1.0
8th Globally
World Steel Dynamics aggregate ranking
27.7 MTPA
Domestic installed capacity (including BPSL and JISPL)
29.2 MTPA
Total installed capacity
India’s leading and most diversified steel producer
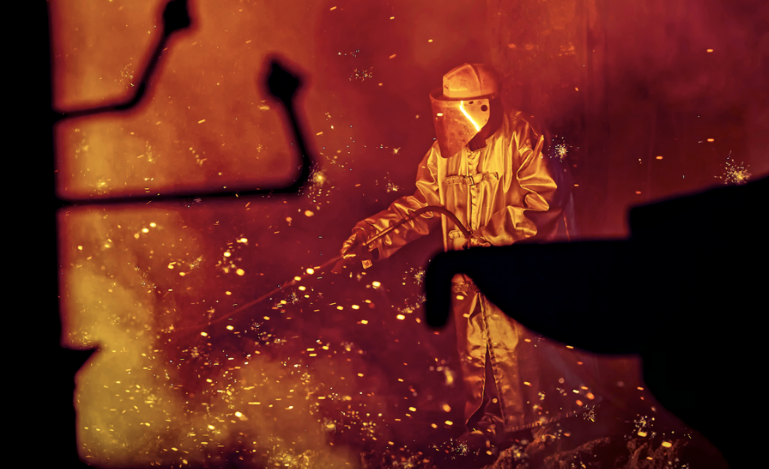
JSW Steel, the flagship company of the JSW Group, is one of the largest and most diversified steel producers in India. Its fully integrated operations encompass mining, raw materials processing, steel manufacturing and downstream value-added products.
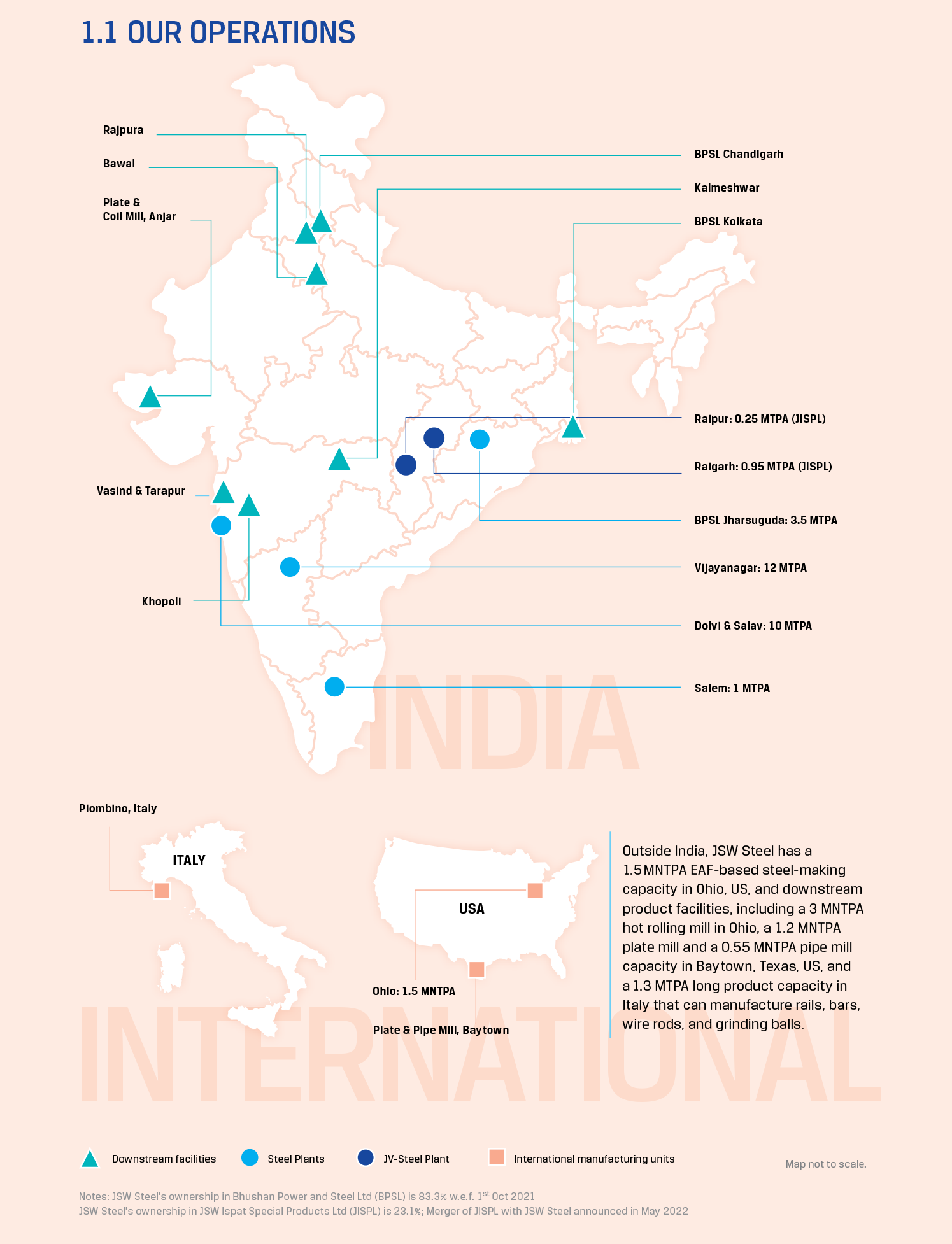
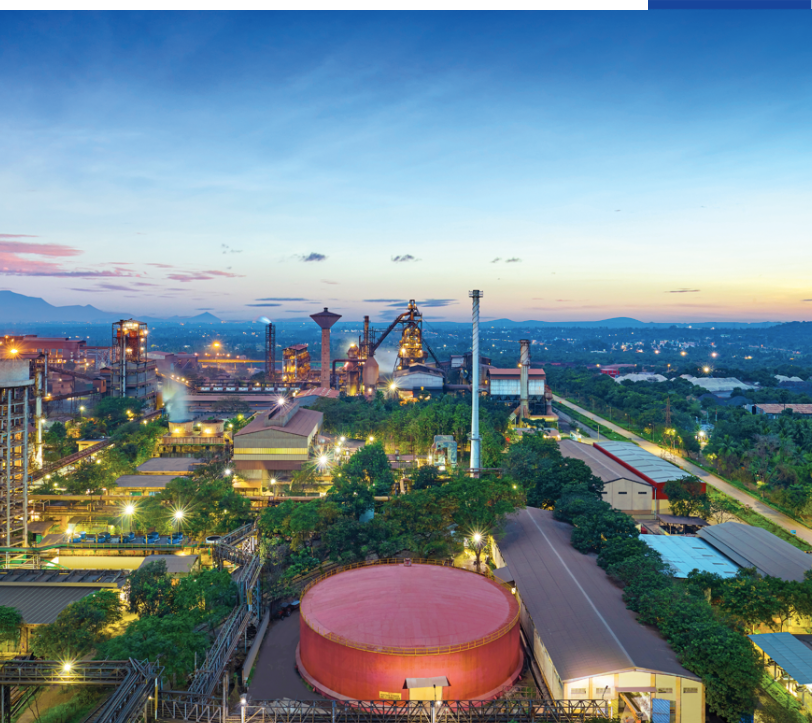
JSW Steel manufacturing facilities in India are geographically diversified and include the Vijayanagar Plant in Karnataka (12.0 MTPA), Dolvi Works in Maharashtra (10.0 MTPA), Salem Works in Tamil Nadu (1.0 MTPA), Bhushan Power and Steel Limited (BPSL) Jharsuguda Plant in Odisha (3.5 MTPA), Raigarh and Raipur plants (JSW Ispat Special Steel Products Limited, a JV) in Chhattisgarh (1.2 MTPA). JSW Steel currently has an installed crude steel capacity of 27.7 MTPA.
The first phase of expansion at BPSL to 3.5 MTPA was completed during FY 2022-23. JSW Steel has embarked on a capacity expansion journey to address the country’s growing demand for steel. The Company’s 12 MTPA manufacturing unit in Vijayanagar, Karnataka is the largest single-location steel-producing facility in India. With a total domestic downstream flat products capacity of ~13.5 MTPA, the Company is progressively adding a competitive edge to its market presence.
JSW Steel has embarked on additional capital expenditure programmes to expand capacities at its plants, and also to modernise and expand capacities of its downstream business. The capacity at Vijayanagar Works is being expanded from 12 MTPA to 19.5 MTPA through brownfield expansion by setting up a 5 MTPA steelmaking capacity though one of its wholly owned subsidiaries, JSW Vijayanagar Metallics Limited and other productivity-enhancing initiatives. The capacity at the Jharsuguda plant is being expanded from 3.5 MTPA to 5 MTPA. Both these expansion projects are expected to be completed by the end of FY 2024-25, thereby bringing the overall capacity to 38.5 MTPA. Gradually, JSW Steel plans to expand its domestic steel capacity to 50 MTPA by FY 2030-31 through a combination of organic and inorganic growth.

Diversified portfolio with focus on value-added products
JSW Steel has a wide range of product offerings that cater to diversified end markets across geographies. We have significantly expanded our product portfolio through a mix of acquisitions, downstream capacity expansions and joint ventures with other leading steel companies.
JSW Steel has downstream facilities, which comprise the coated products division at Vasind, Tarapur, Kalmeshwar Works and Khopoli in Maharashtra, Bawal in Haryana and Rajpura in Punjab, in addition to the downstream facilities at Vijayanagar and BPSL downstream plants at Jharsuguda in Odisha, Chandigarh in Punjab, and Kolkata in West Bengal. Our downstream facilities also include the plate and coil division at Anjar in Gujarat.
JSW Steel completed the commissioning of new 0.5 MTPA continuous annealing line at Vasind and the second tin plate line with an additional capacity of 0.25 MTPA at Tarapur during FY 2022-23. JSW Steel has a downstream flat products capacity of ~13.5 MTPA, which constitutes 49% of the crude steel capacity.
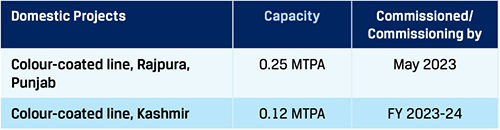
JSW Steel is currently expanding its downstream capacity with the installation of a new 0.25 MTPA colour-coated line at Rajpura (Punjab), commissioned in May 2023, and the setting up of a 0.12 MTPA colour-coated facility in Jammu and Kashmir in FY 2023-24. Both these downstream facilities are expected to be commissioned during FY 2023-24.
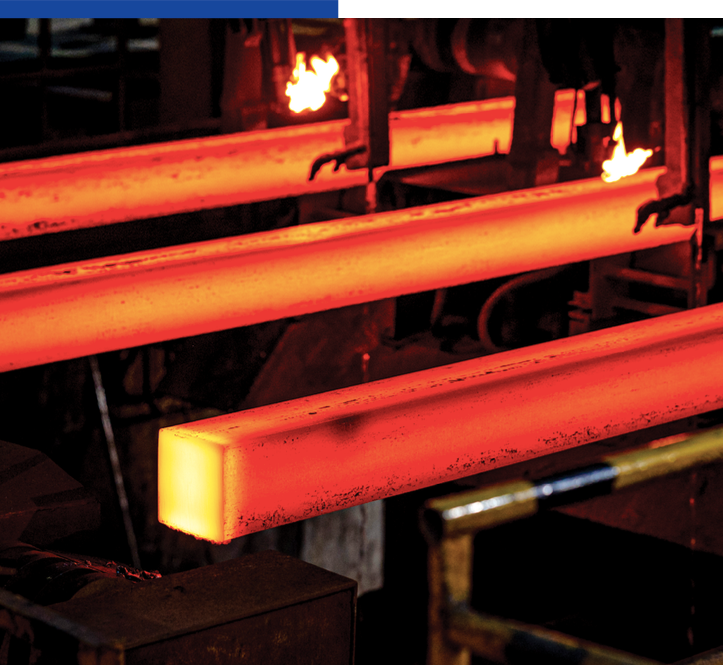
JSW Steel has implemented the best practices in research and innovation to create diversified portfolio of value-added products. Its portfolio includes hot-rolled, cold-rolled, coated, colour-coated, tinplate, alloy steel and electrical steel products. Its long product range comprises TMT bars, wire rods, rails, grinding balls and special steel bars. These products are used in automotive, general engineering machinery projects and construction applications.
~13.5 MTPA
Domestic downstream flat products capacity
Completed/ongoing domestic projects
Over the past few years, there has been an increasing demand for specialty steel across user industries like renewable power, automobile and white goods, among others. India has largely relied on imports to meet domestic demand. To drive import substitution and achieve self-reliance, JSW Steel has rapidly scaled up its value-added product capacities. Further, the Company plans increase the share of high-margin, value-added products in the product mix to protect margins amid steel price volatility.
The Company believes that the breadth of our product range gives it the flexibility to adapt its product mix as per market demands, and enables it to sustain the business and operations despite adverse economic conditions. The strategic collaboration with JFE has allowed the production of high-end value-added steel products for the automotive, electrical appliance and construction industries. Moreover, JSW Steel manufactures a wide range of value-added flat steel products, such as medium-to high-carbon steel, high-tensile and high-strength low-alloy steel grades for the automotive sector, API grade steel for the oil and gas sector, cold-rolled close annealed coils, customised galvanised and galvalume products for the solar sector, galvanised products and colour-coated products in the flat product segment, and rebars, wire rods and structural steel in the long product segment.
JSW Steel currently has one of the largest galvanising and galvalume and colour-coating production capacities in India. It is also one of the largest Indian exporters of coated flat steel products, with a footprint in more than 100 countries across five continents.
Integrating backward to strengthen cost leadership and input security
JSW Steel has built a resilient business model with a relentless focus on cost leadership. The Company uses technology, analytics and innovation as critical levers to optimise costs and improve operational efficiencies. Its strategically located operations, state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, captive resources, and high productivity have led to its leading position on the global conversion cost curve.
JSW Steel has undertaken backward integration projects to optimise costs and reduce external dependencies. Through open auctions, it has secured iron ore mines and coking coal mines in India to improve raw material self-sufficiency. The Company is also focused on the use of renewable energy and has already entered into power purchase agreements for procurement of wind and solar power. It already generates significant power by recycling the heat produced at the steel plants.
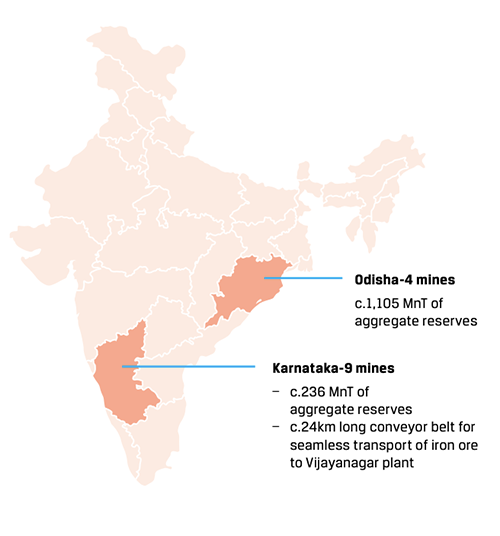
JSW Steel currently operates 13 captive iron ore mines in Karnataka and Odisha, with aggregate reserves of 1.34 billion tonnes. Its key cost-reduction projects include pellet plant and coke oven facilities at Vijayanagar and Dolvi. The Company has also built the world’s largest conveyor system, which extends 24km, from the captive mines to the Vijayanagar plant, to transport iron ore.
41%
Iron ore needs met through captive mines
Augmenting mining capabilities and building logistics solutions
To further enhance mining capabilities and efficiencies, JSW Steel has earmarked ₹14,150 crore of investments for the Odisha mines and related infrastructure facilities over the next three years. Aligned with the National Steel Policy, this investment in Odisha is expected to support Mission Purvodaya in transforming Odisha into an integrated steel hub. Further, the project will enhance JSW Steel’s mining infrastructure, reduce reliance on outsourced mining and provide strategic long-term iron ore security to steel manufacturing locations. The high iron ore grade from these mines and the grinding and washing facilities to improve ore quality will enhance the productivity of steelmaking operations.
JSW Steel is also setting up a slurry pipeline from the mines to Jatadhar Port, including the grinding and filtration plant. The slurry pipeline is expected to provide an environment-friendly logistic solution for the transportation of iron ore from the Odisha mines to the Jatadhar port, and reduce the existing logistics cost. Furthermore, JSW Steel is setting up a 8 MTPA pellet plant at Jatadhar port to cater to the pellet export market and also meet the pellet requirements post future expansions at other locations.
In addition, the digitalisation of mining operations and logistics optimisation will reduce costs further.
₹14,150 crore
Investment planned from FY 2022-23 for next three years towards mining projects and related infrastructure facilities
Strategic acquisitions and joint ventures
JSW Steel is part of strategic joint ventures and has acquired equity interests in various entities, enabling it to add more value-added products, enhance its global footprint, secure raw materials, achieve backward integration and increase its technological know-how. It has also pursued unique opportunities in stressed assets in niche markets.
The Company has entered a 50:50 JV with UK-based Severfield UK PLC, UK, which provides structural steel building solutions. The manufacturing facility is located at Vijayanagar, within the premises of JSW Steel’s plant, and has a capacity of 1,00,000 tonnes per annum. The product portfolio includes engineering, fabrication and erection of structural steel. It also provides cutting-edge flooring technology with composite metal decking through a JV with Structural Metal Decks Limited, UK.
A joint venture with Marubeni-Itochu Steel (JSW MI Steel Service Centre Private Limited) will see the Company set up steel service centres in North and West India to provide just-in-time solutions to the automotive, white goods and construction sector.

Focus on technology driving raw material efficiency and increased productivity
With a strong focus on Industry 4.0 principles, JSW Steel has embarked on numerous projects to improve efficiency across operations. By leveraging advanced algorithms and data analytics, it has developed optimisation models to enhance raw material efficiency, increase productivity and reduce wastage. Additionally, the Company has established a robust Mine-to-Customer digital process that streamlines the entire value chain. From mining to transportation and delivery, integrated digital systems have been implemented that facilitate seamless coordination and real-time tracking. This not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances transparency and customer satisfaction.
Global presence and distribution network
The Company has strategically positioned itself in key locations across India, the USA, and Italy, gaining significant advantage. The majority of the production capacity is met by the Company's four Integrated Steel Plants (ISPs) located in Vijayanagar, Dolvi, Salem, and Odisha. In addition to the ISPs, the market presence is strengthened by the value-added steel products (VASP), which the Company offers through its JVs and subsidiaries.
Moreover, JSW Steel has one of the largest distributor and retailer networks in India, with a distinct customer base.
~16,500
Exclusive and non-exclusive retail outlets
370
Distributors
1,500
Presence across towns
The Company has established a strong export presence spanning 100 countries. Despite facing challenges such as the imposition of export duties and disruptions in both domestic and international markets, the Company achieved remarkable sales figures. The year presented various challenges that had an impact on operations but the Company experienced a strong rebound in exports following the removal of export duties. In fact, during the last quarter, we witnessed a remarkable turnaround, recording one-third of our full-year exports.
Robust capacity utilisation on strong domestic demand
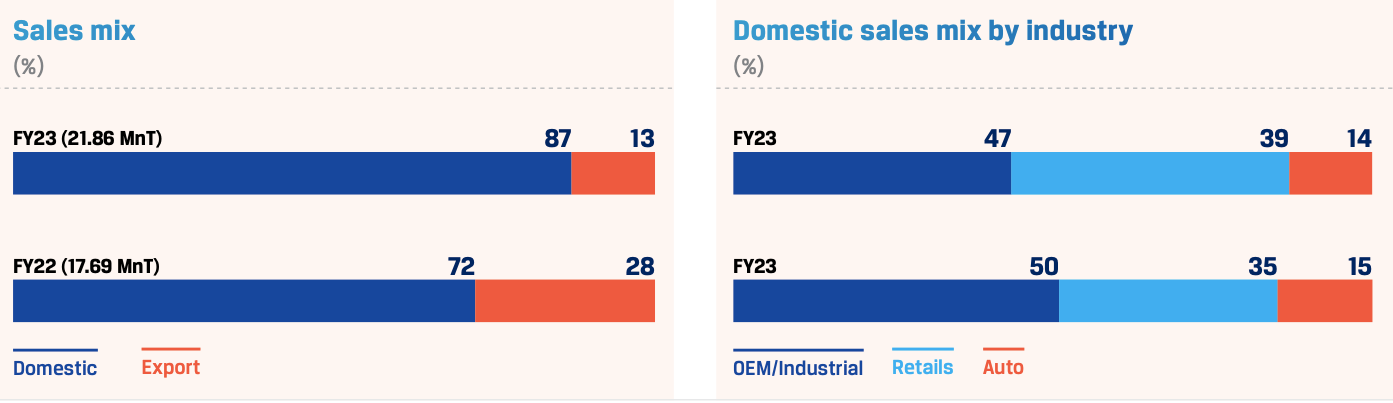
During FY 2022-23, JSW Steel achieved 90% capacity utilisation and reported highest ever consolidated crude steel production of 24.16 MnT, up 24% y-o-y, on strong domestic demand. India operations sales stood at 21.86 MnT, up 24%.

During CY 2022, global steel demand growth remained flat year-on-year, weighed down by aggressive interest rates by major central banks, and China staying off the market to curb a spike in COVID-19 cases by adopting a stringent ‘Zero Covid’ policy.
However, domestic steel demand remained strong on the back of the Government's infrastructure spending push and buoyant housing and construction sectors. JSW Steel is confident about India’s long-term infrastructure-led growth story, with low per capital steel consumption providing significant growth headroom for the domestic steel industry. At the end of FY 2022-23, capacity utilisation levels were at 90%, aided by a 13.3% y-o-y growth in Indian steel demand to 119.9 MnT.
Highlights of operating performance during FY 2022-23
Healthy EBITDA margins despite unfavourable external environment
The first half of FY 2022-23 was marked by external headwinds, including geopolitical tensions, and volatile commodity and raw material prices. Further, the synchronised monetary tightening by major central banks impacted steel demand and led to a fall in steel prices globally, while the sharp rise in coking coal prices weighed on margins. This coincided with the imposition of duties on domestic steel exports in May 2022, which made India's steel uncompetitive in the overseas markets and hurt our profitability. Although domestic steel demand was robust, low-priced steel imports especially from Russia depressed prices.
The second half witnessed a healthy recovery with easing of coking coal prices and other costs, and the subsequent rise in global steel prices, following the relaxation of China's Zero COVID policy and the removal of export duties in November 2022. The continued focus on increasing the share of VASP in the portfolio mix, with significant downstream capacities, and on maintaining cost leadership enabled the Company to protect its margins. For FY 2022-23, JSW Steel delivered an consolidated EBITDA of ₹18,547 crore and EBITDA margin of 11.2%.
Highlights of operating performance during FY 2022-23

Focus on growth and cost reduction projects amid uncertain environment
Despite the uncertain environment, the Company remained focused on growth and cost-reduction initiatives. The planned CapEx for FY 2022-23 of ₹20,000 crore was moderated to ₹15,000 crore, with actual spending reaching ₹14,214 crore. The year saw the successful commissioning of projects such as the capacity expansion of BPSL from 2.75 MTPA to 3.5 MTPA. Cost-reduction initiatives included the commissioning of a 0.75 MTPA Coke Oven Battery A at Vijayanagar in November 2022, and the commissioning of 175 MW and 60 MW power plants at Dolvi. Additionally, efforts were made to enrich the product mix with projects such as the LRPC (Long Products Rolling Complex) Phase 1 expansion of 0.72 MTPA at Vijayanagar in December 2022, and the commissioning of 0.25 MTPA Tinplate line at Tarapur and a 0.5 MTPA Continuous Annealing Line at Vasind in November 2022.
Raising the bar on sustainability
JSW Steel has firmly integrated sustainability into its fundamental business growth strategy, placing significant emphasis on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations. With a comprehensive approach, the Company has identified and established 17 focus areas supported with specific policy commitments to enhance year-on-year performance. Through a series of initiatives, the Company is consistently reducing its environmental impact, leveraging its technological advancements and innovation to deliver sustainable products. Guided by a well-defined sustainability framework, JSW Steel is creating a Better Everyday for all its stakeholders.
JSW Steel has launched a flagship program named as 'SEED' (Sustainable Energy Environment & Decarbonisation) at Vijayanagar. This programme is focused on a series of energy efficiency improvement projects enabling decarbonisation and is estimated to reduce more than 9 MnT of CO2 by 2030.
JSW Steel has been driving product sustainability as a business imperative and product eco-labelling is one such area. The Company is the first manufacturer to receive the prestigious GreenPro ecolabel for its 'Automotive Steel' products. The GreenPro ecolabel, developed by the Confederation of Indian Industry's (CII) Green Business Centre, recognises the highest standards of environmental sustainability and product performance in the Indian manufacturing sector.


JSW Steel aims to reduce its CO2 emission intensity by 42% by 2030, from the 2005 base year aligning to India’s NDC commitment. This reduction will be achieved by energy transition towards renewable energy, adoption and promotion of efficiency improvements in energy consumption, process optimisation, increased use of available scrap and support circularity through better resource management and adoption of Best Available Technologies (BAT).
42%
Reduction in CO2 emission intensity by 2030 (from 2005 base year)

Renewable energy usage at Vijayanagar
We have commenced usage of renewable power at Vijayanagar plant from the 225 MW solar power plant, which is one of the largest captive solar power plants. It has a transmission capacity of 400 kV and can supply power to steel manufacturing plants across the country.
Injection of waste plastic in Blast Furnace
The Company a significant milestone in its commitment to environmental sustainability by initiating waste plastic injection in blast furnaces. It has successfully injected a substantial amount of waste plastic into one of its Blast Furnaces at the Vijayanagar facility, demonstrating the Company's dedication to environmental stewardship and innovative practices in the steel manufacturing sector.
This pioneering approach not only reduces the reliance on fossil fuels but also addresses the pressing issue of plastic waste management enabling circularity and sustainability.
Collaboration with India Hydrogen Alliance (IH2A)
JSW Steel has joined the India H2 Alliance (IH2A) to drive the transition to cleaner energy. IH2A is an industry coalition focused on creating a hydrogen value-chain and economy in India. With the participation of government agencies, sustainability think-tanks, and private sector partners, IH2A aims to reduce hydrogen production costs, promote the growth of a local hydrogen supply chain, and support India’s net-zero carbon goals.
The Company is well-positioned to take the lead in the green hydrogen sector, given its substantial investments in steel, cement, and renewable energy. As the Steel and Cement Work Group Lead within the India H2 Alliance (IH2A), JSW Steel will collaborate with industry leaders and government entities to establish a shared vision for the commercialisation of hydrogen in the steel and cement industries. By exporting green steel produced with hydrogen, India can be positioned as a global leader in the hydrogen value chain and integrate hydrogen into the industrial supply chain. This presents a significant opportunity for leadership and innovation.
Accolades & Recognitions for championing sustainability

Enhancing future-readiness with digital focus
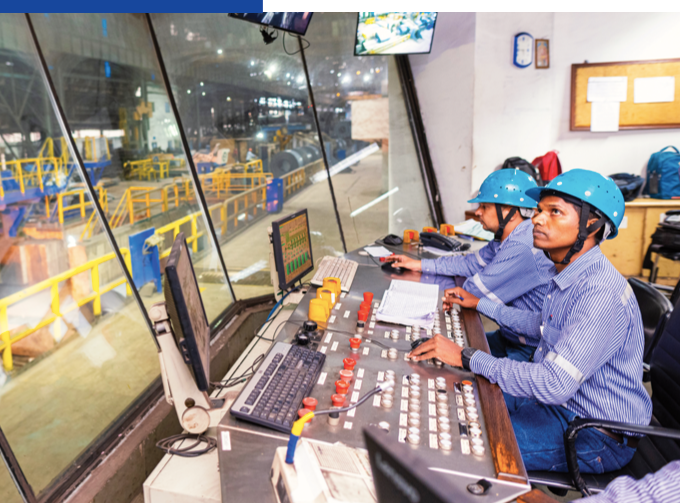
JSW Steel is transforming every aspect of its business by embracing the best available and emergent technologies across functions–Corporate, Human Resources, Manufacturing, Mining, Marketing, and Supply Chain. Harnessing the power of Big Data, Advanced Robotics, Hybrid Cloud and Artificial Intelligence, the Company is driving cultural change, augmenting customer experiences, and developing innovative products. Further, JSW Steel is upskilling in-house talent to create ‘Citizen Data Scientists’–6,000+ employees have been engaged and 130+ assets have been created across 400+ identified projects. Through digitalisation, the overarching objective is to create sustained value for all stakeholders while enhancing sustainability across the value chain.

Digital initiatives are enabling JSW Steel to improve its safety, optimise cost, drive seamless integration of operations, improve product value, and enhance customer delight. Currently, the digitalisation of maintenance activities across various steel plants saves around 1,000 person-hours of downtime and reduces man hours in manual maintenance activities.
Significant strides have been made in digitalisation across various operations. At Odisha Mines, the Company is driving initiatives to enhance efficiency and productivity. Under Project Samarth, the Company's finance function is undergoing a comprehensive digital transformation, with 38 out of 58 initiatives already implemented. Additionally, Project Sampark has successfully implemented the Digital Logistics Management System (DLMS) at our Vijayanagar and Dolvi plants, streamlining the logistics processes.
To further improve operational analytics and decision-making, Integrated Control Towers (ICT) have been installed at Vijayanagar, Dolvi, and Salem. This initiative provides real-time analytics and dashboards for plant operations. In the pursuit of cost optimisation, JSW Steel has developed the Dynachem model, an analytical tool for optimising ferro-alloy costs.
Furthermore, a Central Command Center has been set up at the JSW Mining Barbil office, enabling centralised monitoring and control of mining operations. These digitalisation efforts underscore the Company's commitment to leveraging technology for operational excellence and continuous improvement across the business.
Highlights of digital initiatives
Accolades

JSW Odisha Mines received an award for 'Excellence in ICT' from CII for various Digital projects completed


Steady financial performance despite macro challenges
For FY 2022-23, JSW Steel reported robust consolidated revenue from operations of ₹1,65,960 crore and EBITDA of ₹18,547 crore, despite lower export volumes following the imposition of export duty and pricing pressure in the domestic market.
The Company’s consolidated net gearing (net debt-to-equity) at the end of the year stood at 0.89x (as against 0.83x as on March 31, 2022) and net debt to EBITDA stood at 3.20x (as against 1.45x as on March 31, 2022).
Strong financial discipline
In June 2022, Moody's Investors Service upgraded JSW's Corporate Family Rating (CFR) and its senior unsecured notes rating to Ba1 from Ba2 with Stable Outlook. At the same time, Moody's has also upgraded the guaranteed backed senior unsecured rating on Periama Holdings LLC and the rating on the US$40 million guaranteed revenue bonds issued by Jefferson County Port Authority to Ba1 from Ba2 with Stable Outlook.
In May 2022, Fitch Ratings has upgraded the Company’s Issuer Default Rating (IDR) to "BB" from "BB-", with Stable Outlook. The agency has also upgraded the rating on the outstanding bonds of the Company and its subsidiary Periama Holdings, LLC, to 'BB' from 'BB-'.
In February 2023, CARE Ratings Ltd has reaffirmed the Company’s Issuer Rating and rating for Long-Term Bank Facilities and Non-Convertible Debentures to “CARE AA”; with Stable Outlook and has reaffirmed the ratings for the Short-Term Bank Facilities and Commercial Paper at “CARE A1+”.
In February 2023, ICRA Limited Ltd reaffirmed the Company’s rating for Long-Term Bank Facilities and Non-Convertible Debentures to “[ICRA] AA”; Stable Outlook, and reaffirmed the ratings for the Short-Term Bank Facilities and Commercial Paper at “[ICRA] A1+”.
In March 2023, India Ratings and Research affirmed the Company’s Long-Term Issuer Rating to "IND AA" with Stable Outlook.
Highlights
Completion of merger of Asian Colour Coated Ispat Limited and Hasaud Steel Limited with JSW Steel Coated Products Limited.
Better operating performance from domestic and overseas subsidiaries
Performance of key subsidiaries during FY 2022-23
The year saw better capacity utilisation of JSW Steel coated, BPSL, US and Italy business
JSW Steel Coated Products (Consolidated)
Revenue generated
₹28,772 crore
EBITDA
₹186 crore
BPSL
Revenue generated
₹20,077 crore
EBITDA
₹1,805 crore
US operations
Revenue generated
US$1,145 million
EBITDA
US$27 million
Italy operations
Revenue generated
€407 million
EBITDA
€26 million
2.0
2.8%
Global GDP growth projection for CY 2023
3.0%
Global GDP growth projection for CY 2024
6.6%
Global inflation forecast for CY 2023
4.3%
Global inflation forecast for CY 2024
2.1 GLOBAL ECONOMY
Elevated geopolitical conflict, inflation dampen growth
The world economy maintained a steady growth trajectory at the start of CY 2022, following a gradual recovery from the pandemic, but it was disrupted by the outbreak of the Russia-Ukraine conflict, steadily rising inflation and delayed normalisation of global supply chains. Inflation was on an upswing following the massive stimulus injection to ECONOMIC OVERVIEW 2.1 GLOBAL ECONOMY 2.8% tide over the pandemic. As central banks prepared to squeeze out excess liquidity to rein Global GDP growth projection for CY 2023 3.0% Global GDP growth projection for CY 2024 6.6% Global inflation forecast for CY 2023 4.3% Global inflation forecast for CY 2024 in inflation, constrained supply chains were further aggravated by economic sanctions on Russia and China’s stringent shutdown to contain the spike in COVID-19 cases. This pushed inflation in advanced economies to multi-decadal highs, led by energy and commodity prices. Accelerated rate hikes by major central banks and slowing demand and investment sentiments impacted economic growth during the year.
Core inflation, ex-energy and food prices, remained elevated, reflecting the pass-through of energy prices, strained supply chains and tight labour markets. Global GDP grew by 3.4% in 2022, down from 5.9% in 2021.
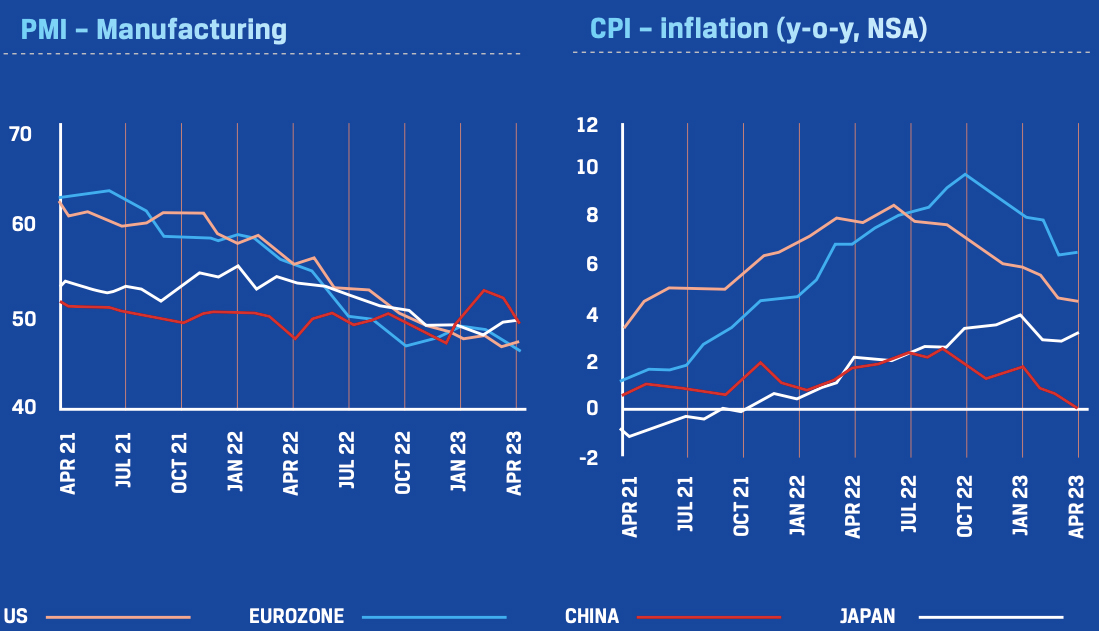
Aggressive monetary tightening by central banks started showing the desired effect on demand. Tightening financial conditions in most regions and reducing liquidity in global markets led to a strong appreciation of the US dollar, further aided by its ‘safe haven’ status during periods of uncertainty. China’s ‘Zero COVID’ policy weakened local demand, which had a spill-over effect overseas, keeping global supplies under pressure and inflation higher.
However, as global demand weakened, commodity prices started easing in the third quarter. China’s earlier than expected re-opening in end of 2022 paved the way for a rebound in global economic activity and recovery in commodity prices.

2.1.1 Outlook
Growth bottoming, inflation easing but downside risks remain
Going forward, inflation trends, central bank actions, expected recovery in China and the Russia-Ukraine conflict will determine the course of the world’s economic growth in CY 2023. Headline inflation has eased, though core inflation is yet to peak. The IMF expects global inflation to drop to 6.6% (from 8.8% in 2022) in CY 2023 and further to 4.3% in CY 2024, but still stay above the pre-pandemic levels of about 3.5%. In response, the pace and intensity of interest rate hikes by major central banks is likely to be benign, but interest rates are likely to remain higher for longer.
Global GDP growth is projected at 2.8% in CY 2023 and at 3.0% in CY 2024, led primarily by Asian economies such as India and China and other developing economies. The outlook for advanced economies such as the US and the Eurozone remains weak, with fears of a recession still looming on the horizon.
Goods and commodity inflation has cooled down significantly but services inflation in developed markets remains elevated due to tight labour markets. Aggressive policy tightening by the central banks in the US and Europe to control inflation has impacted growth and also led to a banking sector turmoil recently, which has potential for further downside risks.
The US economy is decelerating, and combined with the high wage inflation and banking sector issues, could lead to a slowdown in H2 CY 2023. The tight labour markets driven by strong services demand is expected to weaken in Q3 CY 2023. This will help cool inflation but may affect growth. Ongoing financial sector stress could force a pause in further rate hikes. There is a risk that the US will be pushed into a recession in CY 2023, with a significant decline in residential investment, despite the strong jobs market and healthy balance sheets of households.
The Euro area averted a severe recession due to good energy management helped by a mild winter, and manufacturing and services are picking up. Wage-driven inflation and any banking crisis are risks to growth. Moreover, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA), possibilities of a further decline in delivery of Russian natural gas to the Euro area could further dampen growth, especially in the case of a lower availability of liquified natural gas (LNG), which accounted for majority of gas demand, and weather factors such as a dry summer and a cold winter in Q4.
In Japan, manufacturing remains subdued but services have picked up. Wage inflation and global slowdown are risks to GDP growth. China's recovery, post the Zero COVID policy, is being driven more by services than manufacturing. Slowing exports and a lacklustre property market are headwinds. Fiscal and monetary policy is expected to be supportive as inflation remains low in China.
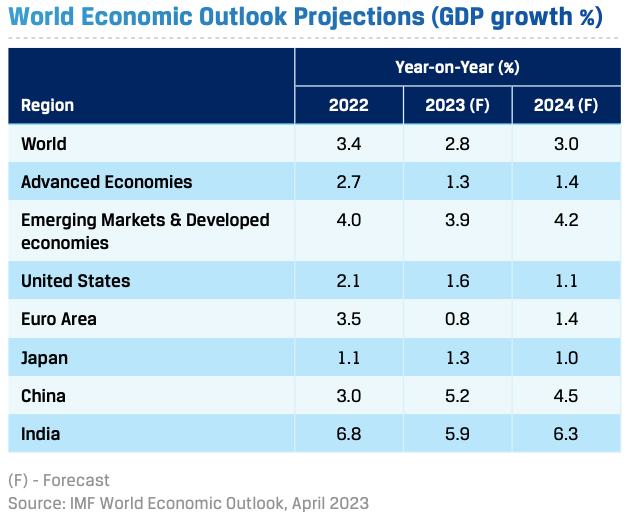
In the US, the labour market remains tight, but the consistent decline in inflation could improve sentiment. The Fed’s pivot to a less aggressive monetary policy could set the tone for CY 2023. The world economy needs a stabiliser, and Asia could very well be the sweet spot, with India and China in the forefront. China is expected to grow at 5.2% in CY 2023, while growth forecasts for India range between 5.9-6.5% for FY 2023-24. The global economy is sustaining the momentum gained in the Q1 of CY 2023 despite the still elevated yet moderating inflation, tighter financial conditions, banking sector stress, and lingering geopolitical conflicts.
2.2 INDIAN ECONOMY
The Indian economy stayed on a steady growth path, demonstrating strong resilience to multiple headwinds stemming from elevated inflation and a volatile global macro environment. The Indian economy is estimated to 1 have grown by 7.2% in FY 2022-23 , driven by strong private consumption, steady manufacturing and normalisation of contact-intensive services sectors. Although inflation remained above the upper band of the RBI’s comfort range of 4-6% for most part of FY 2022-23, it started easing during the third and fourth quarters, as the central bank hiked its policy rates by 250 basis points cumulatively to contain inflation. In April 2023, the RBI hit a pause to its rate hike cycle, and is widely expected to maintain it, if a benign inflationary environment persists.
The Indian economy growth stems from the resilience seen in the rebound of private consumption, seamlessly replacing the export stimuli as the leading driver of growth. The uptick in private consumption has also given a boost to production activity resulting in an increase in capacity utilisation across sectors. The rebound in consumption was engineered by the near-universal vaccination coverage overseen by the government, which brought people back to the streets to spend on contact-based services, such as restaurants, hotels, shopping malls, and cinemas, among others.
In FY 2022-23, growth has been principally led by private consumption and capital formation. The capex of the central government, which increased by 26% in FY 2022-23, was another growth driver in the current year. It has helped generate employment, seen in the declining urban unemployment rate and in the faster net registration in Employee Provident Fund. A sustained increase in private capex is also imminent with the strengthening of the balance sheets of the corporates and the consequent increase in credit financing it has been able to generate. The much-improved financial health of well-capitalised public sector banks has positioned them well to increase the credit supply.
However, the conflict in Europe necessitated a revision in expectations for economic growth and inflation in FY 2022-23. The country’s retail inflation had crept above the RBI’s tolerance range in January 2022. It remained above the target range for 10 months before returning to below the upper end of the target range of 6% in November 2022. During those 10 months, rising international commodity prices contributed to India’s retail inflation as also local weather conditions like excessive heat and unseasonal rains, which kept food prices high. The government cut excise and customs duties and restricted exports to restrain inflation, while the RBI, like other central banks, raised repo rates and rolled back excess liquidity. With monetary tightening, the US dollar appreciated against several currencies, including the India rupee. However, the rupee has been one of the better-performing currencies worldwide, but the depreciation may have added to the domestic inflationary pressures, besides widening the CAD. Global commodity prices may have eased but are still higher compared to pre-conflict levels. They have further widened the CAD, already enlarged by India’s growth momentum. However, the forex reserves remain sufficient to finance the CAD as well as intervene in the currency market to manage volatility in the Indian rupee.

Government’s infrastructure push continues
The government intends to kickstart a virtuous cycle of capex led by public expenditure. This will bring in a new wave of private investments, thus improving aggregate demand. Infrastructure spending of ₹111 lakh crore under the National Infrastructure Plan (NIP) and the National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP) involving ₹6 lakh crore is expected to be completed by FY 2024-25. A full recovery in aggregate demand is, however, dependent on a better recovery in private investments.
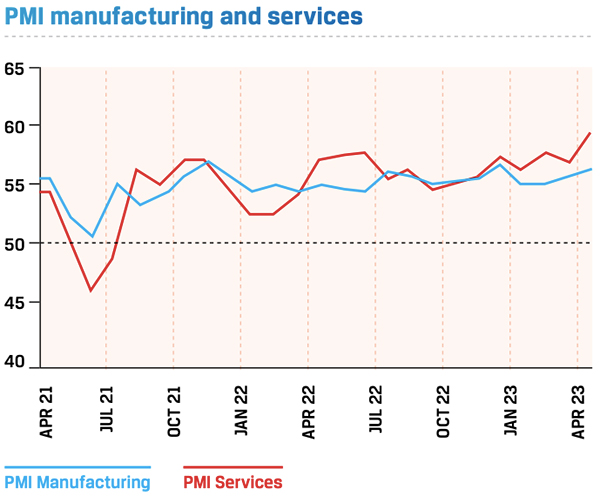
Sector-wise, India saw a resurgence in the manufacturing and services sectors. Manufacturing PMI for May 2023 was at 58.70 and Services PMI was at 61.20. India has the potential to become a manufacturing hub of the world as more and more MNCs are looking to make their supply chains less reliant on China and diversify to other developing and emerging economies.
Buoyant tax collections reflect robust economic activity
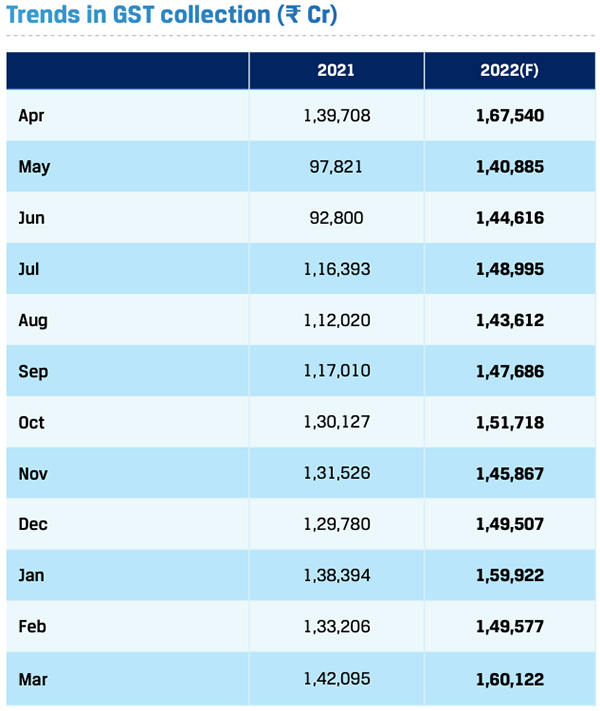
Gross tax revenues (GTR) grew by 22% year-on-year in FY 2022-23. Goods and Services Tax (GST) collections averaged ₹1.51 trillion during the period under review. In March 2023, GST revenues crossed ₹1.60 trillion–the highest monthly collection since April 2022. The strong tax revenues indicate buoyant economic activity and enables the government to maintain its healthy spending during the run-up to the General Elections in 2024.
Exports and imports stable
Meanwhile, India’s trade sector remained resilient in FY 2022-23. Imports (merchandise and services) rose 17.4% y-o-y to US$90 billion. Import demand was driven by domestic recovery. At the same time, adverse shocks in trade and demand for gold led to an expansion of the merchandise trade deficit. A strong trend in service exports and capital inflows governed by foreign direct investments (FDIs) offset the pressure on the current account balance. With little need for external funding, the reserves built up resilience for the trade sector despite global trade disturbances.
Despite a unfavourable trade environment, exports rose 14% y-o-y to US$770 billion. Exports are expected to remain steady with a rise in international demand and favourable price conditions. The risks in India’s restoring trade balance persist from the slow growth of advanced economies and emerging economies, higher energy prices and supply chain changes that occurred during CY 2022, and the effects of which might continue in CY 2023.
With little need for external funding, the reserves built up resilience for the trade sector despite global trade disturbances.
Economy continues to receive strong policy support
The India government has stressed on making India ‘Atmanirbhar’ and has laid down various incentives and policies. The Union Budget 2023-24 proposed a 33% increase in infrastructure spending to ₹10 trillion, or 3.3% of GDP, with the highest ever capital outlay of ₹2.4 trillion for railways. It has also identified 100 critical transport infrastructure projects for last mile logistics and allocated ₹75,000 crore towards it.
The Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS), introduced as a part of the COVID-19 relief package, was extended to boost credit growth. To promote manufacturing and reduce India’s import dependence, the Indian government had launched its flagship programme, Production Linked Incentive Scheme (PLI), for 2 which ₹8,083 crore was earmarked for FY 2023-242.
33%
Increase in infrastructure spending as per Union Budget 2023-24

OUTLOOK

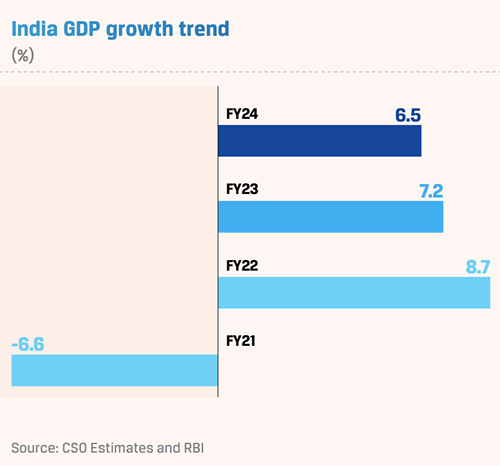
The Indian economy remains resilient and is a bright spot in the decelerating global economy. It is 3 expected to grow 6.5% in FY 2023-24 , primarily due to supportive domestic policies, easing inflation and robust consumption. The government has chosen an investment-led growth approach, which includes a well-planned medium-term fiscal consolidation and expenditure in 2023 to ensure macroeconomic stability. Capital expenditure efficiency, high-quality infrastructure spending, and process improvements are expected to increase transparency and drive growth. Expected rural recovery could provide the required tailwinds. Further, the outlook for residential real estate, auto sector, and renewables remains optimistic. Consumer and business confidence is expected to sustain going forward, as India continues on its high-growth trajectory to assert its strength in the global economic order.
Cooling inflation and the RBI pausing rate hikes is a positive, while global slowdown remains a risk. Monsoon is a key monitorable, especially for rural demand in light of the forecast for El Nino this year.
The Union Budget in India focused on Infrastructure, Manufacturing and Defence, which is a positive for steel consumption. The fiscal position benefits from lower energy prices, the sharp drop in fertiliser subsidies and strong tax collections. The manufacturing sector capacity utilisation is consistently above 72% since December 2021, which is supportive for private sector capex. Moreover, corporates and banks have healthy balance sheets to undertake capex. The banking credit growth has been in double digits for the last 14 months (April 2022 to May 2023). Improving rural consumer sentiment, healthy reservoir storage levels and improving rural wage growth points to ongoing recovery. Demand for commercial vehicles, tractors and passenger vehicles remains healthy, while recovery in two-wheeler demand is expected to be in line with the rural and semi-urban economy.
2 IBEF
3 World Economic Outlook, International Monetary Fund, (IMF) January 2023
3.0
Stable pricing expected
Backed by Asian economies like China, Japan and South Korea
3.1 GLOBAL STEEL INDUSTRY
High inflation curbs demand; supply faces margin pressure
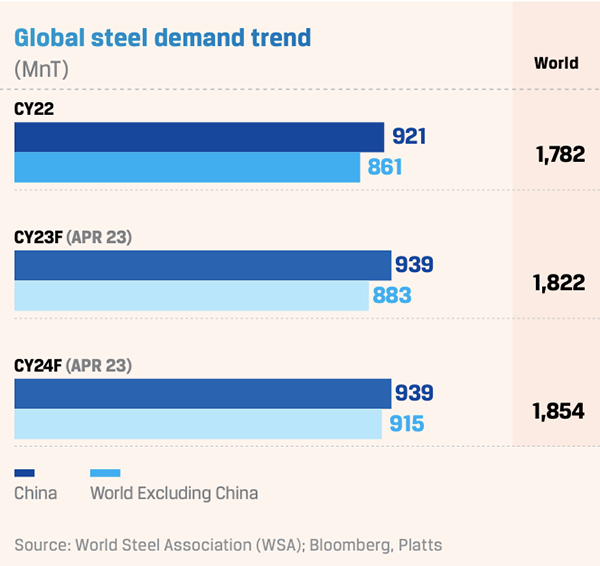
Global steel demand was impacted by high inflation and consequent aggressive monetary policy tightening by major central banks, coupled with supply chain bottlenecks. In 2022, the developed economies experienced a significant decline in steel demand due to factors such as monetary tightening and surging energy expenditure. Following a substantial 3.1 Global steel industry 3.2 Indian steel industry INDUSTRY OVERVIEW 3.1 GLOBAL STEEL INDUSTRY Stable decrease of 6.2% during CY 2022, there is an anticipation of a modest rebound with a pricing expected Backed by Asian economies like China, Japan and South Korea projected 1.3% increase in steel demand for CY 2023. Looking ahead to CY 2024, a more substantial recovery of 3.2% is expected. Further, the looming energy crisis in the EU led to weakened sentiment, aggravated by the fear of potential gas rationing in the absence of Russian supplies. China’s steel demand contracted by 4% in 2022.
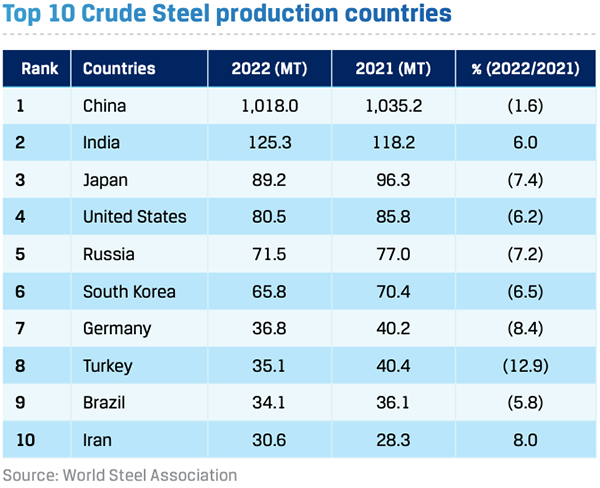
In CY 2022, total crude steel production stood at 1,885 MnT, down 3.9% y-o-y, as steel producers reduced output in response to weak demand and weak margins due to falling steel prices and elevated raw material costs. The world’s largest steel producer China recorded production of 1,018 MnT, a 1.6% y-o-y decline and Japan’s production fell 7.4% y-o-y to 89.2 MnT. This was partly offset by a 6.0% y-o-y increase in production to 125.3 MnT in India.


Improving outlook aided by infrastructure demand
China’s re-opening, lower energy cost and easing supply chain bottlenecks are likely to lead to a ~2.3% increase (after the 2022 contraction) in global steel demand in CY 2023. Chinese steel demand is expected to grow by ~2% in CY 2023, aided by a marginal recovery in the property market. Demand in the US is expected to grow moderately by ~1% in CY 2023, supported by the infrastructure sector following the 2021 Infrastructure Law and Inflation Reduction Act. A strengthening construction sector, easing supply chain and exports could boost steel demand in Japan and South Korea. Meanwhile, India’s steel demand is on track with infrastructure investments and urban consumption driving demand for automobiles and capital goods.
3.1.1 Steel Prices
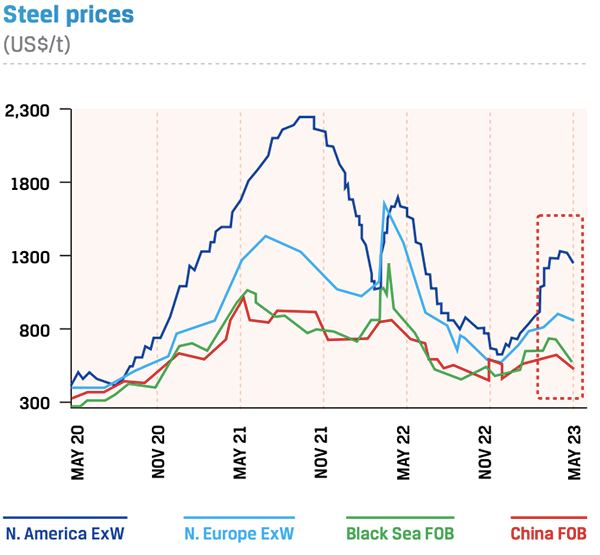
Weak prices owing to inventory build-up
The weaker-than-expected real steel demand and an increase in steel inventory through the supply chain weighed on steel prices in 2022. While the Russia-Ukraine conflict temporarily lifted steel prices in early 2022, the prices corrected sharply from April/May 2022 onwards and stabilised towards end of 2022. Prices are expected to remain stable, backed by Asian economies like China, Japan and South Korea.
3.1.2 Elevated input cost puts significant pressure on margins
The year witnessed very high volatility in raw material costs, especially coking coal, on account of the ongoing geopolitical concerns, while supply chain bottlenecks weighed on steel prices, with margins coming under pressure for most major steelmakers. Iron-ore prices averaged $120 per tonne in 2022, after touching $150 in early 2022 following the outbreak of the Russia-Ukraine conflict. However, China’s muted growth and weak real estate sector amid COVID-19 lockdowns led to a sharp fall to $80/t in October 2022. Iron ore prices saw a sharp rebound to $125/t in early CY 2023 following earlier-than-expected China re-opening and renewed optimism about the demand outlook. Moreover, during March, due to the Russia-Ukraine conflict, coking coal prices surged to over $600/t.

OUTLOOK

Commodity prices are likely to remain volatile in 2023, given the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict and the expected slowdown in three largest economies in the world–the US, China and the EU. Further, the embargo on energy exports from Russia to the EU could lead to realignment of supply chains. Meanwhile, iron ore prices are likely to soften in the second half of CY 2023 due a seasonally stronger supply environment amid a depressed steel demand environment on the back of China’s property market weakness and global manufacturing headwinds.
China’s domestic steel demand has fallen 5% year-to-date while potential weakness in exports due to depressed prices could lead to lower steel production targets for CY 2023, and in turn, weigh heavily on iron ore demand as well as prices. Japan, the third largest steel producer, has recorded 16 consecutive months of falling steel production with the majority of output being directed for the Asia market. Further, with Europe now ramping up capacity utilisation, there would be limited scope to increase steel exports. India is likely to remain an outlier with a healthy steel production growth outlook, but the risk of government measures to protect supply of high-grade ore persists, such as the export tariffs imposed in CY 2022.
Coking coal prices are expected to remain strong on tight seaborne supplies, an uncertain weather outlook and dynamic geopolitics. Further, the recovery of steel production, excluding China, driven by the restart of blast furnaces in Europe, could keep coking coal prices elevated into CY 2023. In Europe, ~14 MTPA of BF capacity is estimated to have returned, translating into ~9 MnT of coking coal demand, assuming 80% utilisation. With 11 MTPA of BF capacity still to return, demand for raw materials will continue to increase going forward.
Meanwhile, overstocking and a warm winter led to a regional inventory build-up of gas and coal. European coal demand is expected to remain until start of next winter. Coal importers including China, Southeast Asia and India continue to buy Russian coal. Further, the reduction in Russia pipeline gas exports to Europe prompted many countries to consume more coal.
3.1.3 Demand outlook for consumption sectors
Automotive
The global auto sector is expected to witness easing supply chain disruptions, leading to higher global vehicle production in CY 2023. Global sales and production is expected to rise about 5% in CY 2023 from the depressed levels seen in CY 2022. Despite weak economic conditions and higher interest rates, vehicle demand will benefit from high pent-up demand, due to industry under-production in the past years. Normalisation of vehicle pricing and mix will likely bring back customer interest.
The Indian automobile industry accounts for 7.1% of India’s GDP and by the end of the year 2024, India has set a target to increase the size of its automobile industry to ₹15 lakh crore, effectively doubling its current size. Additionally, the industry has witnessed a significant inflow of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) amounting to $33.77 billion from April 2000 to September 2022. This FDI inflow represents approximately 5.48% of the total FDI inflows received by India during the same period. This indicates the attractiveness of the Indian automotive industry to international investors and its potential for further expansion.

Construction
The global construction industry is expected to experience moderation in real growth in CY 2023 across the majority of markets. The overall real construction industry value in most regions will likely return to pre-pandemic levels. The growth is driven by the rising government spending on planned infrastructure projects. India, the US, and China are expected to account for a 50% share of the projected construction spending. An enhanced focus on energy security will emerge as an increasingly important driver of infrastructure investment globally in CY 2023.

Capital Goods
Demand for domestic production is the focus of most economies to drive growth. Additional demand from the renewable sector as part of the energy transition initiative, and expected higher outlays on defence spending by Europe in the context of the ongoing war, will complement the growth in steel demand globally. Increasing automation and innovative processes of production also boost steel demand.

3.2 INDIAN STEEL INDUSTRY
3.2.1 Short-term pains,
long-term growth story intact
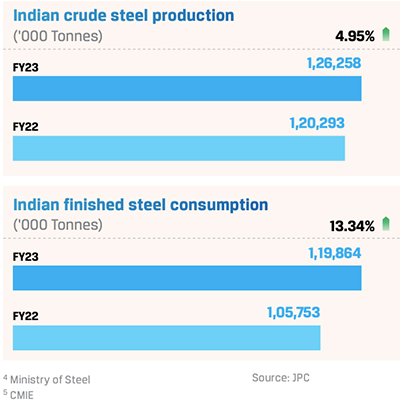
ndia is the second-largest producer of crude steel in the world, with an output of 126.2 MnT in FY 2022-23. Crude steel production rose 5.0% year-over-year while finished steel consumption rose 13.3% to 119.9 MnT4. Although production and consumption increased due to robust domestic demand, margins came under pressure due to high raw material and energy costs. The imposition of export duty on steel led to the built-up of domestic inventories, as exports became unviable in the weak global price environment. Further, few low-priced shipments from Russia and duty-free steel from FTA countries made their way to domestic markets, as imports rose sharply putting more pressure on steel prices5
Production and consumption
The India government has set a target to increase crude steel production capacity from 160 MTPA in FY 2022-23 to 300 MTPA by FY 2030-31 under the National Steel Policy. Further, the NITI Aayog has stated that India will become the world’s production centre for green steel and pave the way for its worldwide adoption. With the fourth industrial revolution, Industry 4.0, underway, the Indian steel industry is leveraging the power of Machine Learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), and smart manufacturing to improve efficiency and strengthen sustainability.
3.2.2 India steel trade
Exports dip; imports rise as cheaper steal dumped in India
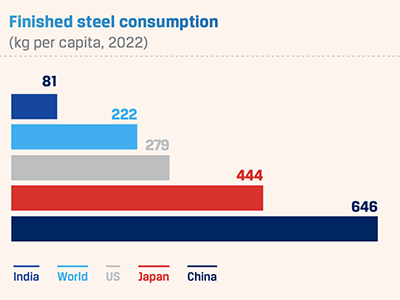
India’s steel exports dipped by 54.1% to 47.41 lakh tonnes from April to December 2022, largely due to the weak global demand and the imposition of 15% export duty on steel products between May 2022 and November 2022.
Further post withdrawal of export duty in November 2022, the import duty on coking coal, anthracite/PCI, and ferronickel, which are used as raw materials in steel making, was hiked to 2.5%. Import duty for coke and semi-coke was raised to 5% from zero, making Indian steel uncompetitive in global markets. On the other hand, finished steel imports jumped 27.4% year-on-year between April 2022 and December 2022, as the slowdown in the US and Europe prompted large steel producers like South Korea, Japan and Vietnam to divert excess production to the Indian markets.
OUTLOOK

Against the backdrop of soft global economic outlook, India remains a bright spot with rising demand for steel. India domestic demand grew 13.3% year on year in FY 2022-23, recording consecutive two years of double-digit growth. According to ICRA, domestic steel demand is estimated to grow at 7-8% in FY 2023-24, owing to strong demand from end-user industries such as construction, infrastructure, automobile, real estate, and consumer durables and enabling steel players to maintain high capacity utilisation levels. In addition, the benefits of easing raw material prices are expected to flow through Q2 FY 2023-24 onwards. Further, the rollback of export duty should support exports, though near-term outlook remains challenging.
Steel demand drivers
Infrastructure and construction: The epicentre of demand
In the reporting period, urban residential real estate cycle remained strong with robust, new launches and high affordability, despite higher interest rates. Renewables saw large investments driven by increasing power consumption and green energy transition. Further, the government’s push for infrastructure and social development continued to be firm. The NHAI pipeline for the next three years remains strong and InvITs are gaining traction with continued interest from foreign players. The NIP, PLI scheme and defence indigenisation are driving private CapEx.
Policy support and key initiatives for steel demand
Budget 2023-24 allocation
Government initiatives
Automotive: Going full throttle
In FY 2022-23, the Indian auto sector witnessed healthy demand for passenger vehicles (PV) and commercial vehicles (CV) as chip availability corrected. The outlook for two-wheelers and tractors is improving. Further, the rural economy is expected to recover on better winter crop, elevated reservoir levels and moderating inflation. With large demand incentives for electric vehicles (EV) from both central and state governments, there is going to be a major shift towards EVs. Infrastructure boost and CapEx investments by the government augurs well for the MHCV and tractor segments going forward. The auto sector also stands to benefit from the PLI boost. However, the CV space is expected to grow slowly due to weak transporter profitability and delayed buying.
Vehicle Scrappage Policy
Under the Scrappage Policy 2022, the central and state governments offer a 25% tax rebate on road tax for vehicles purchased after scrapping older ones. Additionally, the government is actively working to establish scrapping facilities within 150km of every city in the country. As per the latest announcement, all central and state government vehicles over 15 years will be scrapped from April 1, 2023. This will benefit automotive replacement demand and, in turn, drive steel consumption.
Localisation and sourcing of auto parts
Many auto OEMs are trying to localise sourcing using India as an export base for auto parts.

JSW Steel strives for excellence with its state-of-the-art and integrated manufacturing facilities, and differentiated product mix, with increasing share of valued-added products. The Company is well-positioned to capitalise on the existing and emerging opportunities by addressing diverse customer needs, as India and the world look to build a sustainable future. With a steadfast commitment to delivering excellence, JSW Steel has been delivering consistent performance across financial and non-financial metrics, with innovation, digitalisation and sustainability as its core strengths.
4.0
Record total, domestic, auto grade and appliances segment sales.
Business highlights FY 2022-23
24% y-o-y
Growth in India operation sales
10% y-o-y
Highest-ever growth in coated steel sales
57%
Share of VASP in total sales. VASP volumes up 17% as new downstream capacities became operational
36% y-o-y
Increase in supplies to Automotive segment, while auto industry production# grew 26%
30% y-o-y
Growth in sales to appliances segment
83%
Share of Longs Specials (excl. TMT)
13% y-o-y
Increase in sales of Electrical Steel
39%
Share of retail segment in domestic sales
49% y-o-y
Growth in branded sales volume

Export performance
During FY 2022-23, the Company’s share of exports in the total sales mix dropped to 13% from 28% in the year earlier, as export volumes fell 45% largely due to the imposition of export duty in May 2022. However, in Q4, exports surged by 144% QoQ post the removal of export duties.

Contributing to India’s High-Speed Rail Journey
JSW Steel is supplying high-strength TMT Bars, HR Plates, and LRPC for the Mumbai-Ahmedabad High-Speed Rail (MAHSR) project. As the first of the government's planned 12 lines, the MAHSR corridor will span over 500km, allowing for a swift journey of 2 hours and 58 minutes at a maximum speed of 320 km/hr. With this, JSW Steel becomes one of the leading suppliers, accounting for over 50% of the steel provided. The Company is excited about the upcoming feasibility study and assessments for the Varanasi-Delhi bullet train project, spanning approximately 865km. Committed to supplying high-quality steel, JSW Steels aims to continue to support India's ambitious infrastructure initiatives.

Contributing to India’s green energy transition
Steel is used in windmills for towers, generators, rotor hubs, blades, nacelle and gearbox. JSW Steel supplies HR plates for tubular tower, which is used in the top, middle, and bottom sections, as well as the door floor. JSW Steel supplied steel to ~1.4 GW of wind projects.

Enabling automakers to make mobility safer and efficient
JSW Steel is working closely with automakers to make cars safer, lighter and fuel efficient. JSW’s AHSS (Advanced High-Strength Steel) with high-tensile strength and optimum formability enable OEMs to achieve high safety ratings. Major crash and safety components are made with AHSS. The Company has also developed steel for suspension parts that require optimum fatigue life as well as high strength.
4.1 PRODUCT PERFORMANCE
JSW Steel has placed a strategic emphasis on enhancing its share of VASP in the overall sales mix, and has made significant investments in driving product innovation. As a result, the Company maintained its share of VASP sales at over 50% during FY 2022-23.

4.1.1 Flats
Flats, comprising Hot Rolled, Cold Rolled, Colour-coated, Galvanised, Galvalume and Avante Steel doors contributed 75% to the top line in FY 2022-23, up by 26% from the previous year. The increasing sales margins were attributed to sales growth of value-added flat products.
Hot Rolled (HR)
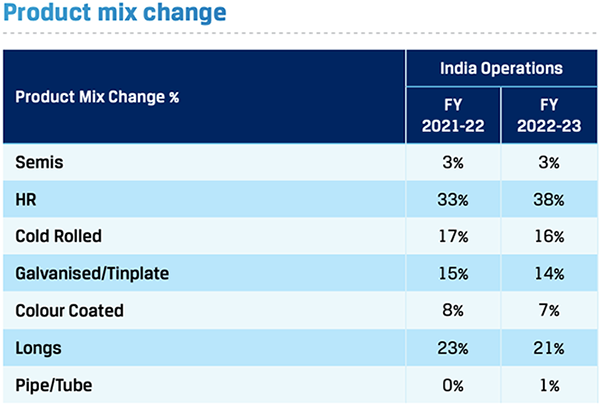
JSW Steel's hot-rolled products are known for their high quality and consistent performance. Using state-of-art equipment and manufacturing processes, Hot Roll coils are manufactured at Hot Strip Mills at Vijayanagar, BPSL and Dolvi. Hot Rolled products are used in structural and general engineering, tubes and pipes, and LPG cylinders. Key industries to which hot rolled product caters are Industrial & Engineering, Automotive, Energy, and Capital Goods. Hot Rolled products constituted 38% of the total product mix in FY 2022-23.
Key projects served in FY 2022-23
42%
Sales growth y-o-y
Cold Rolled (CR)
The Vijayanagar plant has the widest cold rolling mill in India, where the CR Closed Annealed Sheets and Coils are manufactured. It is extensively used in Automotive, Consumer Durables, Industrial & Engineering, and Electrical Panels. Cold Rolled products constituted 16% of the total product mix in FY 2022-23.
19%%
Sales growth y-o-y
Cold-Rolled Close Annealed (CRCA)
The Cold-Rolled Close Annealed (CRCA) category makes up a robust part of the total share of flat product sales. In FY 2022-23, demand driven by the PV segment enabled the CRCA category to sell its highest-ever volume. JSW Steel has taken an early lead in collaborating with auto majors to develop new grades of steel. The Company has developed HSLA and AHSS, which are specialty steel grades that go into impact resistance and light-weighting. These new grades enable Auto OEMs to respond to customer demand for eco-friendly vehicles by using lightweight steel that increases fuel efficiency and helps carbon neutrality.
19%
Sales growth y-o-y
Electrical steel
The Electrical Steel product range continues to provide solutions to achieve higher energy efficiency of electrical equipment like Motors, Pumps, Fans, Domestic Appliances, White Goods, Power Generators and Small Transformers, thereby contributing to a sustainable and Atmanirbhar Bharat. CRNO grades were customised specially for the fast-growing segments of Two-Wheeler EVs and Air Conditioner Compressors. JSW Steel has maintained its preferred supplier status in the Wind Energy and Railway Traction Motor segments by consistently supplying energy-efficient electrical steel solutions.
13%
Sales growth y-o-y
Coated
Coated steel is an anti-corrosive value added material, and Galvanised accounts for more than half of demand, Galvalume and Colour coated are fast growing categories with applications across multiple industries.
Significant headroom for growth as India’s per capita use of coated steel at ~6kg compared with 50-60kg in the US, Europe; rural consumption to be key growth driver; coated steel demand to grow at ~10% CAGR to cross ~13 MTPA in FY 2024-25, which is 1.5 times the growth of domestic GDP (7-7.5%).
JSW coated steel at present services multiple brands for GI (Vishwas), GL (Silveron), Colour Coated (Everglow, Colouron+, Pragati+) and OEM products (Radiance).
Colour coated
JSW’s colour-coated steel is corrosion-resistant and is used in manufacturing value-added products that address construction, warehousing and roofing requirements. JSW colour-coated products, stands strong in the current market landscape, and emerges with a leading market share of 48% and with an overall domestic sales reaching 1.34 MnT. JSWSCPL is the only Company to have brands across multiple price ladder segments, namely Everglow in super premium, Colouron in premium, Pragati in popular and the recently launched Indradhanush in the mass-market segment.
8%
Sales growth y-o-y
JSW Steel has teamed up with JSW Paints to launch new coating variants, including Anti-Dust, Hi-Gloss, and Cool Roof. The Cool Roof paint system is a sustainable product, offering better heat reflectivity to reduce the temperature inside buildings and relieve the heat load on AC systems. The Anti-Dust variant has been designed for public infrastructure projects to help maintain a long-lasting, attractive appearance in challenging environments. The Company is dedicated to maintaining its strong position in the appliance business by providing a range of new colours and coating combinations to its customers. Furthermore, it continues to supply colour-coated products for several prestigious national and international projects.
JSW Steel is expanding its product portfolio aligned with the expansion plans of its clients through the Early Vendor Involvement process. It is collaborating with multinational customers to supply materials to their global operations, while also developing grades that support the 'Make in India' initiative, boost domestic demand, and aid import substitution. The Company is working closely with its customers to source high-quality material for their diverse end-use applications and has undertaken specific localisation projects to assist them.
Benefitting from the PLI Scheme
JSW Steel has qualified for the PLI scheme for specialty steel. The Company has been approved for 6 categories. This includes six projects which are already underway at a committed cost of ₹5,350 crore.
Galvanised and Galvalume
Galvanised and Galvalume products make up 12.4% of the total product mix. JSW Steel is the country's largest producer of Galvalume products that are preferred for roofing and cladding end uses due to their superior corrosion resistance and heat reflectivity, as well as longer lifespan with the same coating weight. As demand in the solar segment continues to surge, new grades are being developed to meet emerging needs and broaden the sector's customer base.
The JSW Galvos brand is designed to address the typical challenges that solar panel installations face, such as harsh outdoor conditions and being embedded in the ground. Galvos is specially equipped to withstand challenging alkaline and corrosive environments, in conjunction with an epoxy/ PU layer, and has been performing well in this segment. Last year, to address the needs of solar trackers, HSLA grades were developed for making torque tubes for Indian and export markets, a first in the industry. These grades have been approved by major global solar players for use in their installations in India and abroad. JSW Steel is collaborating with global developers to offer these solutions worldwide.
GI & GL products constituted 43% market share of domestic market and JSW increased domestic sales by 37% y-o-y. The alloy-coated galvanised and galvalume products are versatile and characterised by high corrosion resistance and heat reflectivity.
37%
Domestic sales growth y-o-y

Tinplate
Tinplate is a highly sustainable packaging material with endless potential as it can be recycled indefinitely, making it more environmentally friendly than many other competing materials. It is also one of the most valuable downstream products in the flat steel segment. The global demand for tinplate is expected to rise as the world looks for sustainable packaging materials. Domestic demand has been steadily improving due to increasing urbanisation, change in food habits that favour packaged food, and a growing variety of food retail options. Following the commissioning of the second tinplate line of 0.25 MTPA at Tarapur in September 2022, JSW Steel now has the largest tinplate capacity in India. JSW’s growth in tinplate as a premium product is 8% y-o-y, and is largely replacing imports with a present market share of 38% in the domestic market.
JSW envisages this category growing steadily and has expanded capacities in order to capture more variants within the prime grades for BIS certified tinplate. Currently, 30-35% of India’s total tinplate demand is met from imports.
8%
Sales growth y-o-y


4.1.2 Longs
Long products are inputs for large-scale infrastructure projects and indispensable elements for road constructions, laying of metro and rail infrastructure, bridges, power and nuclear plants. JSW Steel sold 4.68 MnT of long products, recording 15% y-o-y growth in FY 2022-23.
TMT
JSW Steel’s TMT bars offer superior strength and flexibility. Made with virgin iron ore, it has the highest grade of purity. Itis made through state-of-the-art MORGAN technology, known for producing high-quality HYQST (High Yield Quenched and Self Tempered) through the METCS (Morgan Enhanced Temperature Control System) process. Its features include being easily welded, anti-corrosive and bendable, making it the product of choice for users.
Demand for TMT in India is rising due to the government's thrust on infrastructure development projects. Long products are vital input materials for large-scale infrastructure projects, including road construction, metro and rail infrastructure, bridges, power plants, and nuclear plants.
JSW Steel is providing its TMT long products to over 500 ongoing projects across various categories, with road projects accounting for more than 20%, metro rail projects for approximately 10%, and the rest comprising various railway projects.
Key infrastructure projects underway
For IKEA, Hyderabad, JSW Steel supplied 72%+ of TMT bars.
13%
of the product mix
40%
Sales growth y-o-y in FY 2022-23
Wire rods
Wire rods are made using the latest technology and are designed to offer superior quality and meet multi-application requirements. Manufactured at Vijayanagar, Salem and BPSL, wire rods comprise 5% of the Company’s product portfolio and find applications in automobiles, general engineering, spring applications, welding, machining, and bearings, among others. With the growth of India's Automotive and Industrial Manufacturing sectors, the demand for wire rods has seen a significant increase.
5%
Of the product mix

Alloy steel
JSW Special Alloy Steel is produced at Salem Works, India's largest primary integrated special alloy steel plant. Sales of alloy longs increased by 15% during FY 2022-23 and accounted for 4% of the product mix. A total of seven new grades have been developed for various applications such as automotive, textile machinery, general engineering, and more.
During the year, the Salem plant received 16 product approvals and four steel mill approvals spanning auto, oil & gas, bearing, mining, wind energy, general engineering, and more. The strategic location of Salem provides the advantage of lower transportation costs and faster delivery as it is well connected to highways and stockyards across India.
Various technology initiatives, including digitisation, have helped improve operational efficiency and enhance product quality.
Moreover, Boron Wire Rod grades have been successfully developed and commercialised at the Vijayanagar plant, further expanding the product portfolio. With the government's PLI scheme aimed at promoting the domestic production of specialty steel products, JSW is anticipating enhanced product development and accelerated prototyping in this category, as applications are now being accepted.
4%
Of the product mix

4.2 BRANDING INITIATIVES
Consumer is at the core of all marketing and branding initiatives with a high degree of focus on expanding retail footprint and enhancing brand value through strategic marketing programs that drive awareness and consideration. JSW Steel's marketing strategy is in sync with its organisational strategy of becoming the market leading producer of premium, specialised and value added products. Our ability to build strong brands that have a meaningful presence in consumers' lives has led to prestigious wins, including the 'Iconic Brands of India for 2022' and 'Excellence in CX1 2022' awarded by Economics Times.


New product launches
LRPC (Low Relaxation Pre-stressed Concrete Steel Strands):
JSW Steel has recently introduced a new product, the Low Relaxation Prestressed Concrete Steel Strands (LRPC). This 7-ply HT Steel Wire strand is being produced under the subsidiary Neotrex Steel Pvt Ltd and is specifically designed for the construction industry. The LRPC is being utilised for prestressing concrete in various construction applications such as bridges, flyovers, high speed rail corridors, elevated metro corridors, nuclear reactors, windmills, LNG tanks, cement silos, high-rise buildings, commercial structures such as cineplexes, IT parks, shopping malls, etc. LRPC-based structures offer multiple benefits like reduction in concrete usage, labour, and time, while also providing longer spans, sleeker structures, higher structural safety, and increased usable space.


Retail initiatives
JSW Steel strives to establish a powerful connection with its retail network and influencers, prioritising an exceptional purchasing experience for its consumers. With over 16,500 exclusive and non-exclusive retail outlets, 370 distributors, and a widespread presence across more than 1,500 towns in India, the Company's retailing and distribution network is one of the largest in the country. This extensive network enables JSW Steel to cater to its customers' varied demands and provide them with a seamless procurement process.
5.0
6th
Largest steel plant globally
12 MTPA
Capacity
5.1 VIJAYANAGAR WORKS
Vijayanagar Works is JSW Steel’s flagship plant with a capacity of 12 MTPA and is the sixth largest steel plant globally. One of the most productive steel plants in India, it produces 800+ tonnes per person per annum.
Competitive strengths

Year in review
6.3 MnT
of iron ore requirement met through Karnataka captive mines
Colour-coating line of
0.3 MTPA
commissioned during the year as part of the Cold Rolling Mill 1 expansion
Commissioned the Coke Oven Battery A of capacity
0.75 MTPA
resulting in reduction of procurement of coke from third parties
Installation of Rebar Coil rolling and Billet Grinding facility at Wire Rod Mill, to roll special grades
Implemented the best available technology (MEROS) at Sinter Plant-2 for sinter flue gas treatment, i.e., SOx and NOx reduction
Downhill conveyor from the Devadari mines to the intermediate point of pipe conveyor was commissioned during Q4 FY 2022-23

Digitalisation initiatives
Digital Initiatives for project monitoring at the 5 MTPA Vijayanagar expansion

Environmental initiatives
Vijayanagar Works has undertaken a number of initiatives in line JSW Steel’s decarbonisation commitments for 2030 with Project SEED (Sustainable Energy Environment and Decarbonisation)


Environmental initiatives
Workplace safety
Road safety management
STRATEGIC INITIATIVES
FY 2023-24
− Commissioning of Coke Oven Battery B of capacity 0.75 MTPA
− Enhance capacity of Coke Oven Plant by 1.5 MTPA to support the 5 MTPA steel-making expansion
8.5 MTPA
Flat products
1st
Plant to adopt Conarc technology
5.2 DOLVI WORKS
JSW Dolvi Works is a 10 MTPA integrated steel plant located strategically in Maharashtra on the west coast of India. JSW Steel acquired the 3.3 MTPA Dolvi plant in 2010 and has since increased the capacity to 10 MTPA through brownfield expansions. Dolvi is connected to Dharamtar Jetty which has a cargo-handling capacity of 28 MTPA, across 1,400+ acres.
Dolvi Works is largely focused on flat steel production. Of the total 10 MTPA capacity, ~8.5 MTPA is for flat products and ~1.5 MTPA is for long products.
It is the first plant in India to adopt a combination of Conarc technology for steelmaking and compact strip production for producing hot-rolled coils, providing the unit with the flexibility to use a combination of solid charge and hot liquid metal. It is also the first one in the country to utilise dry Gas Cleaning Plant (GCP) and Energy Recovery System (ERS) in SMS.

Year in review

Competitive strengths
Cost-reduction initiatives
Digitalisation initiatives
Dolvi Works uses digital technology to drive operational efficiency. The plant has improved predictive power to reduce over-injection in the BF, implemented Computer Vision Machine Learning (CVML)-based production enhancement and enhanced predictive maintenance. It also aims to implement automated logistics operations (SAMPARK) to reduce process and turnaround times and enhance end-to-end logistics visibility. The plant has increased productivity through a reduction in green ball rejection, post utilising video analytics for pellet plant balling disc optimisation. It helps achieves dynamic product optimisation by getting advanced information about incoming hot metal through Torpedoes to Steel Melting Shop, thereby making optimised hot metal distribution in shells.
STRATEGIC INITIATIVES
FY 2023-24
− Increase the capacity utilisation at Dolvi
− Increase use of renewable energy to substitute for thermal power
One of the
largest special
alloy steel plant for longs products
Grinding Media
Steel Ball Mill
commissioned
5.3 SALEM WORKS
JSW Steel’s Salem plant is India's largest specialty steel plant, with a production capacity of 1 MTPA.
Competitive strengths

Cost-reduction initiatives

Projects commissioned in FY 2022-23
Grinding Media Steel Ball Mill
As part of our product diversification strategy, we have taken an initiative to set up a 0.2 MTPA Grinding Media unit, with unique Skew Rolling technology, a first of its kind in India. This facility will make forged Grinding Media balls, from 25-150 mm diameter available to Indian and global markets. This technology has been chosen in adherence to the Company's commitment to sustainability.
Bright Bar capacity enhancement
To increase value addition of finished products, introduced one Centreless Grinding Machine to enhance the Bright Bar production capacity.
PCI upgradation
System upgradation of handling up to 200kg PCI rate in the higher production level of hot Metal Production. Various safety measures and automation systems have been incorporated in this modification.
Strategic priorities for FY 2023-24
Auto inspection lines for Bar Rod Mill and Blooming Mill
Two Auto Inspection Lines consist of straightener, Shot blasting, Internal and Surface Quality Checks, Cutting and Chamfering, Bar End Marking, Bundling and Packing activities among others to handle ~20kt/month.
Automated slow-cooling facility for Blooming Mill
To meet the quality requirements of customers, the automated slow-cooling facility has been introduced. It eliminates the risk of handling hot bars manually, through a uniquely developed fully automated process.
FEMS
Final Electro Magnetic Stirrer(FEMS) in Caster -2 to achieve a more homogeneous liquid steel composition (segregation). With the use of F-EMS, the solidification structure of the cast product will be improved.
Township construction
100 houses are aimed for development under this priority.

STRATEGIC PRIORITIES
FY 2023-24
− Auto inspection lines for Bar Rod Mill and Blooming Mill
− Automated slow cooling facility for Blooming Mill
− Online auto marking facility
− Township construction (100 houses)
6.0
11% y-o-y
11% y-o-y Growth in revenue from operations
19% y-o-y
Growth in steel sales volume (highest ever)
6.1 STANDALONE
In the first half of FY 2022-23, high inflation across major economies due to supply chain disruptions and the Russia-Ukraine conflict impacted the global economic environment. Growth slowed down in 2022, driven by elevated inflation leading to tightening monetary policy actions by central banks globally. Geopolitical tensions led to elevated energy prices and shortages. Aggressive tightening by the US Federal Reserve caused sharp depreciation of other currencies and created financial market volatility and macro imbalances.
During the second half of FY 2022-23, supply chains improved and inflation across major global economies cooled off, but there was a risk of a mild recession in the developed markets. The reversal of Zero Covid policy in China and the country's re-opening, as well as declining inflation globally, provided tailwinds to global growth in the second half of FY 2022-23.
While India has been relatively resilient, high inflation and policy rate tightening across the world have become formidable headwinds. The domestic steel industry was impacted by falling global prices and the imposition of a 15% duty on certain steel exports in May 2022.
In India, though inflation has been above the RBI’s threshold levels, the economy has been growing steadily, and has been the fastest-growing economy for the next three years. The government’s infrastructure push, improvement in capacity utilisations, a broad-based revival in credit growth, strong corporate and bank balance sheets, and upbeat consumer and business confidence are all factors contributing to steady growth. However, slowing global growth and macro imbalances pose the threat of being significant headwinds.
Inherent demand from the auto and construction and infrastructure segments remains strong, which supported overall steel consumption during the period under review.
6.1.1 Production and sales
In FY 2022-23, the Company reported its highest ever crude steel production at 20.87 MnT, with an average capacity utilisation level of 91% as against capacity utilisation of 89% in FY 2021-22. The crude steel production increased by 18% y-o-y primarily due to ramp up of Dolvi Phase II expansion of 5 MTPA which was commissioned in FY 2021-22.
During the year, the Company reported its highest-ever growth in steel sales volume at 19.67 MnT, up by 19% y-o-y. The Company exported 1.8 MnT of steel, lower by 50% y-o-y, and accounted for 9% of the total sales, as against 22% in FY 2021-22. Domestic sales stood at 17.90 MnT, an increase of 38% y-o-y driven by domestic demand for steel. The domestic steel demand grew by 13% y-o-y to 120 MnT primarily due to Government’s thrust on infra, housing and increasing the share of manufacturing in GDP and increased demand from the auto sector.
The Company’s branded products’ sales was at 39% of total retail sales.

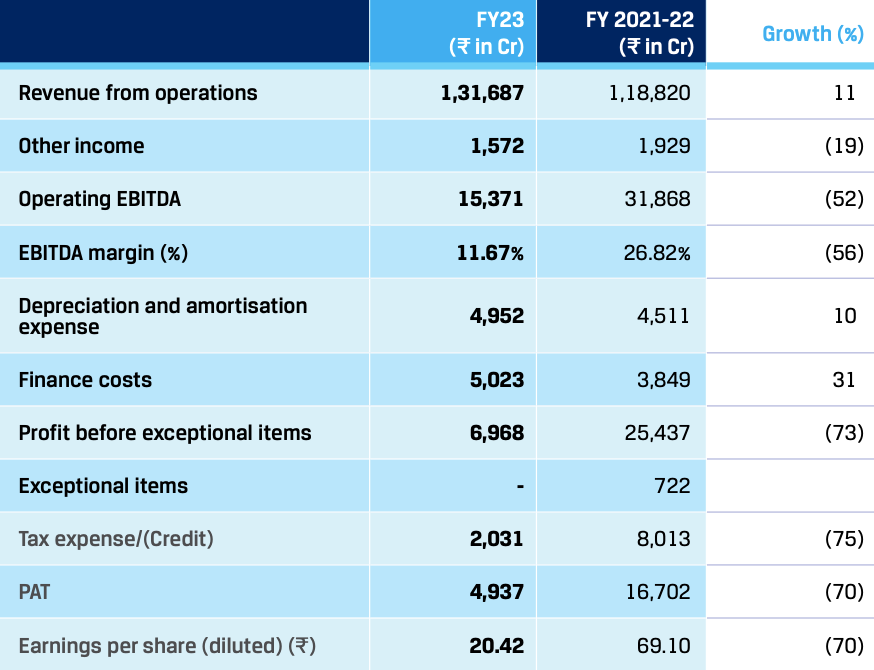
6.1.2 Revenue and EBITDA
Revenue from operations rose 11% y-o-y to ₹1,31,687 crore, backed by strong domestic sales volumes, partially offset by lower sales realisations. The sales realisation was lower by 6% y-o-y on account of decline in steel prices attributed to lower international steel prices and imposition of export duty on steel from May 2022 to November 2022. The imposition of export duty on steel led resulted in steel fall in exports.
During the first half of FY 2022-23, the Company’s performance was significantly impacted by the sharp fall in steel prices. This was due to a decline in international steel prices caused by a slump in steel demand and imposition of export duty in India. The benefit of lower raw material prices flowed through with a lag. Further, one-off items such as NRV (Net Realisable Value) provisions and inventory losses, mark-to-market unrealised loss on foreign currency loans and payment of export duty on exports further impacted operating performance.
The Company registered better operating margins in the second half of FY 2022-23, primarily due to a reduction in costs, mainly lower coking coal prices and stable sales realisation.
Overall despatches from Karnataka and Odisha’s captive mines constituted 41% of iron ore requirements of the Company. Unprecedented increase in international coal and other raw material prices due to geopolitical issues and rupee depreciation of ~8.5% resulted in increase in total cost.
The Company achieved an annual Operating EBITDA of ₹15,371 crore, a decline of 52% y-o-y with an EBITDA margin of 11.7%. The EBITDA per tonne was ₹7,814 during FY 2022-23, lower by 59% y-o-y, primarily on account of decline in sales realisations and increase in input costs of coal, power and fuel.
Domestic steel demand remained robust driven by strong growth in overall consumption and government spend on infrastructure. Moreover, supply fluctuations in the commodities’ market drove input prices higher, specifically coal and gases. The Company focused on improving market share in the domestic markets, as exports were impacted due to the rolling out of export duty.

Revenue Analysis
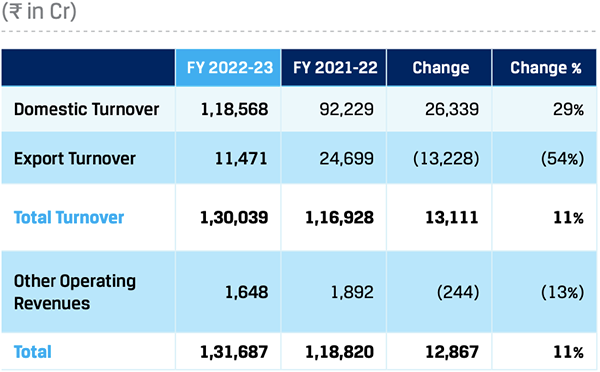
The domestic turnover increased to ₹1,18,568 crore in FY 2022-23 from ₹92,229 crore in FY 2021-22. The domestic turnover increased by 29% y-o-y primarily due to increase in domestic despatch volumes by 38% due to better domestic demand on account of driven by Government infrastructure spend partially offset by decline in sales realisations by 6% due to lower international prices and imposition of export duty. The export turnover was lower at ₹11,471 crore in FY 2022-23 as compared ₹24,699 crore in FY 2021-22. The export turnover declined by 54% y-o-y on account of decline in export volumes by 30% and decline in steel prices.
6.1.2.1
Other Operating Income
Overall other operating revenue was ₹1,648 crore in FY 2022-23 as compared to ₹1,892 crore in FY 2021-22. Theother operating income was lower by ₹244 crore, largely due to the lower Export Incentive income by ₹177 crore and lower Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) grant income by ₹364 crore due to subdued exports during the year under review. However, this decrease was partially offset by higher Government grant (Package Scheme of Incentive) recognised to the extent of ₹262 crore due to higher sales volume in the State of Karnataka and Maharashtra on account of robust domestic demand.
6.1.3
Other Income
The other income for the previous year included an amount of ₹702 crore representing fair valuation gain on re-measurement of optionally fully convertible debentures held by the Company in one of its joint ventures. This lower income was partially offset by higher interest income from cash balances, higher interest income from loans extended to subsidiaries (including that of previous years) and higher fixed deposits and dividend income received from its investment in subsidiaries and Group companies.
6.1.4
Materials
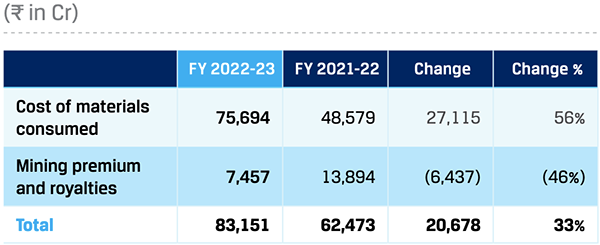
The expenditure on material consumption increased by 56% y-o-y to ₹75,694 crore primarily on account of 58% increase in coking coal costs ($ 333 per tonne in FY 2022-23 vs $ 211 per tonne in FY 2021-22) due to supply chain disruptions and the Russia-Ukraine conflict, increased iron ore procurement from third parties and increased consumption of raw materials due to increase in production volumes by 18%.
6.1.5
Employee Benefit Expenses
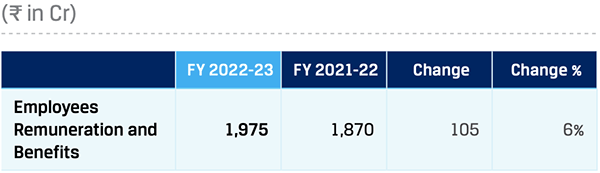
Employee benefits expenses were higher in FY 2022-23. This was due to annual increments and ESOP charge on account of new ESOP 2021 grants, which was partially offset by the reversal of provisions related to leave encashment following the revisions to leave policies. The overall headcount increased to 13,884 as on March 31, 2023, from 13,474 as on March 31, 2022.
6.1.6
Manufacturing and Other Expenses
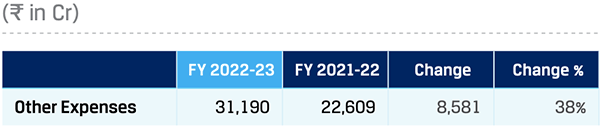
Manufacturing and other expenses increased 38% y-o-y to ₹31,190 crore primarily on account of increase in production by 18%, higher power and fuel cost and higher freight expenses due to increase in volumes.
Stores and spares consumption increased 40% y-o-y to ₹4,789 crore, due to increased prices of electrodes and refractories, and increased consumption of spares and consumables due to commissioning of 5 MTPA phase II project at Dolvi, commissioning additional facilities like coke oven plant at Vijayanagar, 235 MW power plant part of the 5 MTPA expansion at Dolvi and other facilities, and commissioning of the downstream facilities at Vijayanagar in FY 2022-23.
Power and fuel costs increased by 55% y-o-y to ₹13,842 crore primarily due to increase in steam coal prices by 132% y-o-y owing to supply constraints, higher power purchases and higher natural gas prices coupled with increased consumption due to increase in production volumes by 18%.
Freight expenses increased by 14% y-o-y to ₹5,971 crore primarily on increase in domestic despatches partially offset by decrease in ocean freight due to lower export sales.Hedging Cost/Net exchanges Loss increased to ₹1,548 crore due to increase in hedging cost on account of increase in coking coal and steam prices and mark-to-market unrealised loss on foreign currency loans on account of Indian rupee depreciation of 8.5% against the US dollar.
6.1.7
Finance Cost
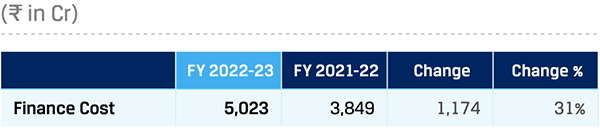
Finance cost increased 31% y-o-y to ₹5,023 crore primarily due to increase in interest rates as the benchmark rates of domestic and foreign currency borrowings increased due to tightening of monetary policies by the central banks to contain inflation. The increase in finance cost is also attributable to full impact of the capitalisation of Dolvi 5 MTPA project carried out in the previous year and other allied assets, capitalisation of Cold Rolling Mill (CRM)1 expansion project at Vijayanagar and cost-saving projects and impact of forex fluctuations as the rupee depreciated by 8.5% during the year.
6.1.8
Depreciation and Amortisation
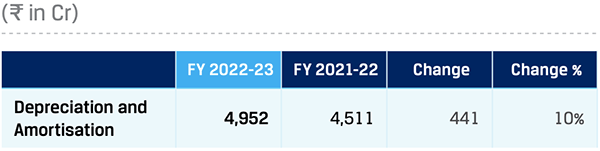
Depreciation and amortisation increased 10% y-o-y to ₹4,952 crore primarily due to depreciation charged on asset capitalisation of ₹8,502 crore during the year relating to CRM1 expansion, Battery A of Coke Oven 5 of capacity 0.75MTPA at Vijayanagar, 235 MW captive power plant at Dolvi, mining equipment at Odisha, full impact of the capitalisation of Dolvi 5 MTPA project carried out in the previous year, cost-saving projects and sustenance capital expenditure.
6.1.9 Tax Expense/Credit
The tax expense was ₹2,031 crore in FY 2022-23, compared to ₹8,013 crore in FY 2021-22 primarily due to lower profitability. The effective tax rate marginally decreased to 29.15%. in FY 2022-23.
29.15%
Effective tax rate in FY 2022-23
6.1.10 Exceptional Items
Subsequent to the previous year end, a subsidiary company in USA received a final arbitration order on its dispute with the lessors of coking coal mining lease and plant lease and a consequential notice of termination of lease. Accordingly, an impairment provision of ₹722 crore was recorded in FY 2021-22 towards the value of the loans given to overseas subsidiary.
6.1.11
Property, Plant and Equipment
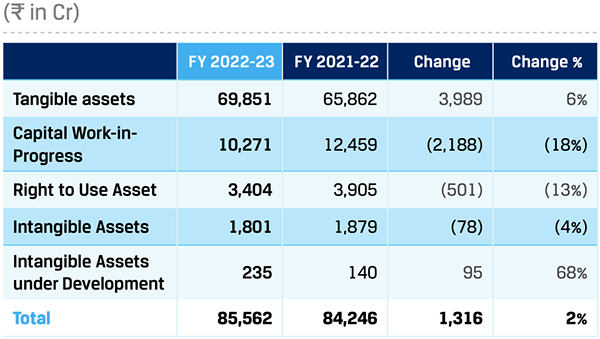
Net block of Property, Plant and Equipment increased by ₹3,989 crore primarily on account of capitalisation aggregating to ₹8,502 crore CRM1 expansion, battery A of coke oven 5 of capacity 0.75 MTPA at Vijayanagar, 235 MW captive power plant at Dolvi, mining equipment at Odisha and cost saving projects and sustenance capital expenditure offset by depreciation charge for the year. The capital work-in-process decreased to ₹10,271 crore on account of lower capital expenditure incurred during the year as against the capitalisation carried out during the year.
6.1.12
Investments
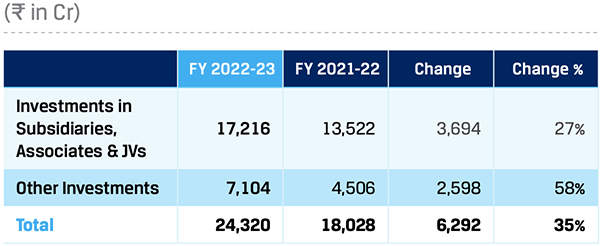
Investments increased to ₹24,320 crore due to an additional investment of ₹6,728 crore, primarily in equity investments in JSW Vijayanagar Metallics Limited to set up the 5 MTPA steel project at Vijayanagar, JSW Paints Private limited and purchase of Piombino Steel Limited Non-convertible Bonds. This increase in investments was partially offset by decrease in investments ₹435 crore, mainly attributable to decline in share price of JSW Energy Limited.
6.1.13
Loans and Advances
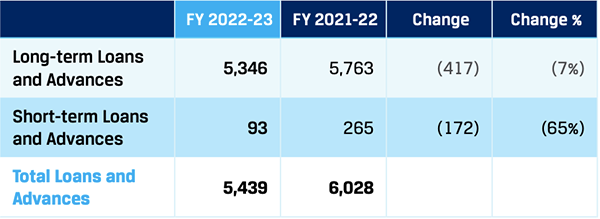
Loans and advances decreased primarily due to repayment of loans by certain domestic and overseas subsidiaries.
6.1.14
Other Financial Assets
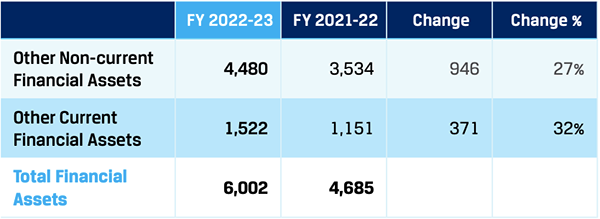
Increase in other financial assets was primarily due to increase in the GST incentive receivable from the state of Maharashtra and Karnataka and additional placement of security deposit for service contracts and accrual of interest income on loans provided to certain overseas subsidiaries.
6.1.15
Other Non-Financial Assets
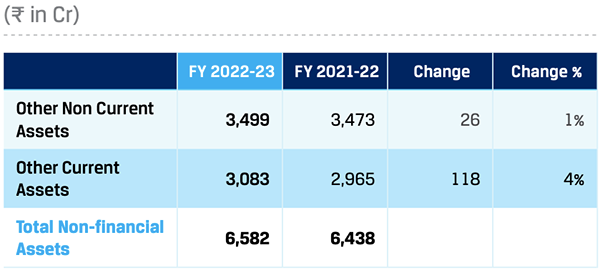
Increase in other non-financial assets was primarily due to accumulation of GST input tax credit, increase in the advance to suppliers for raw materials and other supplies due to increase in raw materials cost owing to increase in commodity prices.
6.1.16
Inventories
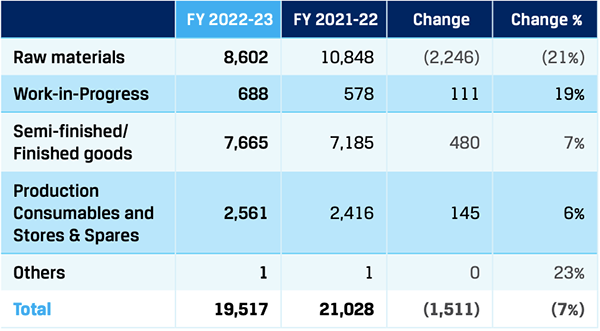
The decrease in inventory was primarily on account of a decrease in coking coal inventory by ₹2,702 crore as coal inventory reduced by 5.5 lakh tonnes and coal prices fell by 16% to ₹23,348 per tonne. The work- in-progress and semi-finished/finished goods increased by ₹591 crore primarily due to increase in steel inventory by 2.27 lakh tonnes.
Average raw materials inventory (including own mines’ iron ore) holding as on March 31, 2023 decreased to 48 days from 79 days as on March 31, 2022 primarily due to the reduction in lower coking coal inventory.
Average finished goods inventory holding decreased to 16 days as on March 31, 2023 as compared to 18 days as on March 31, 2022, primarily due to decrease in finished goods inventory on account of higher volumes and replenishment of work-in-progress inventory.
6.1.17
Trade Receivables
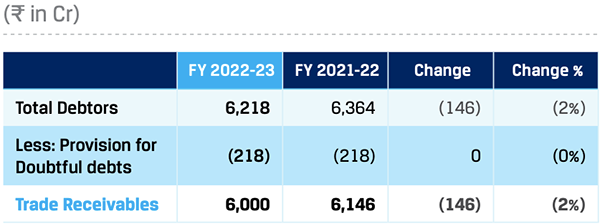
Trade receivables marginally declined to ₹6,000 crore. However, the average collection period as on March 31, 2023, was 17 days compared to 15 days as on March 31, 2022, primarily on account of market sentiment.
6.1.18 Cash and Bank Balances
To meet short-term cash commitments and repayment obligations, the Company parks surplus funds in short-term and highly liquid instruments which represent cash and cash equivalents and other bank balances.
Cash and Bank Balances
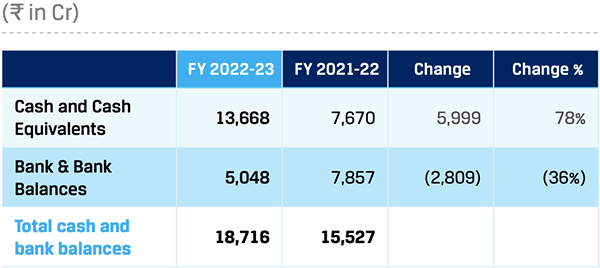
Cash and bank balances increased to ₹18,716 crore from ₹15,527 crore primarily on account of cash surplus generated in the fourth quarter due to liquidation of working capital.
6.1.19
Borrowings
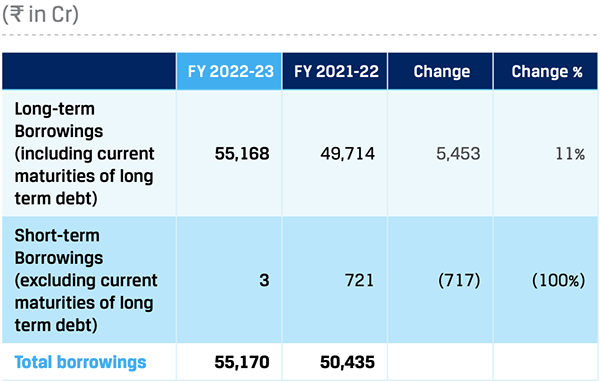
Long-term borrowings (including current maturity of long-term debt) increased primarily due to drawal of rupee term loans and issuance of Non-convertible Debentures to incur capital expenditure and general corporate purposes. The Company repaid short-term loans in view of the cash surplus available at the end of the year.
6.1.20
Trade Payables
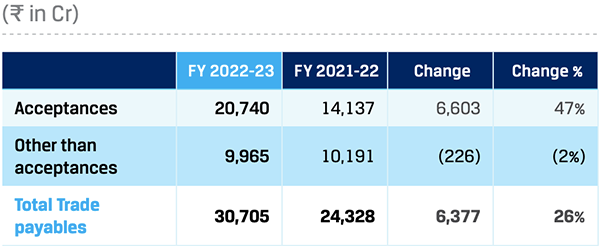
Trade payables increased by ₹6,377 crore primarily due to increase in acceptances caused by increase in coking coal price and other coal prices due to supply chain disruptions and the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
6.1.21
Other Financial Liabilities
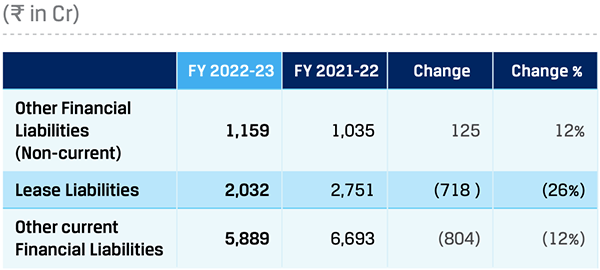
Other current financial liabilities increased by ₹125 crore to ₹1,159 crore mainly due to increase in allowances for financial guarantees. Lease liabilities were lower by ₹718 crore to ₹2,032 crore due to repayment of principal amount on leases and modification of certain leases which is partially offset by increase in lease liabilities for certain logistics assets taken on lease. The other current financial liabilities decreased to ₹5,889 crore due to payment of liabilities towards bid premium/royalties for own mines and reduction in retention money for capital projects.
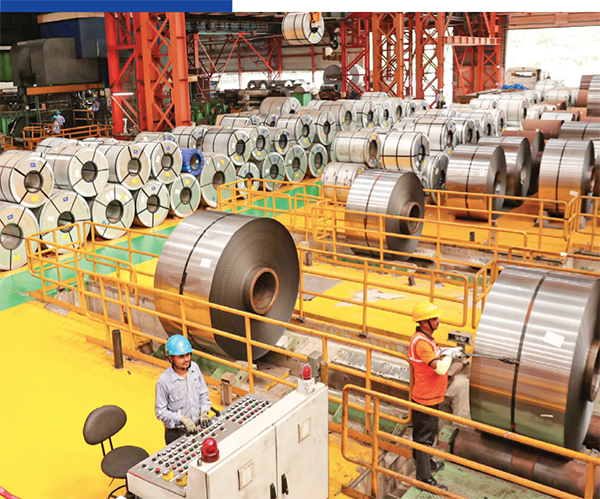

6.1.22
Deferred Tax Liabilities
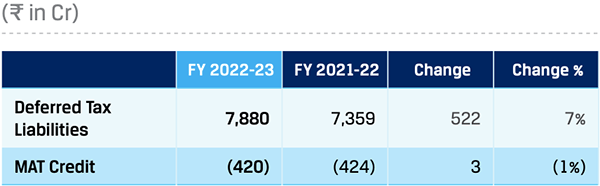
Deferred tax liabilities increased to ₹7,880 crore higher due deferred tax liabilities created on account of capitalisation of expansion projects, cost saving projects and sustenance CapEx.
6.1.23 Capital Employed
Total capital employed increased 8 % y-o-y to ₹1,12,204 crore in FY 2022-23 primarily due to capitalisation of Property, Plant and Equipments. Return on average capital employed was 9.6 %, down from 32.6% due to lower profitability.
6.1.24 Own Funds
JSW Steel’s net worth increased from ₹63,501 crore to ₹63,659 crore as on March 31, 2022. Book value per share was at ₹263.36 as on March 31, 2023, as compared to ₹262.70 as on March 31, 2022.
6.1.25
Other Key Financial Indicators
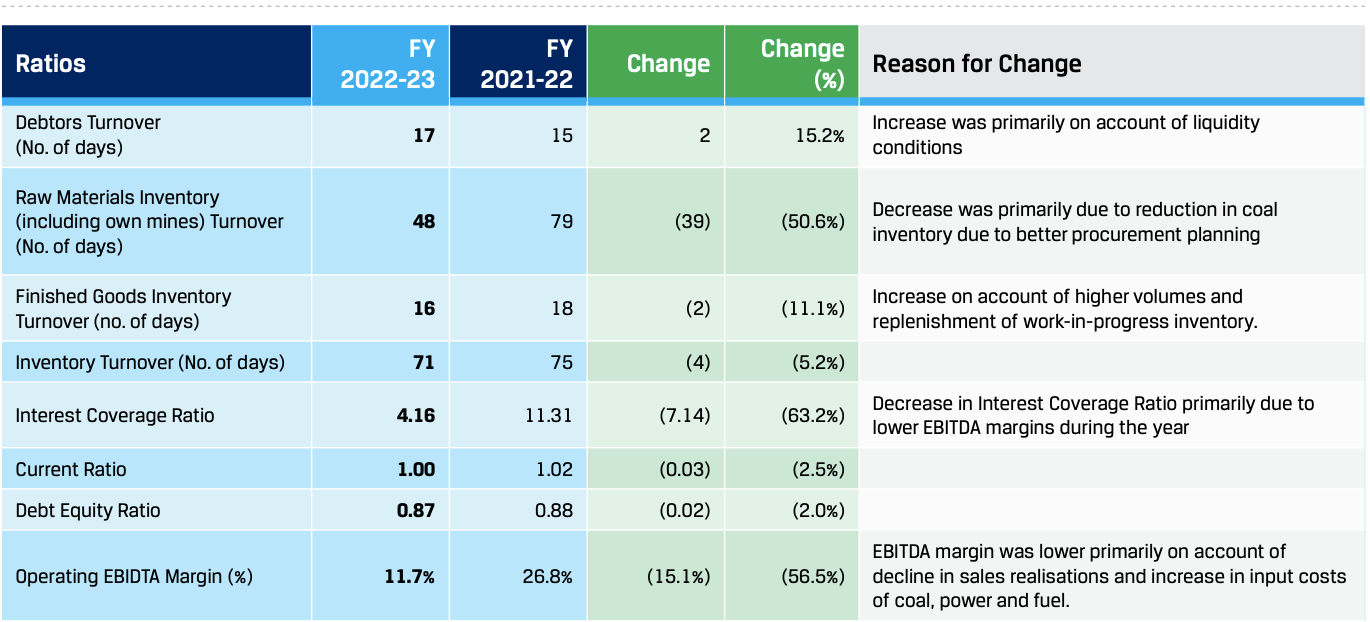

6.2 CONSOLIDATED
In FY 2022-23, the Company’s consolidated revenue from operations increased by a staggering 13% y-o-y to ₹1,65,960 crore. Operating EBITDA was recorded at ₹18,547 crore. Operating EBITDA reduced mainly due to lower sales realisations, higher coal, power and fuel costs, and lower contribution from US subsidiaries.
Overseas
UNITED STATES
CHILE
MAURITIUS
NETHERLANDS
UNITED KINGDOM
MOZAMBIQUE
ITALY
SINGAPORE
Indian
Joint Controlled Entities
Associates

7.0DIGITALISATION
JSW Steel has initiated Industry 4.0, an ambitious endeavour to digitise the complete production value chain across all its steel plants located in different regions. This transformation involves connecting and optimising a complex network of interrelated functions using a range of targeted technologies. The technologies include AI and ML, geospatial tracking, Internet of Things (IoT), advanced robotics, simulation, cloud computing, and process automation. The Company's digital vision primarily focuses on providing comprehensive solutions for mining, manufacturing, supply chain management, finance, and sales marketing.
The ultimate goal of digitalisation for us is to create a significant impact across all functions by seamlessly automating control. The objective is to ensure that every aspect of the value chain, from inventory management to product dispatch, and from the manufacturing shop floor to sales, operates in real-time, guided by situational data, and optimised on a minute-to-minute basis. By embracing digitalisation, JSW Steel aims to enhance efficiency, responsiveness, and overall performance throughout its operations.

8.0HUMAN RESOURCES
The Company recognises that the key to achieving its aspiration of becoming a larger, superior, and more efficient steel producer lies in the drive and capability of its workforce. Talent management plays a vital role in the Company's strategic planning. Employees are provided with the policies needed to foster a favourable work environment. In addition to competitive compensation packages that align with industry standards, employees get access to ample learning and career advancement opportunities. Additionally, comprehensive measures towards the health and safety of our employees are deployed and the Company's motivates them to excel and perform at their highest potential.
9.0CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY
The ethos of 'Better Everyday' serves as the foundation for JSW Steel's community and social initiatives. The Company firmly believes that social inequality in India stems from a lack of opportunities rather than inherent potential, and it is committed to addressing this imbalance. The Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) programmes are guided by the Company's key principles, including engaging multiple stakeholders, fostering localised involvement, promoting grassroots-level participation, and ensuring scalability, replicability, and sustainability.


10.0RISK MANAGEMENT
JSW Steel follows the globally recognised 'COSO' framework for Enterprise Risk Management (ERM). This framework aids in establishing internal controls that are integrated into business processes, providing a comprehensive understanding of the potential positive and negative impacts of various factors on the organisation. The primary objective is to create sustainable value for all stakeholders and optimise the organisation's activities. JSW Steel greatly emphasises identifying risks, and effectively managing known and potential risks to:
In compliance with Regulation 21 of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015, and the Companies Act, 2013, JSW Steel has implemented this risk management framework. As part of its oversight and mitigation mechanism, the Company has formed a sub-committee of Directors responsible for overseeing the ERM framework's functioning and ensuring the implementation of adequate safeguards are taken that keep the organisation resilient and able to handle the following: