163,646 crore in FY 2022-23. Turnover from Indian Operations increased by `6,616 crore (4% y-o-y) primarily due to the increase in domestic despatch volumes by 8% y-o-y on account of better domestic demand driven by the Government’s infrastructure spend, partially offset by the decline in sales realisations by 6%. The domestic volume increase was primarily driven by 11% y-o-y growth in the Construction and Infrastructure segment sales, 12% y-o-y growth in the Industrial segment, 5% y-o-y growth in the Auto segment and 3% y-o-y growth in the Retail segment. Export volume was up 23% y-o-y. Export volume contributed 14% in FY 2023-24 as compared to 13% in FY 2022-23 mainly due to higher exports to Europe and the Middle East. The exports of steel products were higher in FY 2022-23 as there was no export duty levy during the year as compared to export duty levy of 15% between May 2022 and November 2022.
Turnover from Overseas Operations increased 3% y-o-y primarily due to higher volumes on account of improved market conditions.
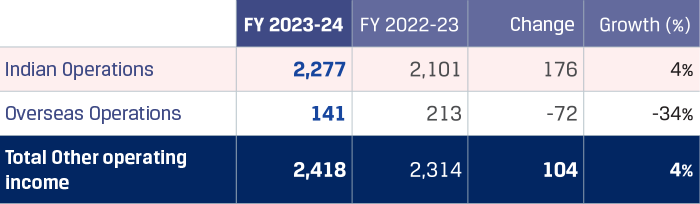
Other operating revenue for Indian operations was `2,277 crore in FY 2023-24 as compared to `2,101 crore in FY 2022- 23, higher by `176 crore. Other operating income increased largely due to higher Government incentive due to lower sales realisation, scrap sales and job work income. This increase was partially offset by reduction in a lower export incentive income as the Company exported under the Advance Authorisation Scheme as against availing duty draw back income in the previous year decrease in Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) grant income.
Other operating income for overseas operations was `141 crore in FY 2023-24 as compared to `213 crore in FY 2022-23 lower by `72 crore. Other operating income is lower primarily due to one-time gain received in previous year towards scrap sales on demolition, rebates and refunds received towards electricity and power charges.
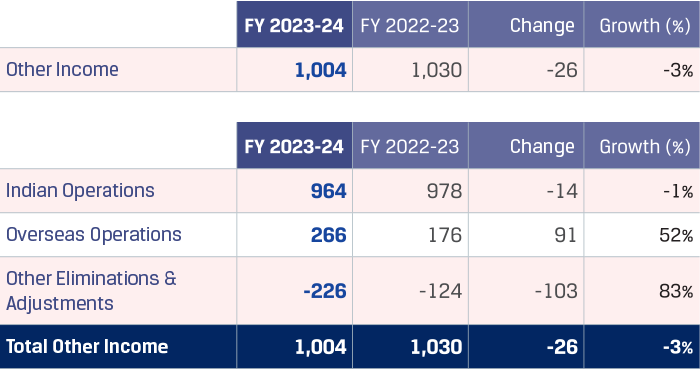

Other income was `1,004 crore in FY 2023-24 as compared to `1,030 crore, lower by `26 crore. Other income was lower due to one-time gain on deemed disposal on dilution of stake in a joint venture of `135 crore, and insurance claim of `30 crore. The decrease is partially offset by increase in interest income from bank deposits by `143 crore.
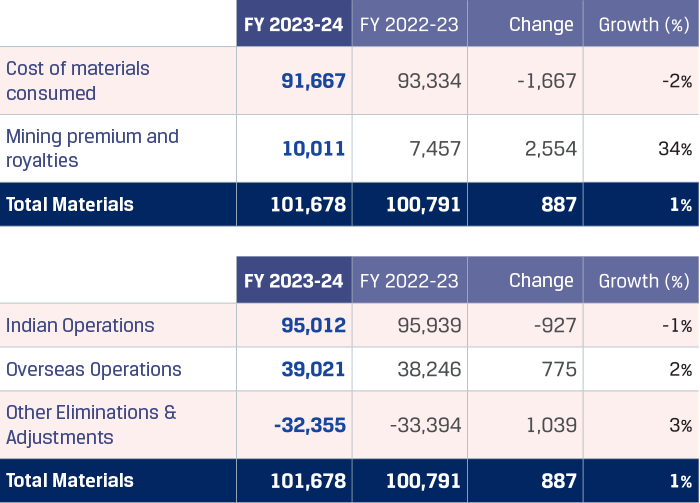
Overall expenditure on material consumption increased by 1% y-o-y to `101,678 crore on account of the decrease in cost of Indian Operations and the increase in cost of Overseas Operations.
Expenditure on material consumption for Indian operations decreased 1% y-o-y to `95,012 crore primarily on account of 24% decrease in coking coal prices in FY 2023-24 as coking coal prices were higher due to supply chain disruptions and the Russia-Ukraine conflict in FY 2022-23. This decrease on raw materials cost was partially offset by an increase in iron ore cost and increased consumption of raw materials due to increase in production volumes by 8%.
Mining premium and royalties cost increased by 34% in FY 2023-24 to `10,011 crore from `7,457 crore in FY 2022-23, on account of an increase in mining premium and royalty cost due to increase in iron ore IBM prices consequent to elevated international iron ore prices leading to increase in exports of iron ore /pellets, resulting in pressure on domestic supply.
Expenditure on material consumption for overseas operations increased by 2% y-o-y to `39,021 crore primarily on account of increased volumes.
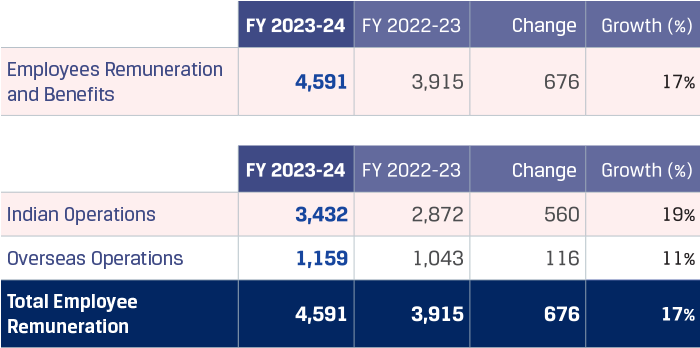

Employee benefits expenses for Indian operations were higher by `560 crore at `3,432 crore in FY 2023-24. The increase was primarily due to annual increments provided to employees, additional manpower cost from Raigarh unit pursuant to merger of JSW Ispat Special Products Limited (JISPL) from July 31, 2023, increase in overall headcount due to capacity additions and increase in managerial remuneration consequent to increase in profits.
Employee benefits expenses for overseas operations were higher by `116 crore at `1,159 crore in FY 2023-24. The increase was primarily due to annual increments provided to employees, increase in overall headcount due to increase in capacity utilisation. The overall headcount increased to 25,550 as on March 31, 2024 from 23,587 as on March 31, 2023.
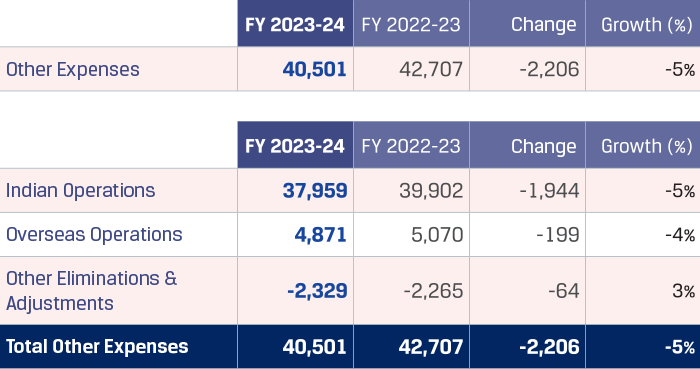
Manufacturing and other expenses for Indian operations decreased 5% y-o-y to ` 37,959 crore primarily due to decrease in power & fuel costs by 14% partially offset by increase in other manufacturing costs on account of increase in production volumes by 8% and higher ocean freight and domestic freight cost due to increase in sales volumes by 10%.
The power and fuel cost decreased by 14% to ` 14,818 crore from `17,186 crore primarily on account of decline in steam coal prices, decline in natural gas prices and partial replacement of thermal power with renewable power available at lower costs. The steam coal prices and natural gas prices were higher in FY 2022-23 owing to energy crises following the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
Stores and spares consumption increased 8% y-o-y to `6,868 crore, primarily on account of overall increase in production by 8%. The freight expenditure increased 11% y-o-y to `8,295 crore primarily on account of increase in exports of steel products by 23% and due to increase in domestic sales volume despatches by 8% and increase in iron ore despatches.
Hedging Cost/Net exchanges loss decreased by 81% y-o-y to `346 crore as the rupee depreciation against the US dollar was 1.4% during FY 2023-24 as against the rupee depreciation of 8.5% in the previous year.
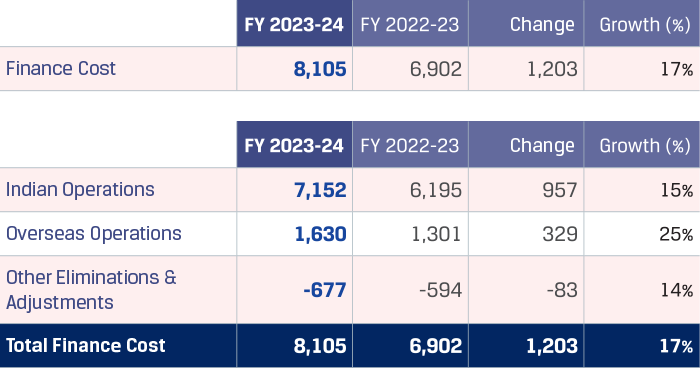
Finance cost increased 17% y-o-y to `8,105 crore primarily on account of higher borrowings and an increase in benchmark rates of domestic and foreign currency borrowings as the central banks across the world increased interest rates to contain inflation. The increase in finance cost was also attributable to increase in borrowings pursuant to merger of JSW Ispat Special Products Limited (JISPL) from July 31, 2023 and increase in interest cost on acceptances as the SOFR rates increased during the year.
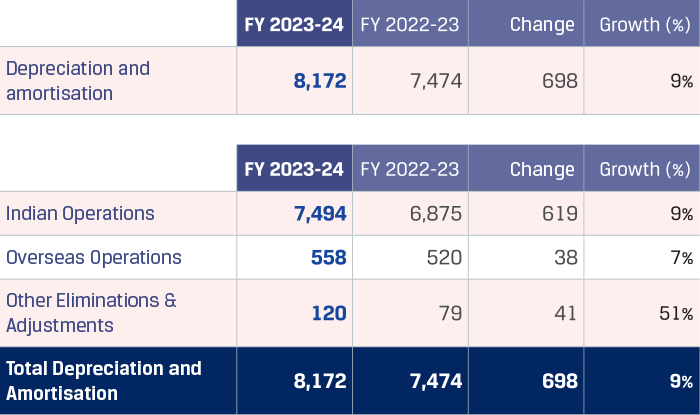
Depreciation and amortisation increased by 9 % y-o-y to `8,172 crore primarily due to
Tax expense was `4,407 crore compared to `I1,516 crore in FY 2022-23 primarily due to higher profitability and a non-cash tax charge of `1,031 crore pertaining to the previous years on account of the tax regime change of the Company.
During the year ended March 31, 2024, the Company had elected to exercise the option permitted under Section 115BAA of the Income Tax Act, 1961 to pay corporate income tax at 22% plus surcharge and cess (aggregating to tax rate of 25.17%) from the financial year 2022-23. Accordingly, the Company had re-measured its current tax and deferred tax charge for the year ended March 31, 2023 basis the new tax regime and recognised a non-cash tax charge of H1,031 crore pertaining to the previous year mainly representing write off of MAT credit not availed and change in tax rate on deferred tax assets of the Company. In view of this exercise of the option to transition to the new regime, the Company has recognised provision for current tax and deferred tax for the year ended March 31, 2024 at the tax rate of 25.17% with necessary tax adjustments.
Effective tax rate

Exceptional Items Includes
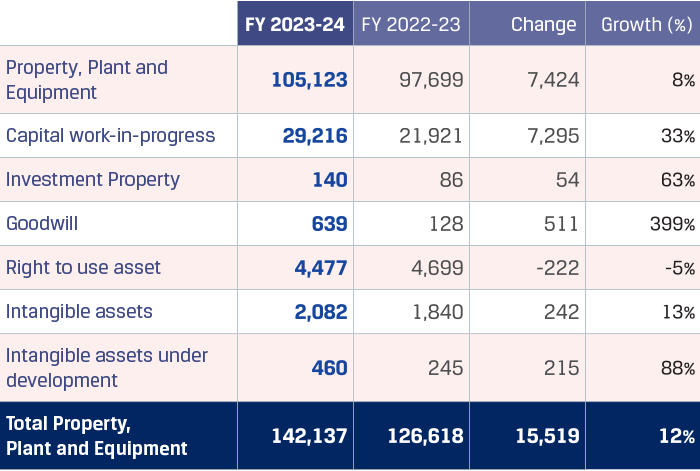
Net block of Property, Plant and Equipment increased by `7,424 crore primarily on account of acquisition of Raigarh and Raipur assets amounting to `3,860 crore pursuant to the JISPL merger becoming effective on July 31, 2023, `511 crore pursuant to acquisition of NSAIL, capitalisation of assets amounting to `10,850 crore relating to Battery B of coke oven 5 of capacity 0.75 MTPA at Vijayanagar, Dolvi Phase II raw material handling system, HSM mill at JVML, special projects and sustenance capex across all the plant locations partially offset by depreciation charge for the year.
The Right to use asset decreased by `222 crore to `4,477 crore primarily on account of acquisition of the DRI plant, CDQ facilities and power plant under the Build Own Operate and Transfer agreement during the year.
Pursuant to the merger of JISPL with the Company, the purchase consideration paid has been allocated in accordance with the Ind AS 103 'Business Combinations' on the basis of fair value of the acquired assets and liabilities. Accordingly, the Group has recognised goodwill of `458 crore on account of this acquisition.
Pursuant to the acquisition of NSAIL by the subsidiary of the Company, the purchase consideration paid has been allocated in accordance with the Ind AS 103 'Business Combinations' on the basis of fair value of the acquired assets and liabilities. Accordingly, the Group has recognised goodwill of `51 crore on account of this acquisition.
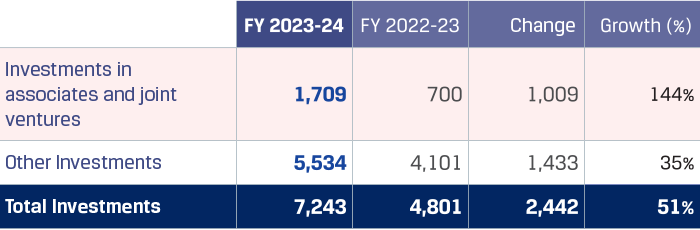
Investments increased to `7,243 crore from `4,801 crore in FY 2022-23, an increase of `2,442 crore due to increase in fair value of JSW energy shares by `2,927 crore, additional investment of `250 crore in JSW Paints, partially offset by reduction in investment in Creixent Special Steels Limited of `760 crore pursuant to the merger of CSSL with the Company effective July 31, 2023.
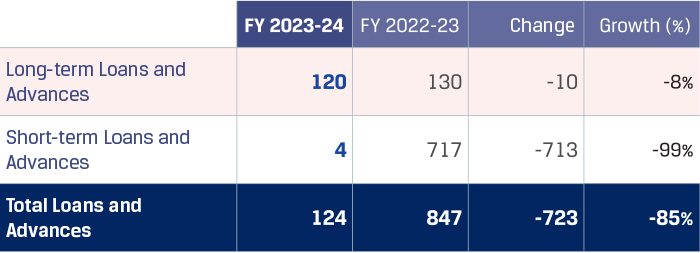
Loans and advances decreased by `723 crore primarily due to the redemption of ICD given by JSW Coated by `505 crore, and cancellation of loans pursuant to merger of CSSL & JISPL with the Company effective July 31, 2023
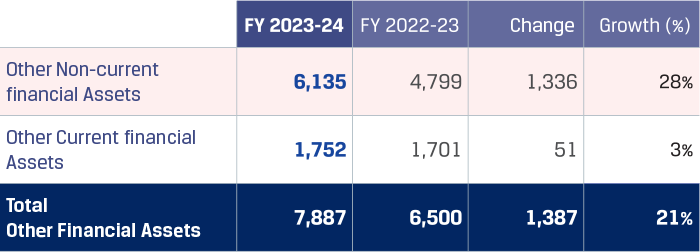
The other Non-current financial assets increased to `7,887 crore on account of increase in the GST incentive receivable from the state of Maharashtra and Karnataka.
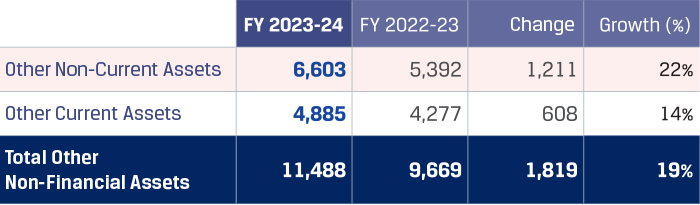
The other Non-current assets increased by `1,211 crore to `6,603 crore primarily on account of accumulation of GST input tax credit and increase in prepaid amounts, which was partially offset by a decrease in the capital advances made to suppliers for capital projects on account of completion of supply of goods or services.
The other current assets increased by `608 crore to `4,885 crore on account of increase in GST input tax credit available for set off by reduction in advances to suppliers and reduction in security deposits.
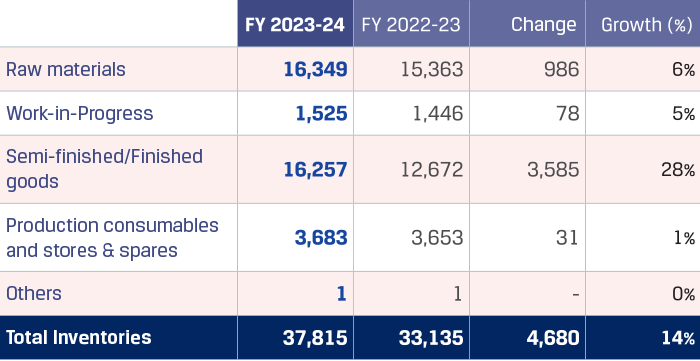
The increase in raw materials inventory was primarily due to an increase in iron ore fines and coking coal inventory by `901 crore as iron ore fines inventory increased by 1.9 lakh tonnes. The coal inventory also increased by 7.62 lakh tonnes and average coal prices fell by 10% in FY 2023-24.
Work-in-progress and semi-finished/finished goods increased by `3,585 crore primarily due to an increase in steel inventory by 3.91 lakh tonnes and captive mines’ iron ore inventory by 19.63 lakh tonnes at Indian operations.
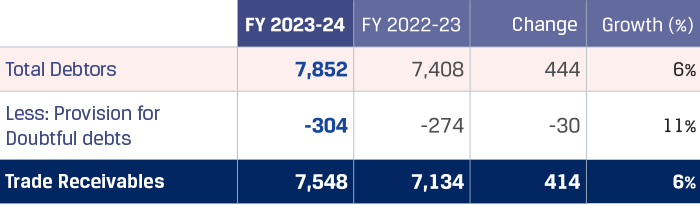
Trade receivables increased by `414 crore to `7,548 crore due to higher sales volumes during the year. The average collection period was maintained at 16 days.
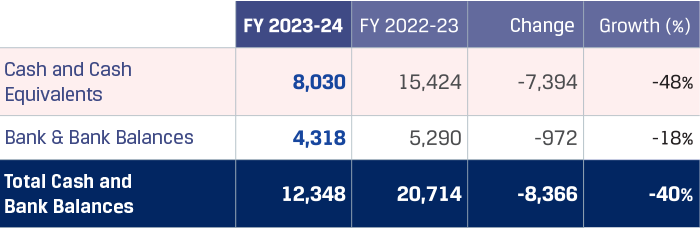
To meet short-term cash commitments and repayment obligations, the Company parks surplus funds in short-term and highly liquid instruments which represent cash and cash equivalents and other bank balances. Total cash and bank balances decreased to `12,348 crore from `20,714 crore primarily on account of lower cash and bank balances due to a reduction in term deposit accounts with maturity less than 3 months at inception and reduction in maturity more than 3 months but less than 12 months at inception as the cash and balances were utilised for capex and working capital requirements.
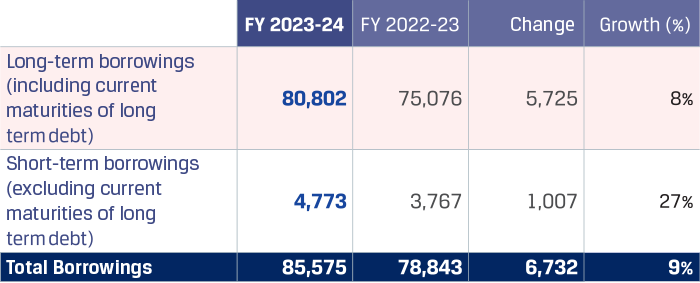
Long-term borrowings (including current maturity of long-term debt) increased primarily due to the net drawing of secured and unsecured term loans for incurring capital expenditure and general corporate purposes which was offset by the redemption of debentures of `840 crore. Deferred government loans increased by `316 crore.
Short term borrowings increased by `1,007 crore to meet the working capital requirements in Indian operations and overseas operations.
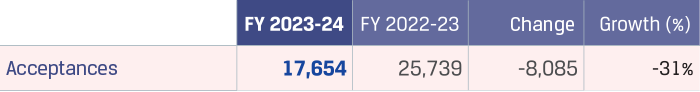
Acceptances decreased by `8,085 crore to `17,654 crore during FY 2023-24 due to decline in coking coal prices and repayment of acceptances.
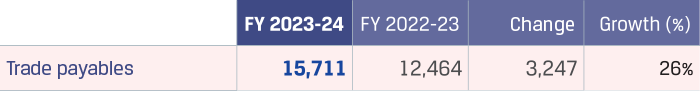
Trade payables increased by `3,247 crore partially due to increase in payables for goods, JISPL and NSAIL acquisition during the year.
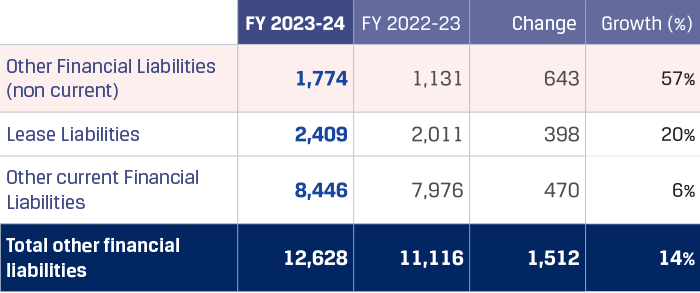
Other financial liabilities increased by `643 crore to `1,774 crore primarily on account of increase in retention money payable for capital projects. Lease liabilities increased by `398 crore to `2,409 crore primarily on account of addition in lease liabilities for railway wagons taken on lease, increase in lease liabilities pursuant to contracts entered for cargo handling at ports and lease assets acquired as a result of the JISPL merger, partially offset by the repayment of principal amount on leases. Other current financial liabilities increased by `470 crore to `8,445 crore primarily on account of increase in interest accrued but not due on borrowings, higher provisions for marketing rebates, payable for capital projects, which was partially offset by the decrease in retention money payable for capital expenditure.
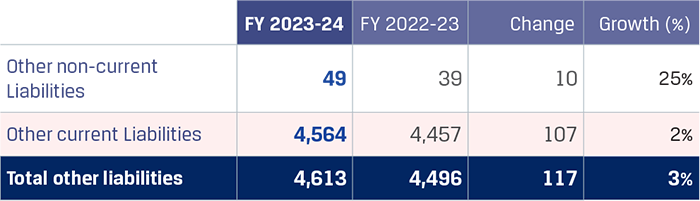
Other current liabilities increased by `107 crore due to an increase in export obligation deferred income and an increase in statutory liabilities due to provisions made for Goa Green cess and other statutory payments, partially offset by decrease in advances from customers as the advances received under the five-year Advance Payment and Supply Agreement (APSA) were settled by way of export of steel products.
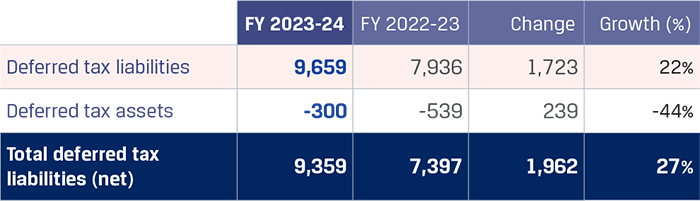
Deferred tax liabilities increased by `1,723 crore to `9,659 crore due to reversal of deferred tax assets on account of utilisation of tax losses acquired pursuant to merger with JISPL and DTL has increased due to transition to new regime and resultant write off of DTA as well. MAT credit was written off due to transition to the new tax regime.
JSW Steel’s net worth increased from `65,694 crore as on March 31, 2023 to `77,669 crore on a consolidated level as on March 31, 2024. Book value per share was at `307.85 as on March 31, 2024, as compared to `263.36 as on March 31, 2023.
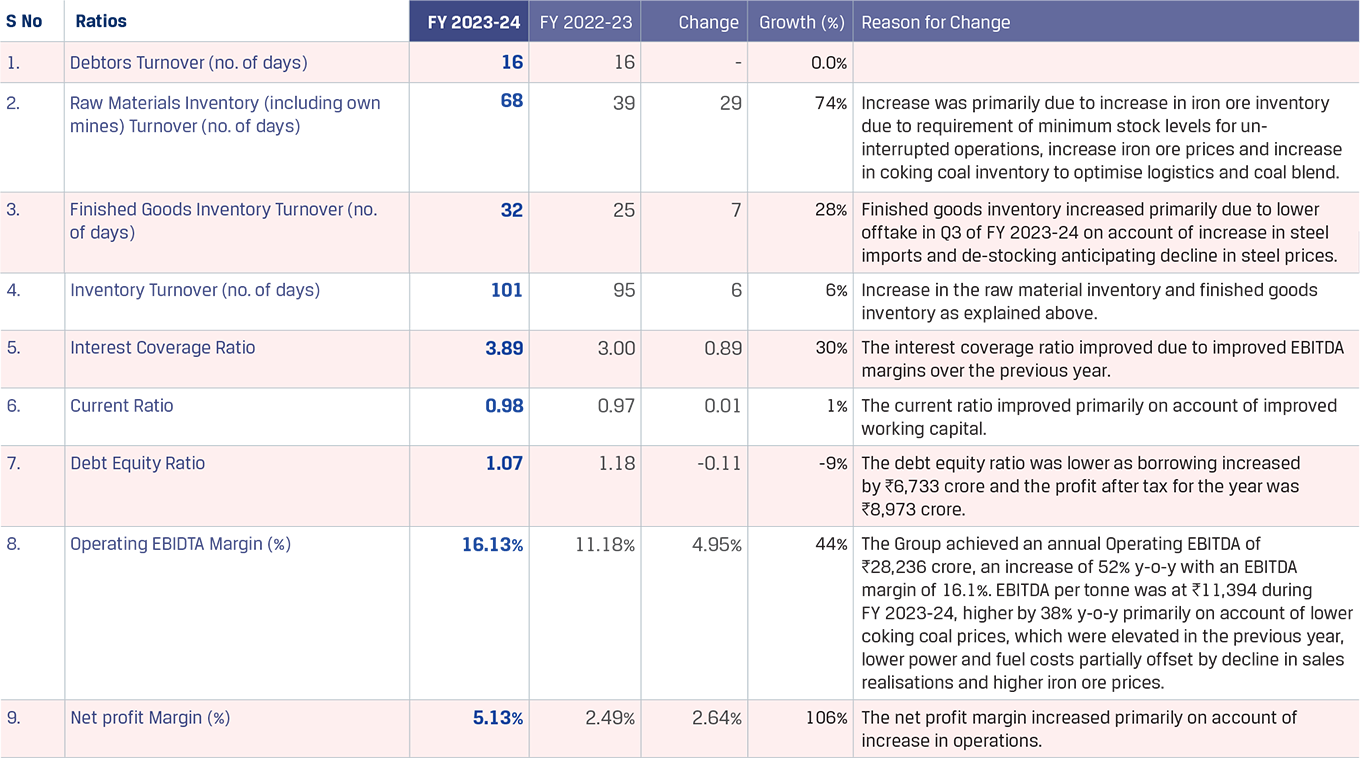

JSW Steel's digital transformation strategy leverages Industry 4.0 technologies to drive improvements across its operations. By integrating advanced digital solutions—from IoT sensors in mining to machine learning in manufacturing processes—the Company enhances efficiency, quality, safety, and sustainability. Key initiatives include digital twins for real-time process optimisation, predictive analytics for proactive maintenance, and AI-driven systems for improved decision-making and safety standards. These digital advancements streamline operations and create a culture of innovation and continuous improvement within JSW Steel. The successful implementation of these technologies has set new industry benchmarks, transforming traditional practices and contributing to a more sustainable and efficient future in steel manufacturing.
READ MORE

JSW Steel understands that achieving its goal of becoming a more efficient and superior steel producer hinges on the dedication and skills of its workforce. Talent management is a pivotal part of the Company's strategic framework. Employees benefit from policies designed to cultivate a supportive work environment. In addition to industry-competitive compensation packages, the Company provides extensive learning and career development opportunities. Embracing diversity and inclusion, JSW Steel fosters a culture where all employees feel valued and empowered. Moreover, by leveraging digitalisation, the Company enhances employee capabilities and operational efficiency. Robust health and safety measures are in place to ensure the well-being of employees, driving them to achieve and maintain peak performance levels.
READ MOREThe Company’s commitment to Corporate Social Responsibility is an integral part of its 'Better Everyday' ethos, which is aimed at addressing social inequalities in India by creating opportunities. It also aims to uplift communities through initiatives that drive infrastructural and rural development across the nation. Its CSR initiatives are guided by principles of engaging diverse stakeholders, fostering community involvement at the local level, promoting grassroots participation, and ensuring programmes are scalable, replicable, and sustainable. By adhering to these principles, JSW Steel aims to make a meaningful impact on society while advancing its business objectives.
Lives impacted to date through the focus areas of:
Health and nutrition
Beneficiaries
Education
Beneficiaries
Water, env. and sanitation
Beneficiaries
Waste management
Beneficiaries
Skills and livelihoods
Beneficiaries
Agriculture and allied livelihoods
Beneficiaries
Art, culture and heritage
Restoring the Mughal Gardens of Kashmir
Sports Promotion
Beneficiaries

The ERM framework of JSW Steel provides a structured approach to identify, prioritise, manage, monitor, and report on key and emerging risks. The Company adheres to the globally recognised Committee of Sponsoring Organisations (COSO) framework for ERM, which facilitates the seamless integration of internal controls into its business processes.
JSW Steel’s risk management approach incorporates both bottom-up and top-down strategies. The bottom-up process involves the identification and regular assessment of risks by its plants and corporate functions, followed by the implementation of effective mitigation strategies. Concurrently, the Company's Risk Management Group (Senior Leadership Team) and the Risk Management Committee (RMC) adopt a top-down approach to identify and evaluate long-term, strategic, and macro risks to its business.
The RMC, operating as a sub-committee of the Board of Directors, oversees the entire risk management process within the organisation. Chaired by an Independent Director, the RMC ensures that the ERM framework effectively addresses the following critical aspects:
JSW Steel recognises that emerging and identified risks must be mitigated to: