
At JSW Steel, incisive use of technology, advanced analytics and our innovation capabilities help us in retaining our position on the global cost curve. We engage in targeted projects across our costs, manufacturing and logistics operations to progressively reduce our overheads and enhance overall efficiency. Despite margins being challenged in FY 2021-22, we could deliver higher volumes, create a better product mix and achieve notable EBITDA growth.





Conversion cost per tonne of steel

Iron ore transported using pipe
conveyor

Capacity
utilisation

RoCE

EBITDA per tonne of steel sold*

Operating EBITDA margin
*Steel + coated
Setting up of 8 MTPA pellet plant and 1.5 MTPA coke oven plant at Vijayanagar
In order to decrease the facility’s requirement of expensive lump iron ore, we have set up India’s largest pellet plant. The 8 MTPA plant was commissioned in FY 2020-21 and was made operational during the year. This has led to a reduction in the procurement of lump ore, in turn reducing the overall cost of production.
The construction of Coke Oven Battery of 1.5 MTPA at Vijayanagar is currently under progress and is expected to be commissioned in phases in FY 2022-23. We are also planning to expand the coke oven capacity by another 1.5 MTPA at Vijayanagar, which is expected to be commissioned in phases from Q4 2023. Cumulatively the projects will contribute to substantial cost savings.


We are setting up a 175 MW Waste Heat Recovery Boilers (WHRB) and a 60 MW captive power plant to harness flue gases and steam from the Coke Dry Quenching (CDQ) process. These power plants are expected to be commissioned in the first half of FY 2022-23.
At JSW Steel, our Group Digital Vision is “Delivering ‘wow’ by digitally transforming and nurturing JSW’s ecosystem and creating sustainable value”. This function at JSW is led by a Chief Digitization Officer. The vision is further anchored by the following key objectives:
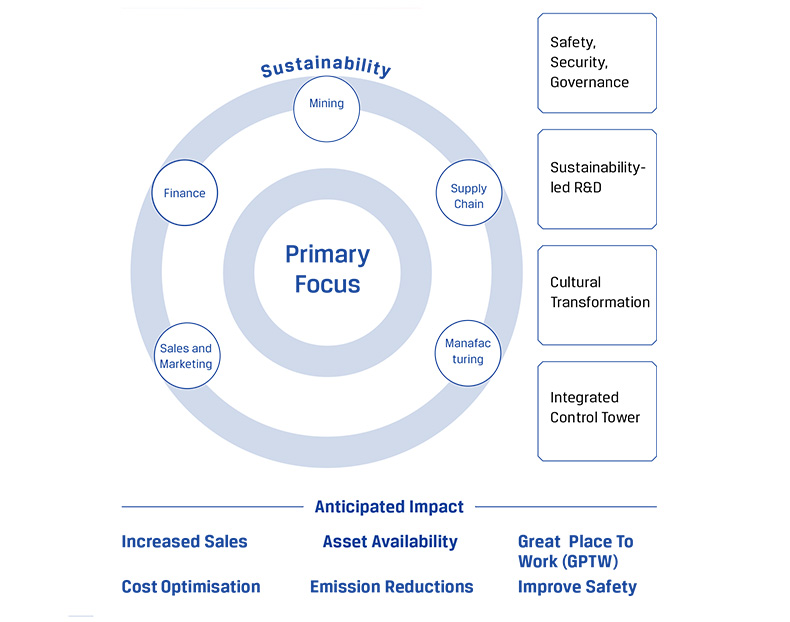
Core Systems (SAP, ST, GCP, Azure, Darwin Box), IoT, A/ML, Analytics, Cloud/Edge Computing RPA-leveraging JSW Digital team as well as Startup ecosystem
Lean, Fail-fast, Hackathon, Six Sigma, Agile, Design Thinking supported by Process Excellence & Transformation (PET) Team
Data Science & loT Skilling, Tech sessions, Online courses, Symposiums enabled through Cultural Transformation efforts


We envisaged our digitalisation journey in four waves of intervention and we are now in the final stage of immersion. The past three waves achieved the following objectives:
In Wave 4, our vision is to scale digital to best-in-class between 2022-24 to:

Digital assets created

Employees engaged in the digital journey

Digital lighthouses and projects
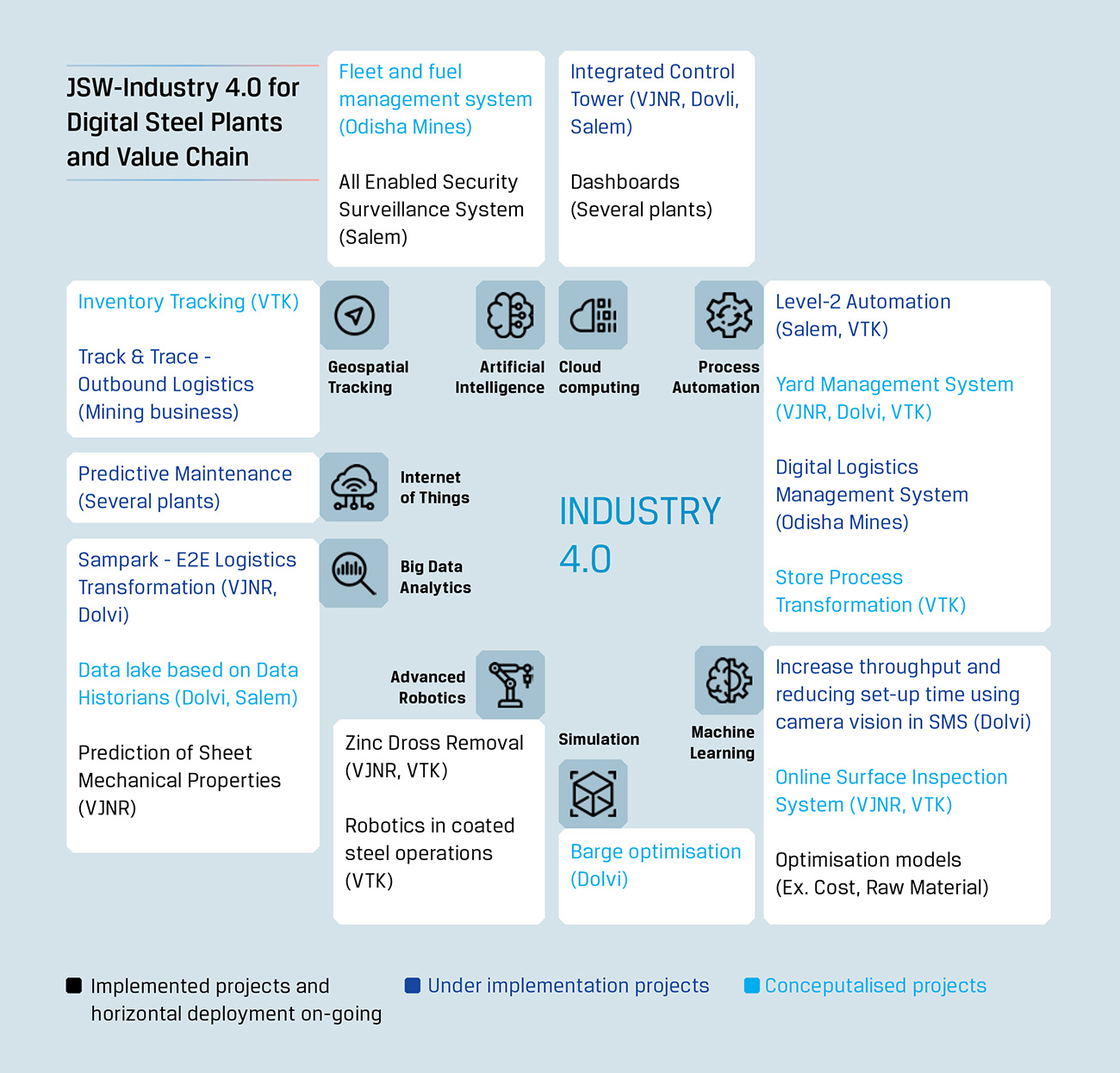
We have extensively deployed data analytics and artificial intelligence to streamline our business operations. Data analytics plays a critical role in bolstering our innovation capability and thus the success of our organisation. We have achieved significant savings through its implementation. Today, most of our operations work apply data analytics. We are also incorporating big data management and advanced analytics, so that employees can make fact-based, timely and prompt decisions. Data collection is enabled through multiple plant automation systems, and IoT enabled sensors. We consume data in an integrated manner – from Edge to the centralised repository. Data generated from Edge is consumed by models built to optimise operations, improve throughput and predict asset availability. During FY 2021- 22, we completed several excellent projects such as implementing ICT in manufacturing, Dynachem, Dynamix and Ferro Alloy Optimisation among others.

The project is set to optimise logistics cost by leveraging technology and, in the process, improve resource utilisation, accommodate supply/demand variations without impacting delivery and provide best-in-class OTIF (on-time-in-full) through real-time coordination between functions. This will deliver the desired results for the business by combining processes, integrating with IT and OT systems, creating new digital interventions to capture last mile data, creating man-less weighbridge automation and giving a powerful App to all stakeholders.

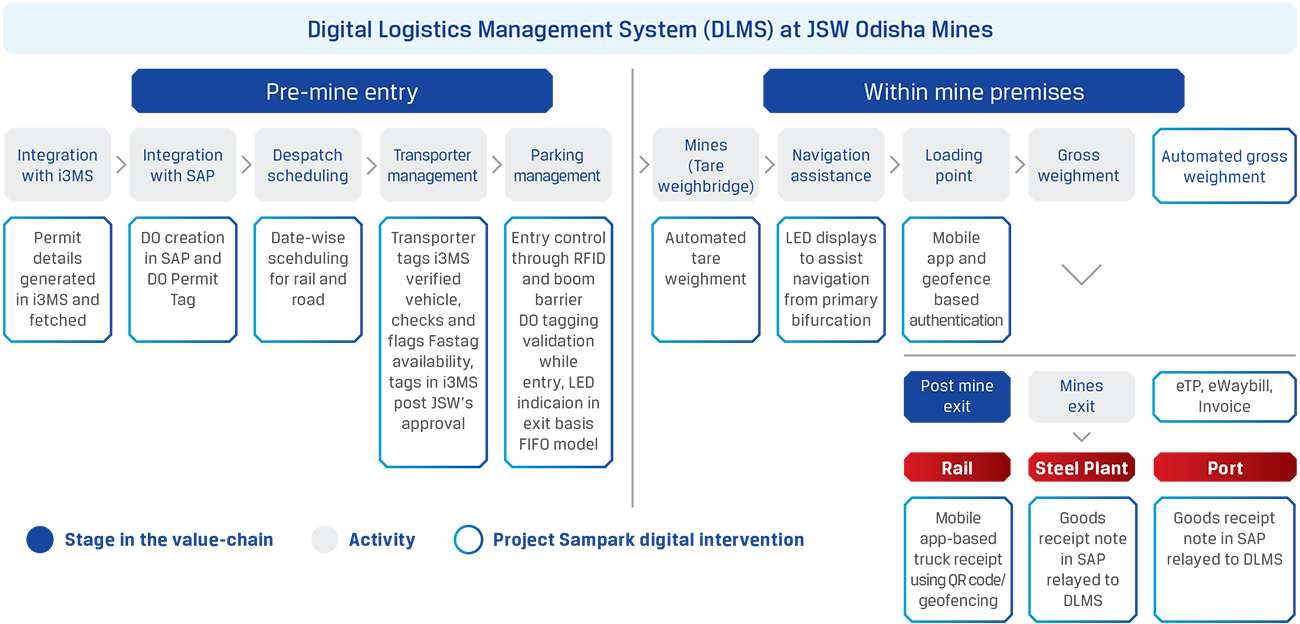
Digital Logistics Management System DLMS, Odisha Mines
The project was set up to optimise inbound as well as outbound logistics of the mines. The benefits include real-time monitoring and control, reduced TAT, no blind navigation, paperless and errorless system, optimisation of manpower and minimised pilferage among others.

The project was conceived to drive process and technology transformation in the finance process for JSW Steel in Procure to Pay, contract compliance, Record to Report, Direct Tax, Indirect Tax and Treasury. The programme aims to improve productivity, efficiency and accuracy and measure Key Performance Indices across the process areas through the following ways:
01
Drive end-to-end finance digital transformation across all JSW Steel plants and locations
02
Drive standardisation and automation across finance processes and enable processes to become intelligent, productive and touchless

Improve efficiency and boost safety through yard management automation
Eliminating human dependence on cranes operations at coil yards through the use of digital and man-less cranes, thus preventing operational delays and safety incidents
Project SAMPARK - Paperless technology powered logistics
Real-time visibility to the plant management, supply chain team as well as external stakeholders; Identification of operational improvement opportunities
Digitally-enabled finance function
Use cases such as touchless invoice processing, cash management dashboard, cost forecasting, inventory optimisation, intelligent tax engine, etc., prioritised based on value and implementation velocity
Analytics to optimise Vijayanagar SMS process time and energy burden
loT enabled, system integrated, and machine learning driven optimisation models reduce arcing time. Thereby, improving production efficiency and reducing power consumption
Holistic digital cultural transformation agenda
10+ interventions tailored to organisation levels and employee competencies, including inhouse batch of 50+ data scientists

Digital ideas

Horizontally deployable projects